- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- <iframe src="https://www.slidestalk.com/u181/Data_Communications_Chapter1?embed" frame border="0" width="640" height="360" scrolling="no" allowfullscreen="true">复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
数据通信:网络与数据通信
展开查看详情
1 .Chapter 1 Introduction to Computer Networks and Data Communications
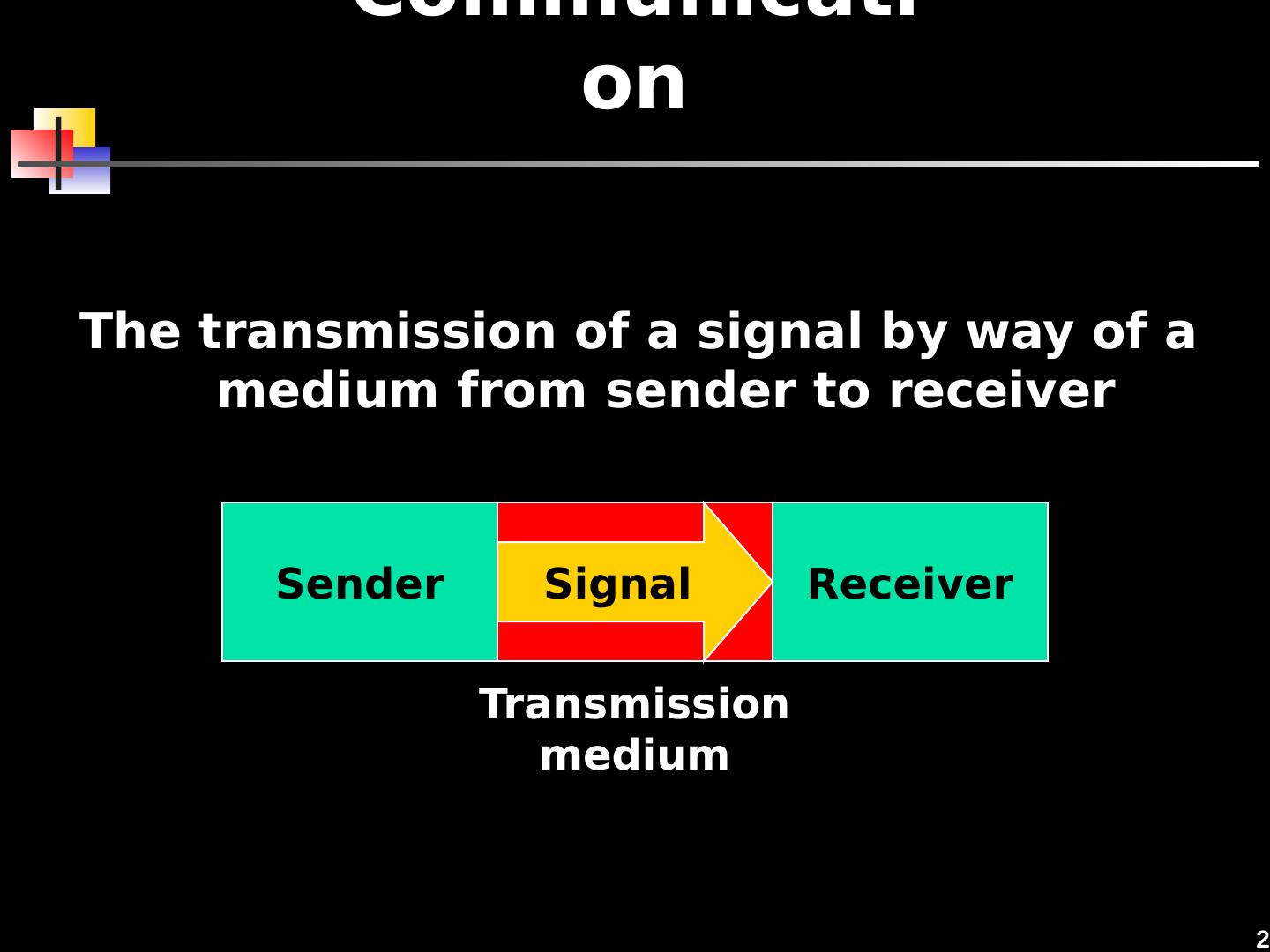
2 .2 Communication The transmission of a signal by way of a medium from sender to receiver Sender Receiver Signal Transmission medium
