- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
计算机系统信息安全:安全评估技术
展开查看详情
1 .TCSEC & CC 南京大学计算机系 黄皓 教授 2010年 12月27日
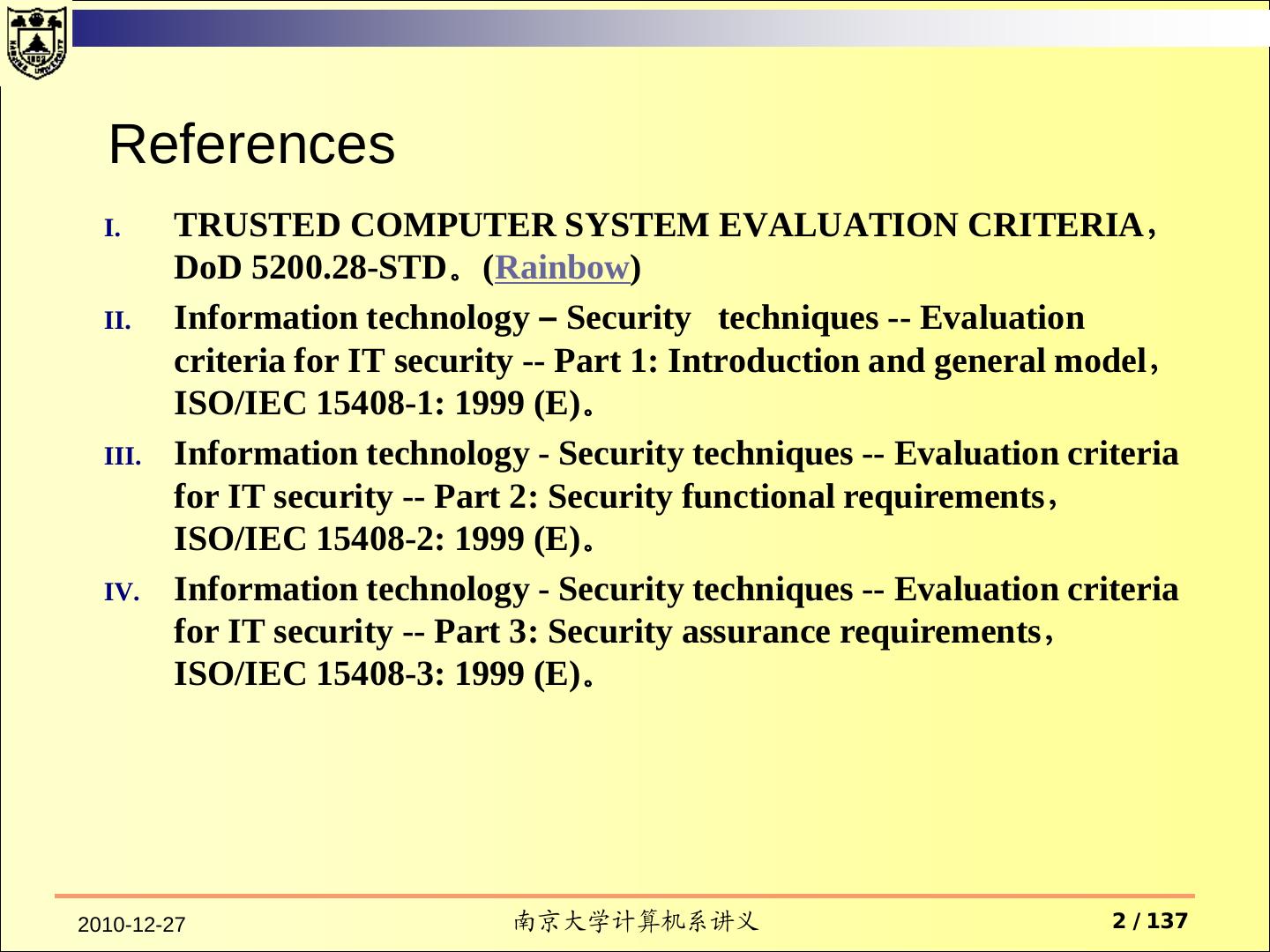
2 . References I. TRUSTED COMPUTER SYSTEM EVALUATION CRITERIA, DoD 5200.28-STD。(Rainbow) II. Information technology – Security