3 .3 Communication Problems Completeness & comprehension Attenuation & noises Competing resources Routing & addressing Security
4 .4 Networks Computer network Voice network Data network Local area network Metropolitan area network Wide area network Personal area network Network management
5 .5 Data Communications Data Communications: The movement of computer information (data) from one point to another by means of electrical or optical transmission systems Is a sub-field of telecommunications Telecommunications: Includes the transmission of voice and video as well as data
6 .6 Network Configurations Microcomputer-to-local area network Microcomputer-to-Internet Local area network-to-local area network Personal area network-to-workstation Local area network-to-metropolitan area network Local area network-to-wide area network Wide area network-to-wide area network Sensor-to-local area network Satellite and microwave Cell phones Terminal/microcomputer-to-mainframe computer
7 .7 Convergence An Additional Basic Connection – telephone-to-network Telephone systems are ubiquitous and now carry more data than voice Common configuration – telephone connected to POTS Newer configuration (VoIP) – telephone-to-LAN via gateway or telephone to gateway via DSL/cable
8 .8 Network Components Hardware Computer Network Interface Card (NIC) Hub Switch Bridge Router Software Network protocols
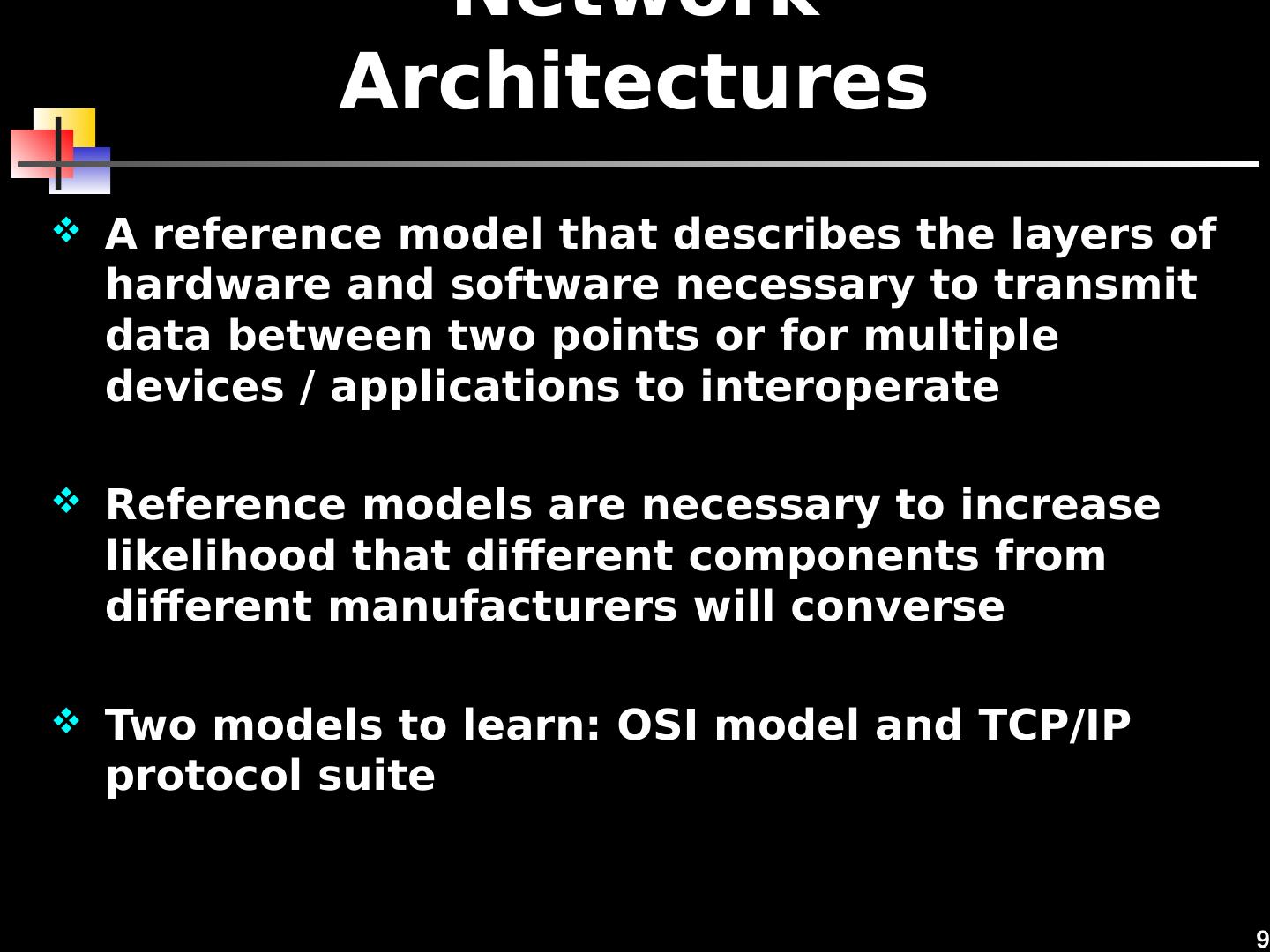
9 .9 Network Architectures A reference model that describes the layers of hardware and software necessary to transmit data between two points or for multiple devices / applications to interoperate Reference models are necessary to increase likelihood that different components from different manufacturers will converse Two models to learn: OSI model and TCP/IP protocol suite
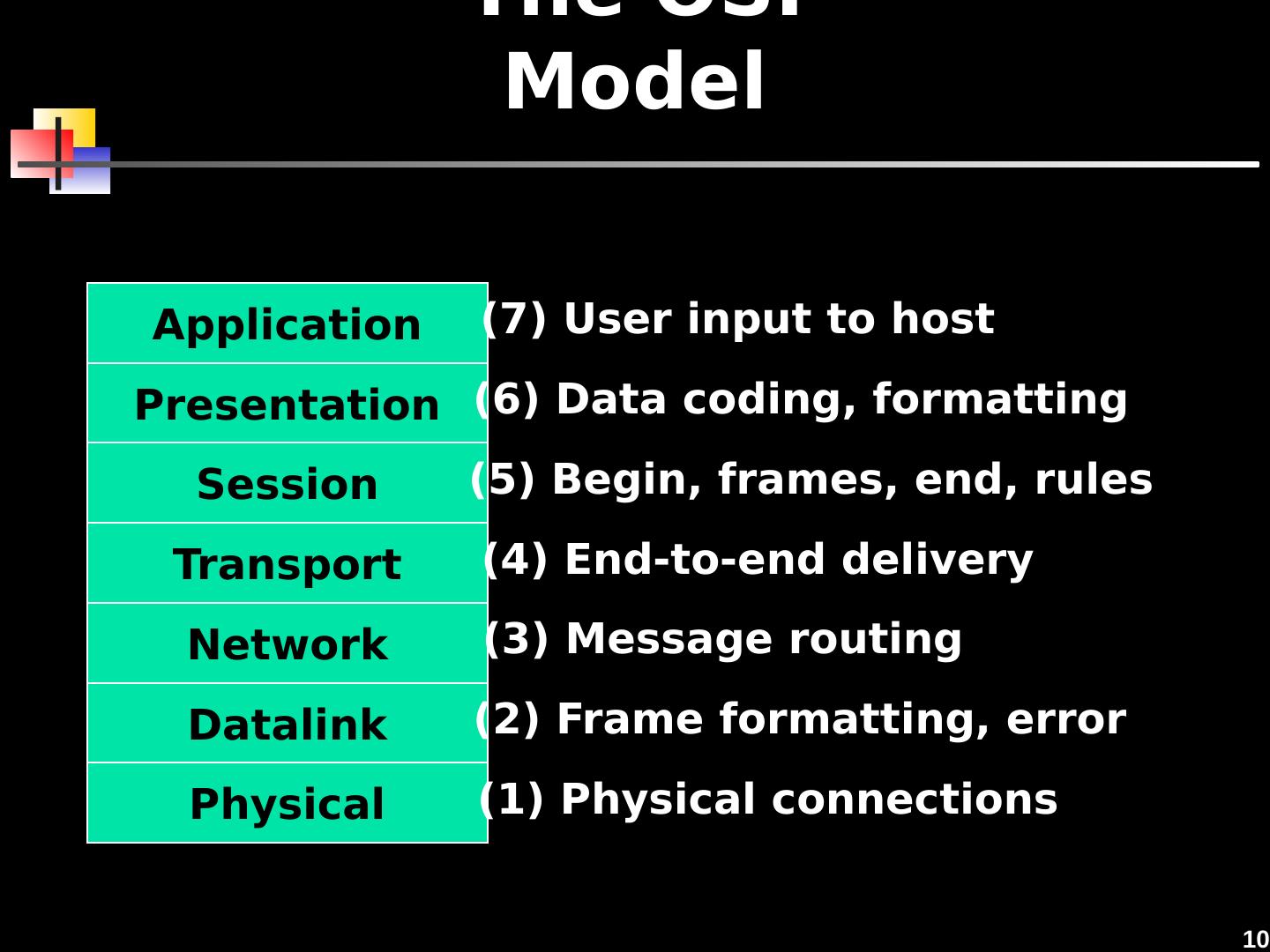
10 .10 The OSI Model Application Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical (7) User input to host (6) Data coding, formatting (5) Begin, frames, end, rules (4) End-to-end delivery (3) Message routing (2) Frame formatting, error (1) Physical connections