techniques -- Evaluation criteria for IT security -- Part 1: Introduction and general model, ISO/IEC 15408-1: 1999 (E)。 III. Information technology - Security techniques -- Evaluation criteria for IT security -- Part 2: Security functional requirements, ISO/IEC 15408-2: 1999 (E)。 IV. Information technology - Security techniques -- Evaluation criteria for IT security -- Part 3: Security assurance requirements, ISO/IEC 15408-3: 1999 (E)。 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 2 / 137
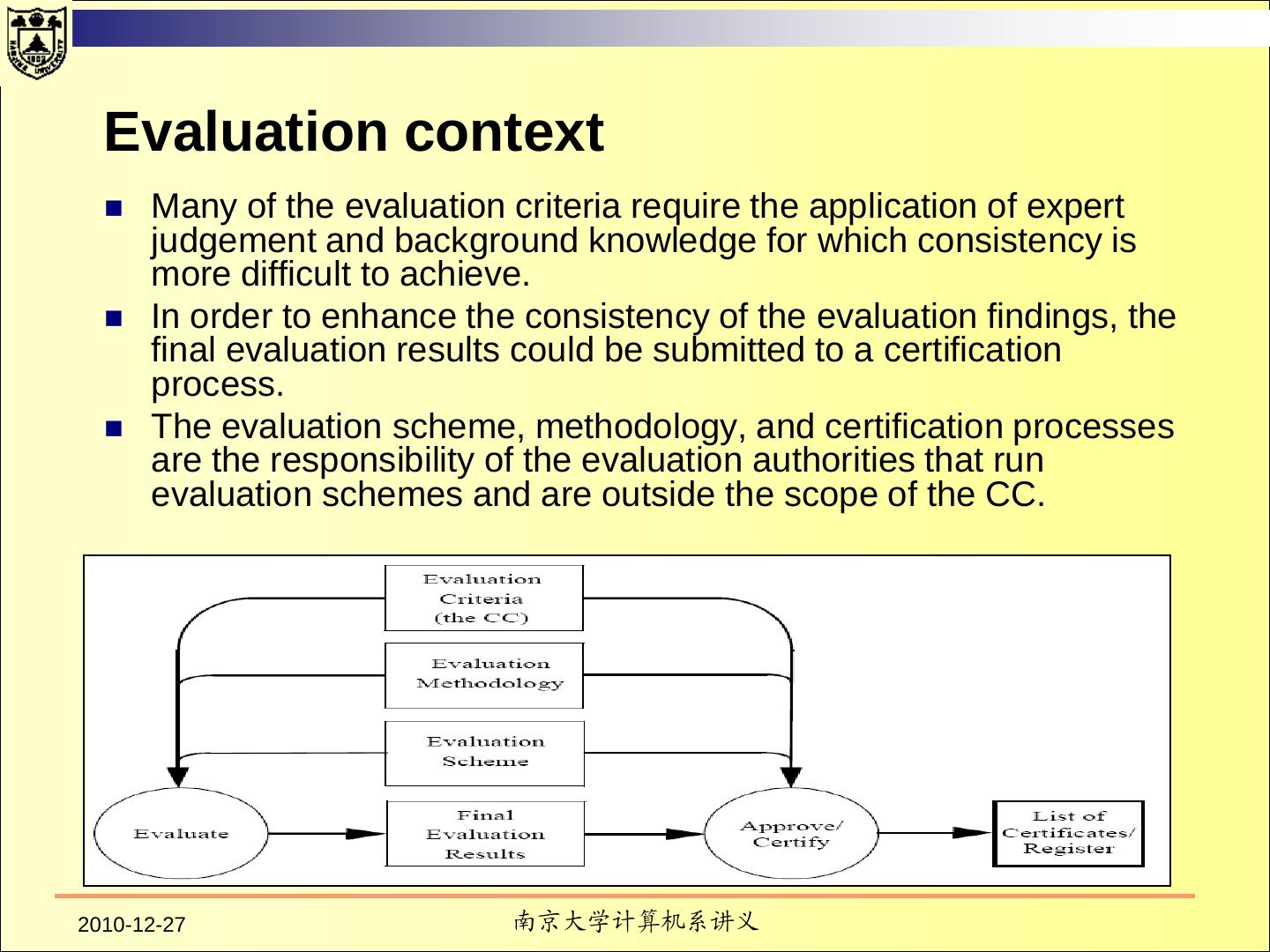
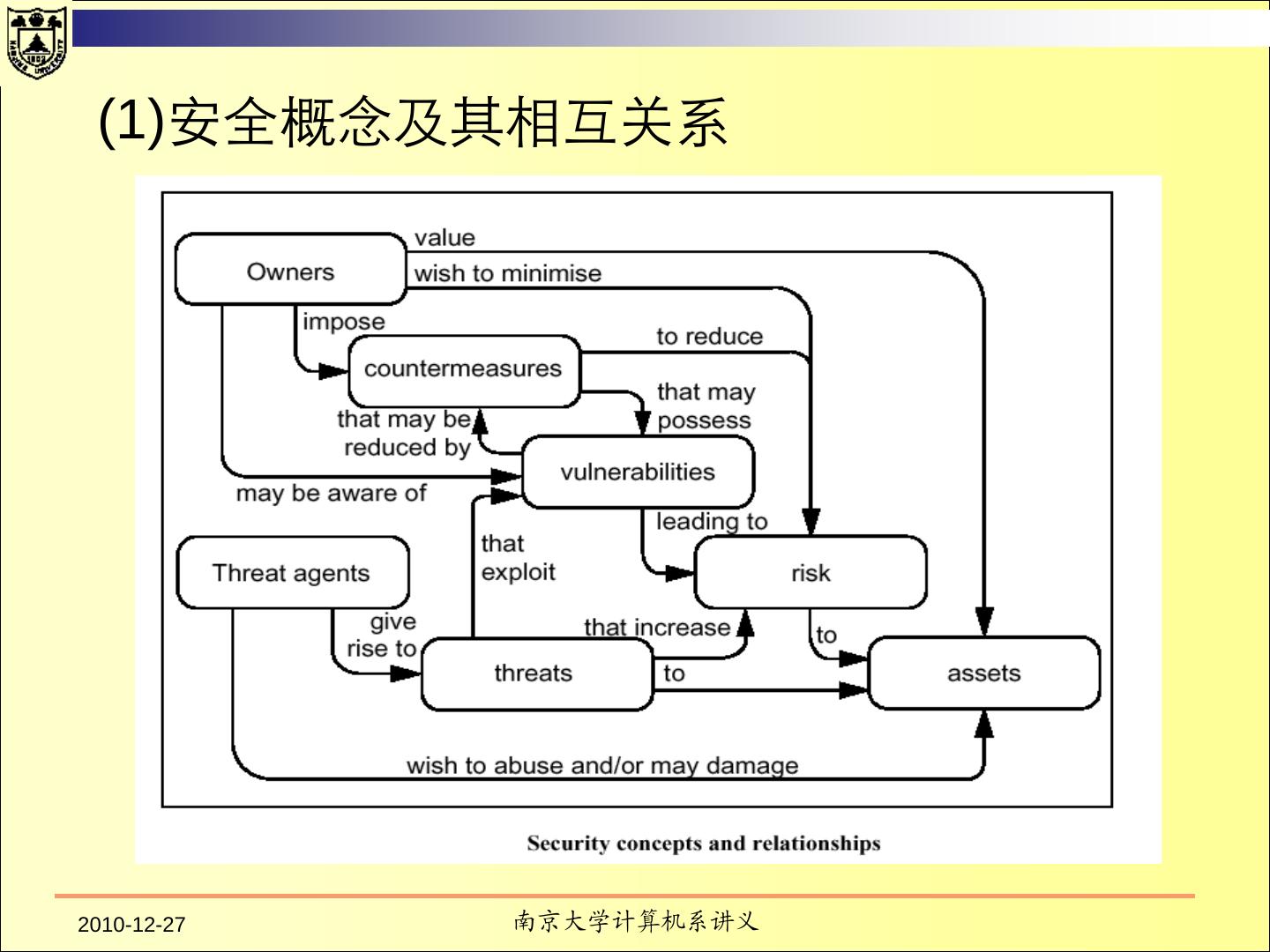