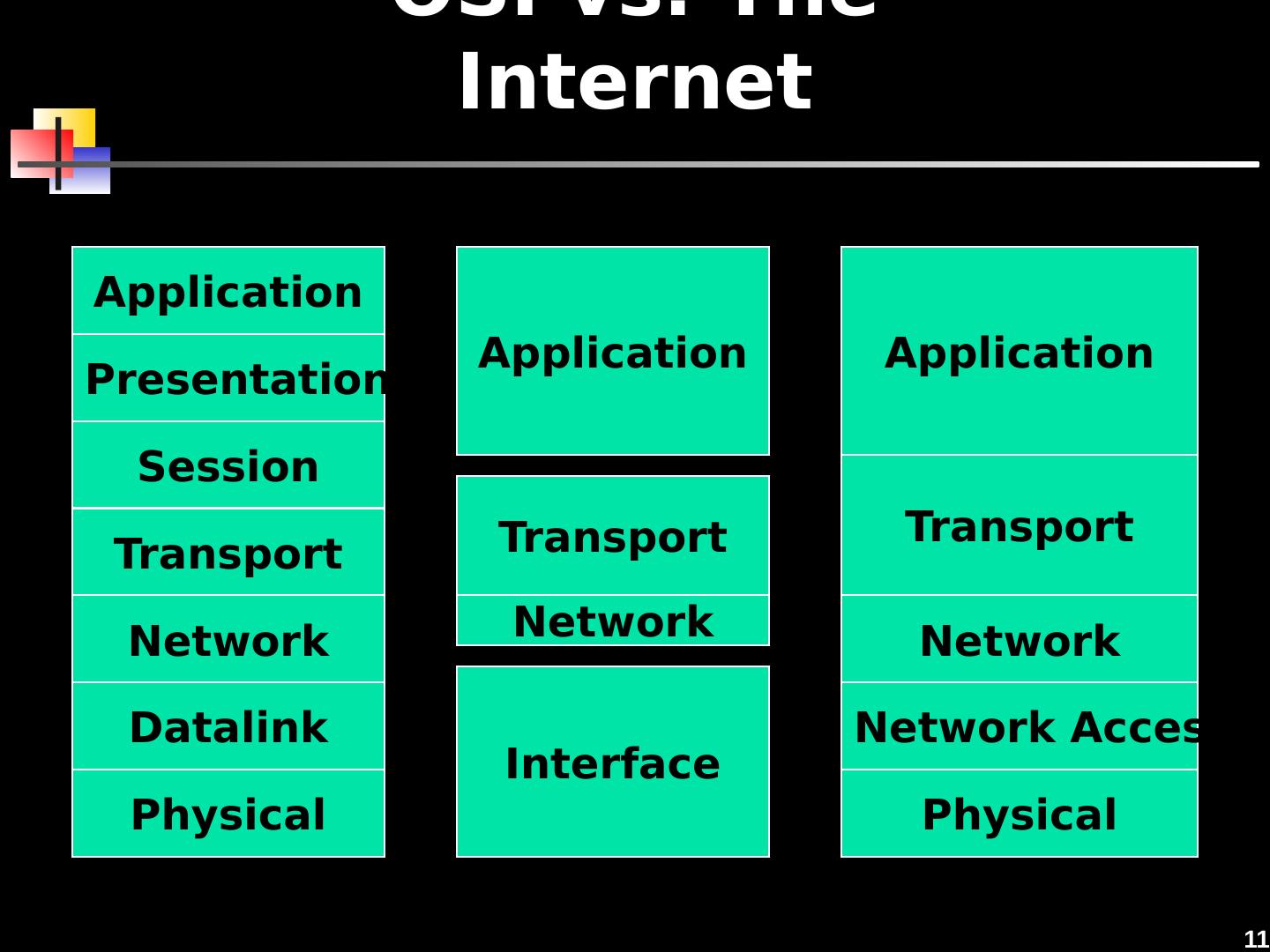
11 .11 OSI vs. The Internet Application Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical Application Transport Network Interface Application Transport Network Physical Network Access
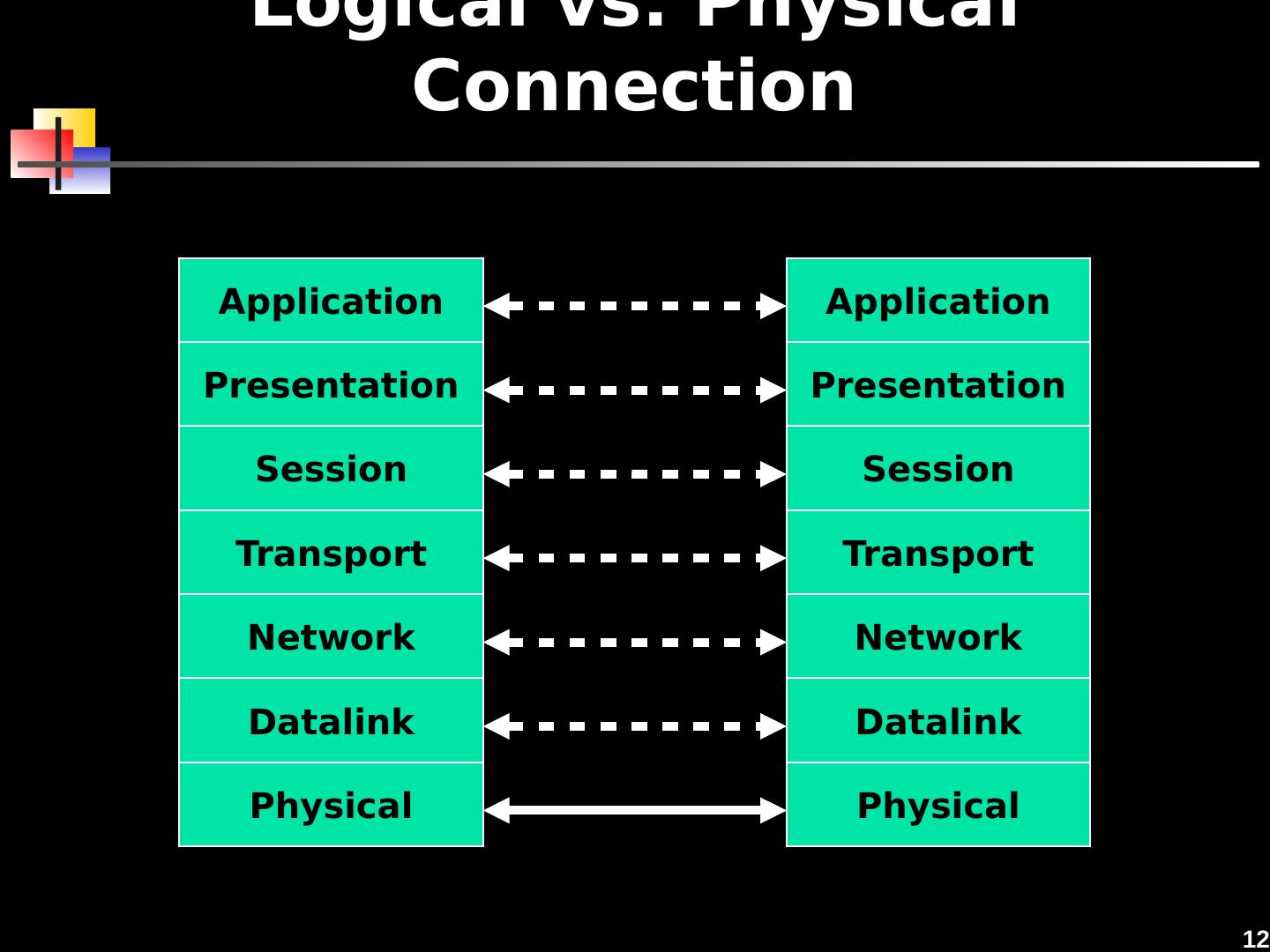
12 .12 Logical vs. Physical Connection Application Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical Application Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical
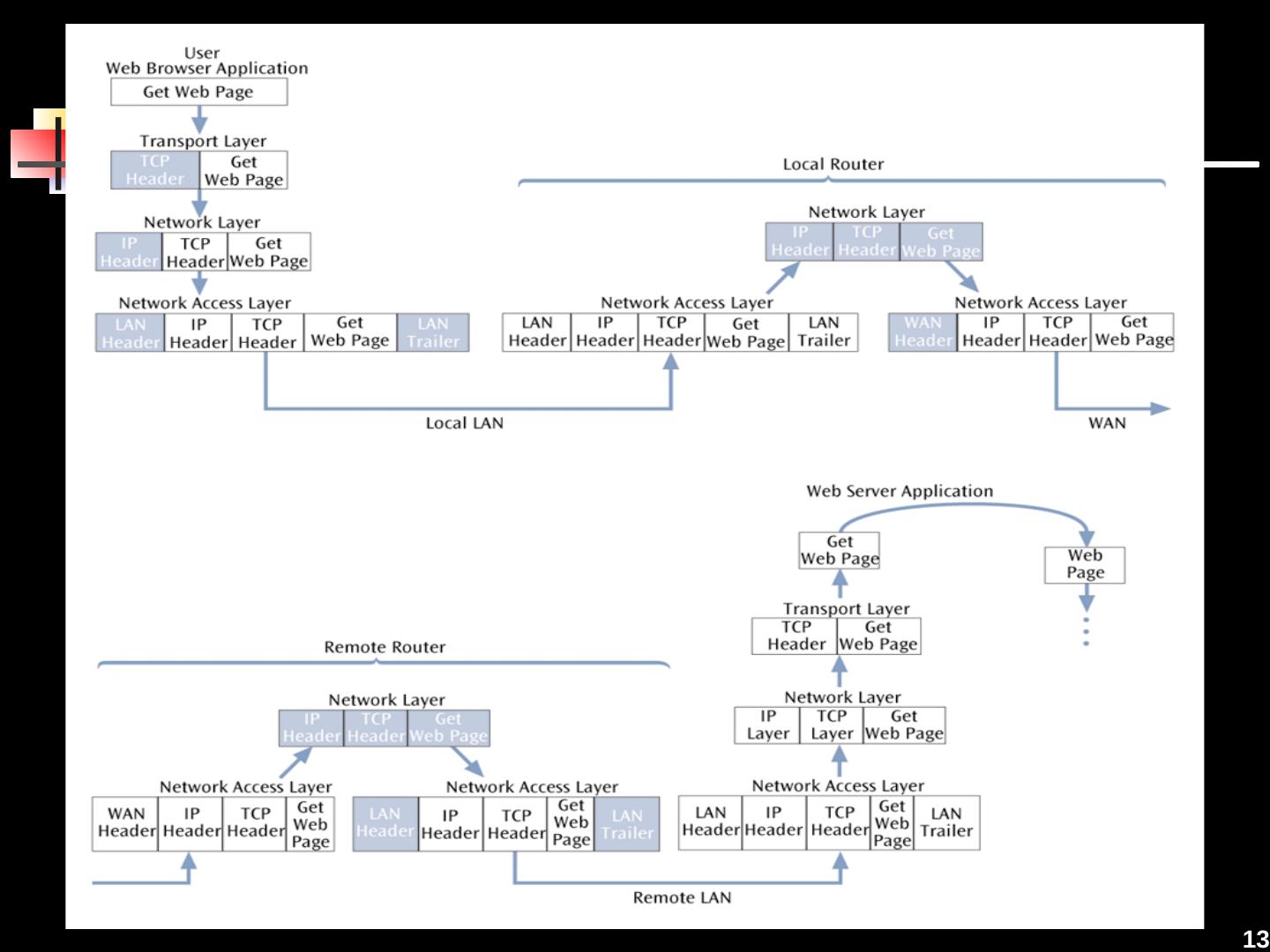
13 .13