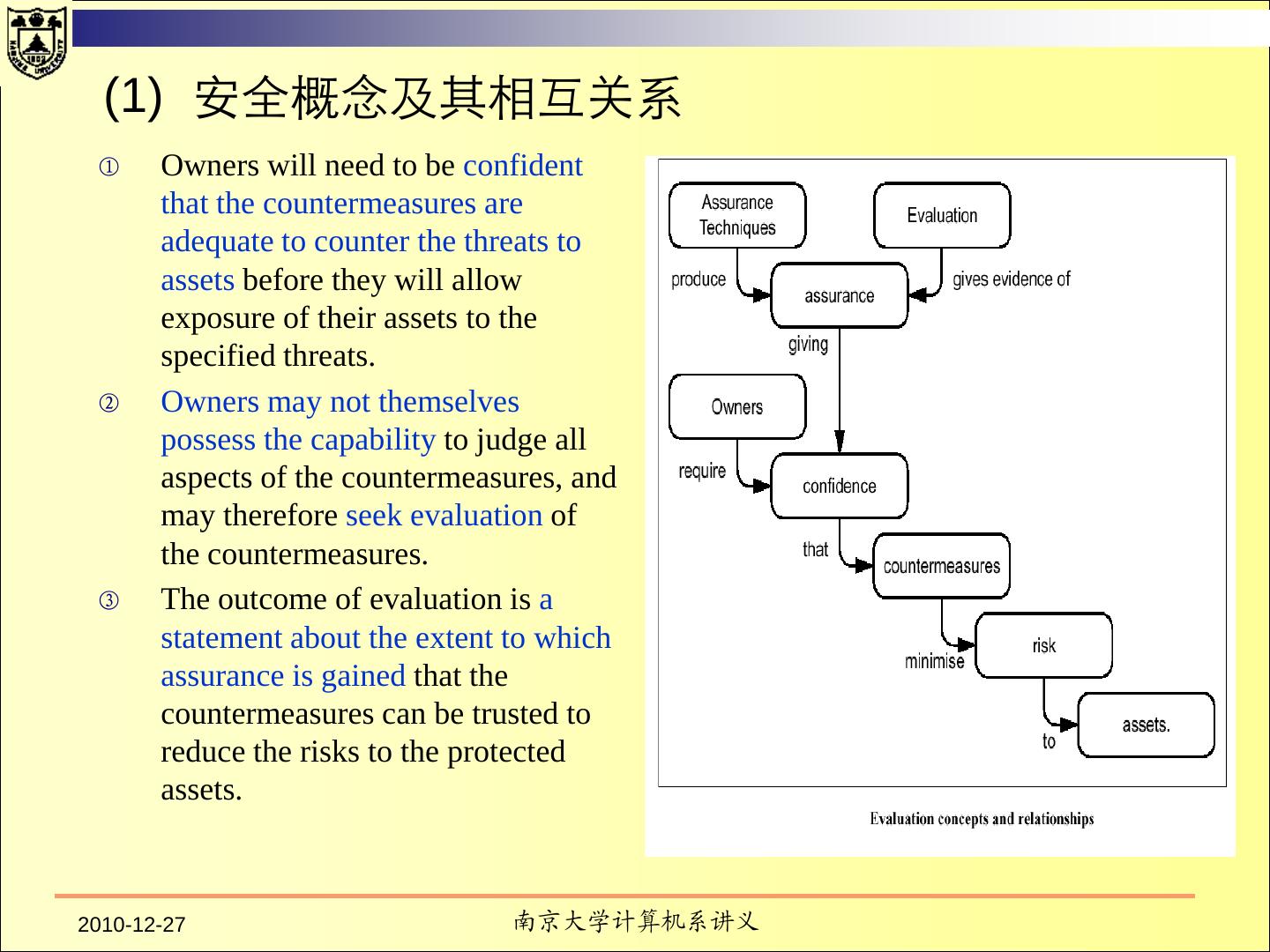
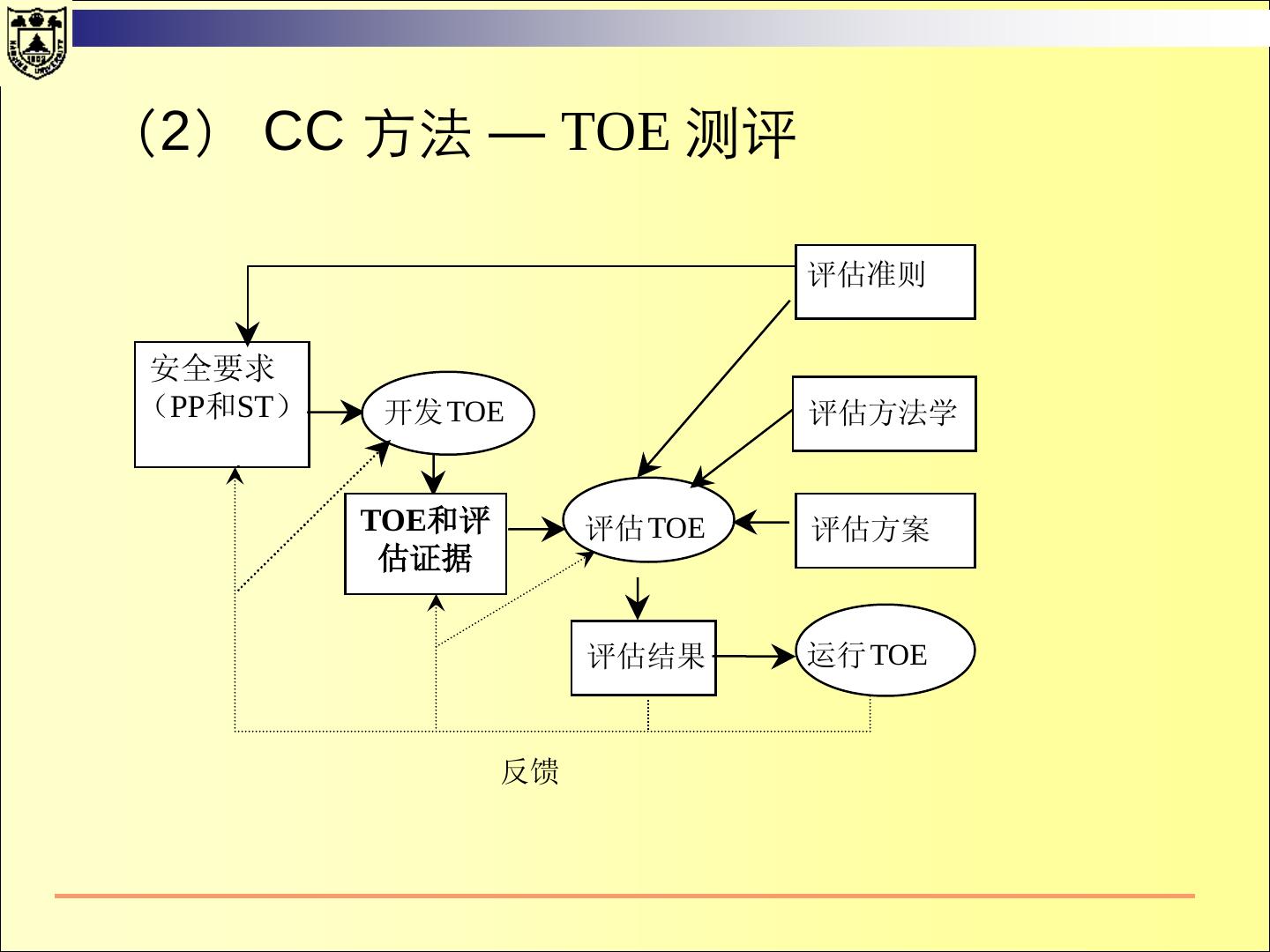
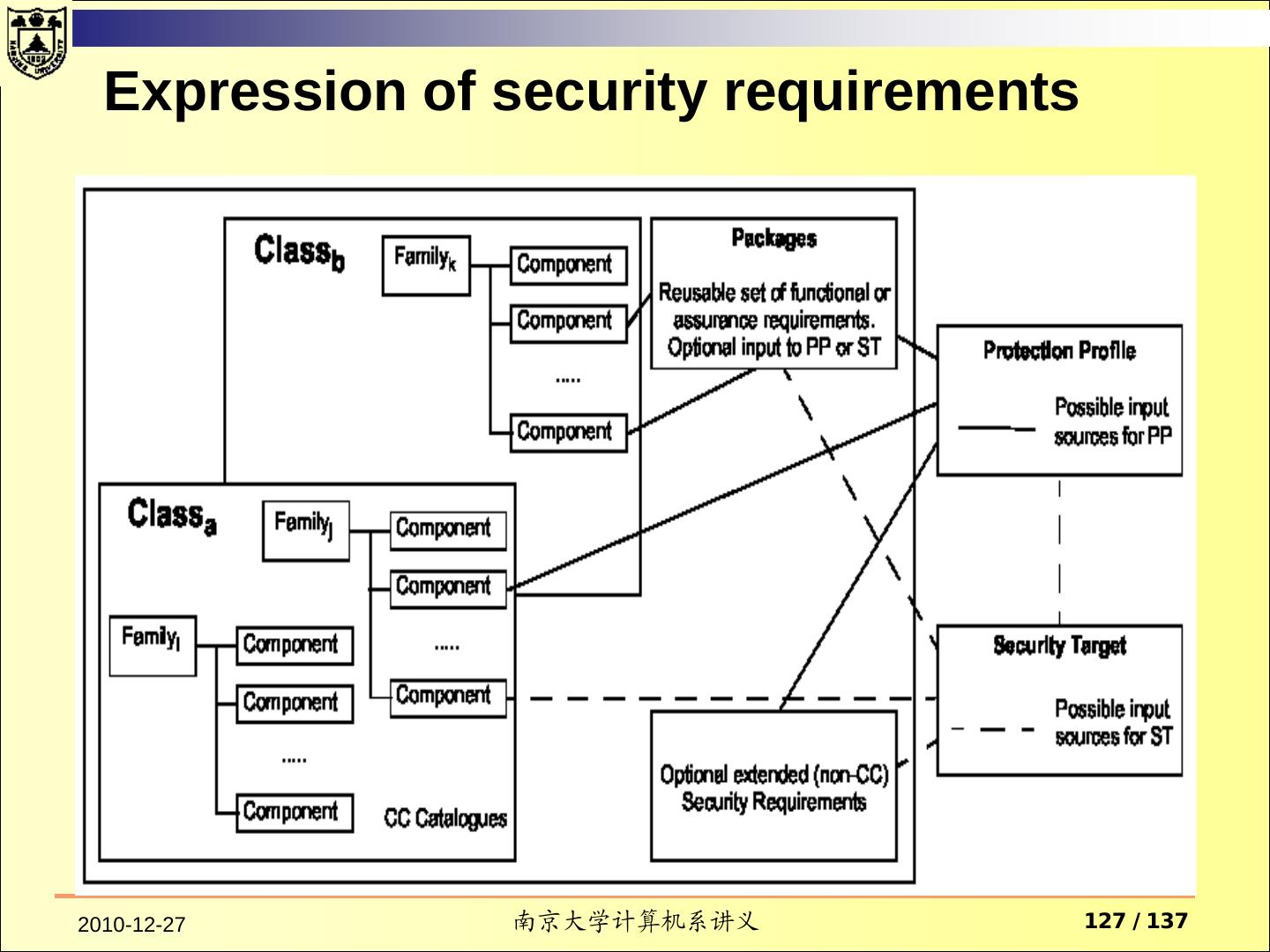
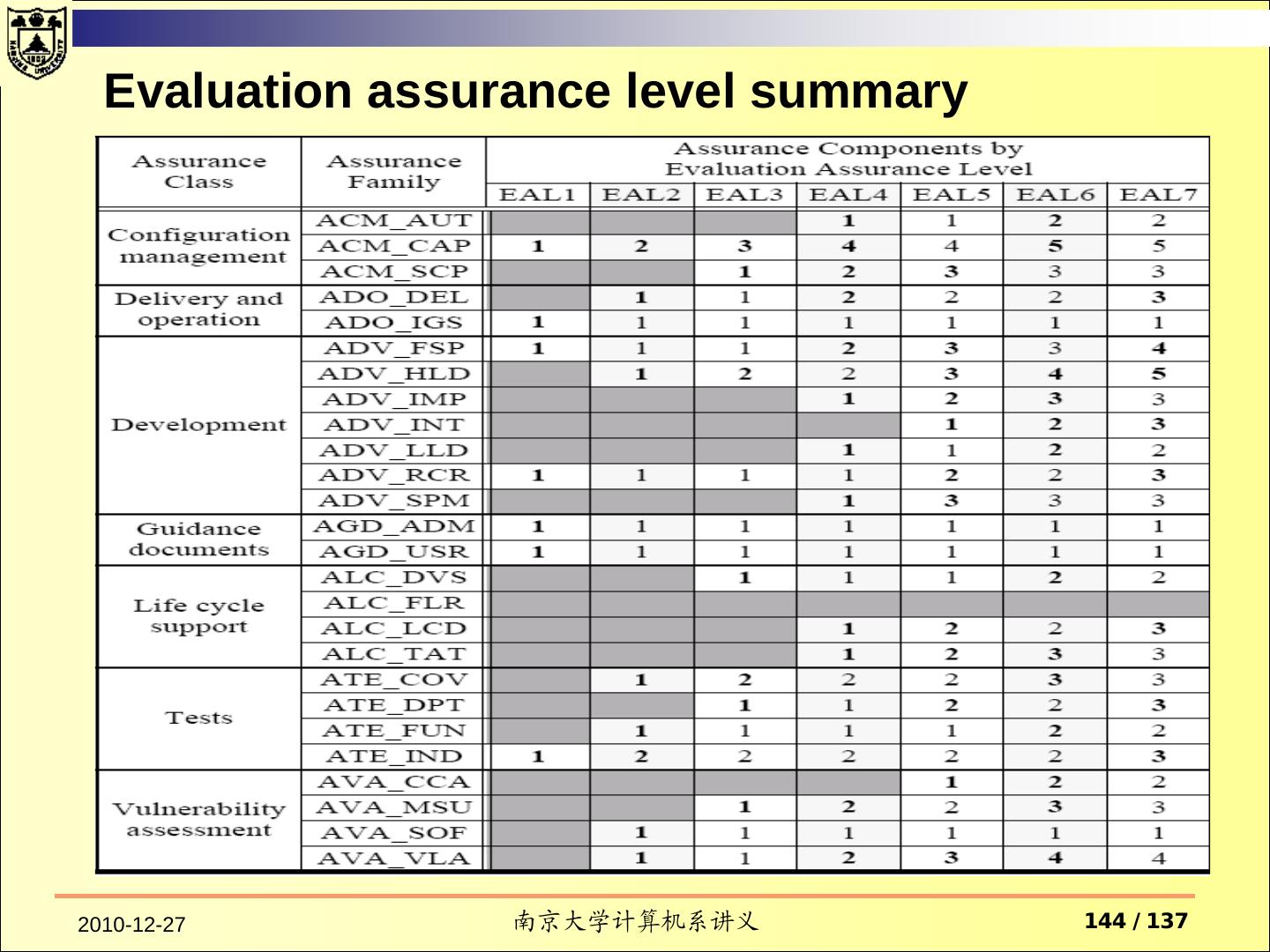
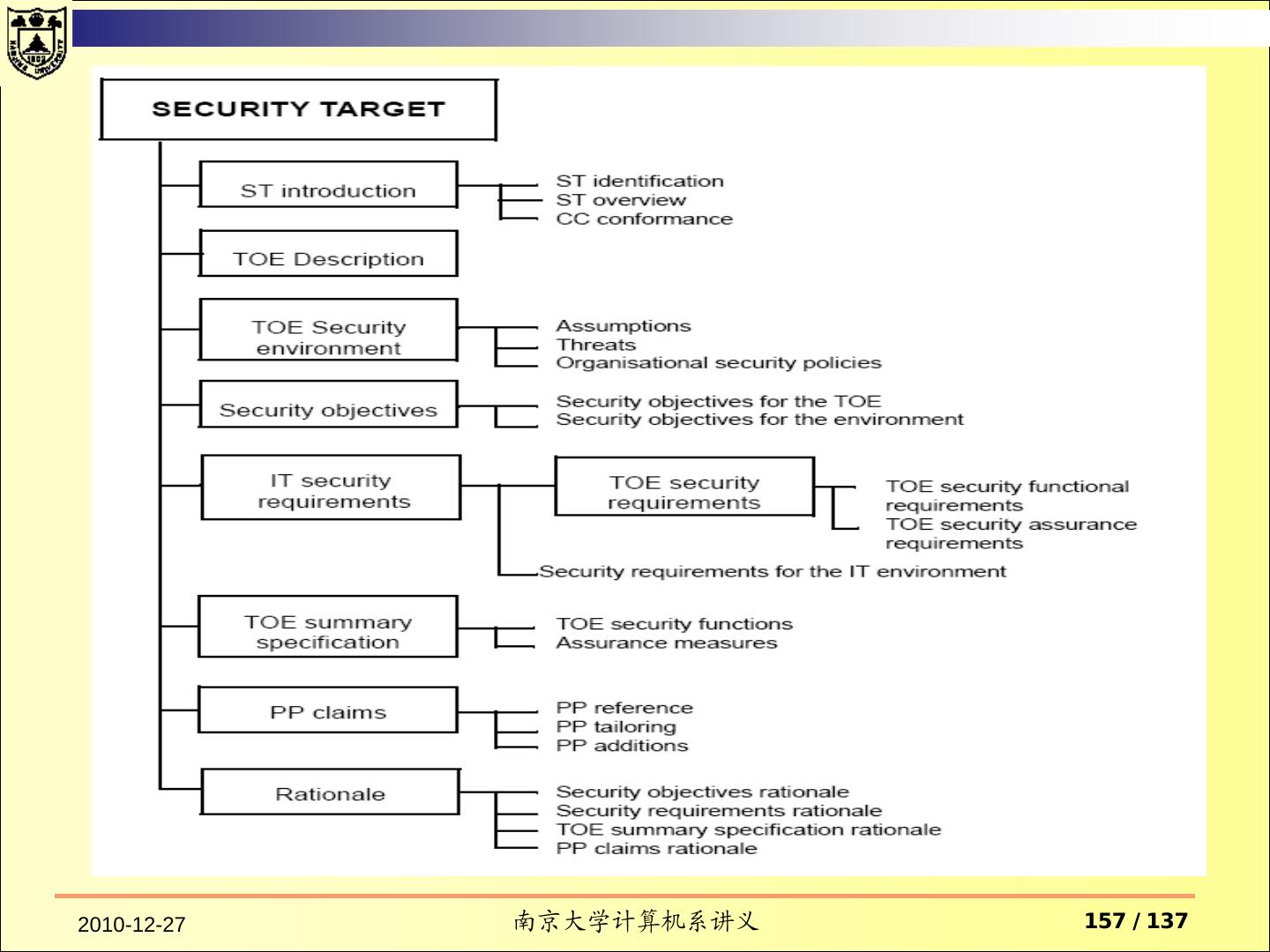
3 . Contents TCSEC Purpose Fundamental Computer Security Requirements Structure of the Criteria Common Criteria 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 3 / 137
4 .Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC) — December 26, 1985
5 . Purpose — Three objectives Provide guidance to manufacturers To provide a standard to manufacturers as to what security features to build into their new and planned, commercial products in order to provide widely available systems that satisfy trust requirements (with particular emphasis on preventing the disclosure of data) for sensitive applications. Evaluate the degree of trust To provide DoD components with a metric with which to evaluate the degree of trust that can be placed in computer systems for the secure processing Provide a basis for specifying security requirements 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 5 / 137
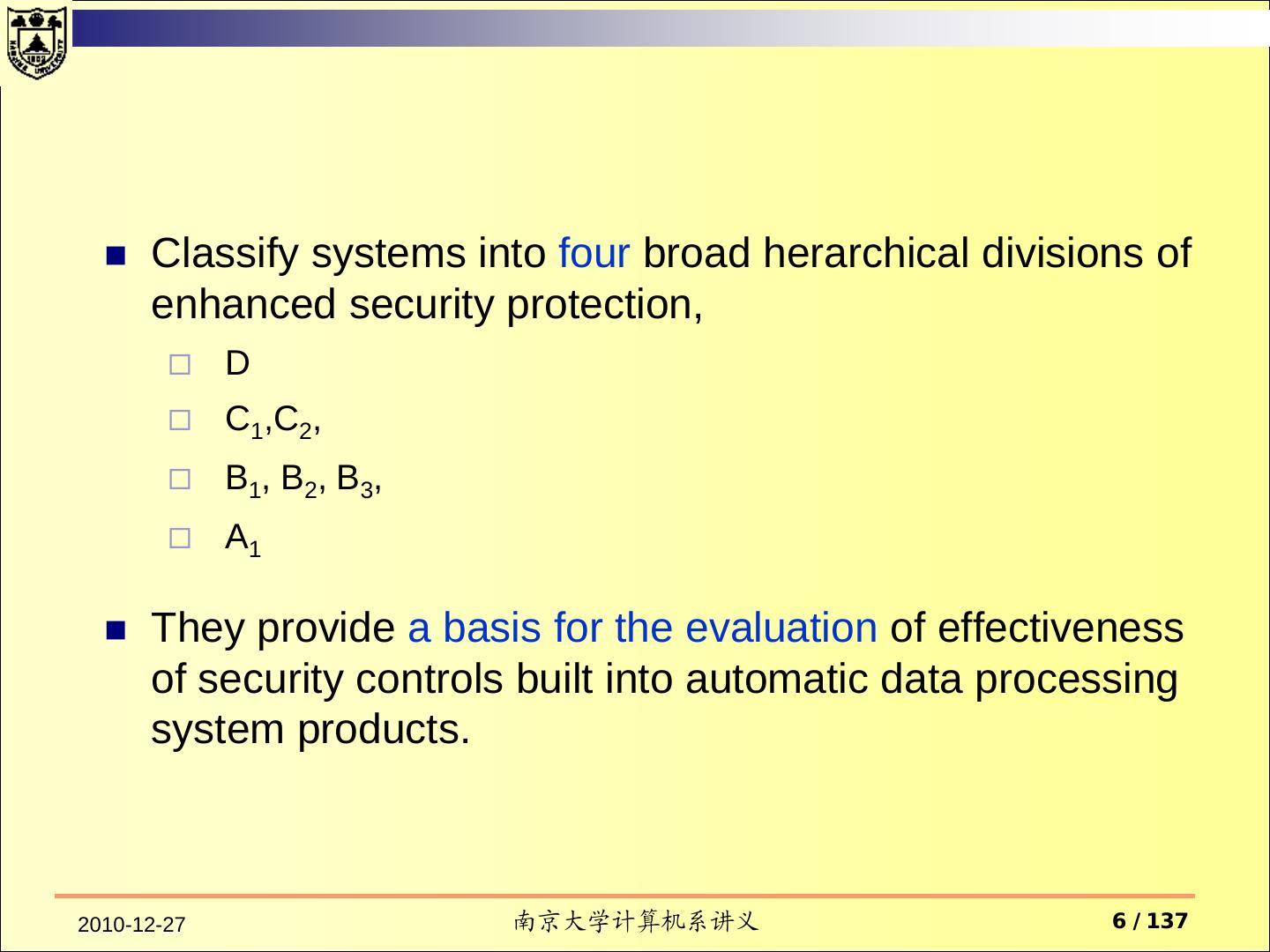
6 . Classify systems into four broad herarchical divisions of enhanced security protection, D C1,C2, B1, B2, B3, A1 They provide a basis for the evaluation of effectiveness of security controls built into automatic data processing system products. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 6 / 137
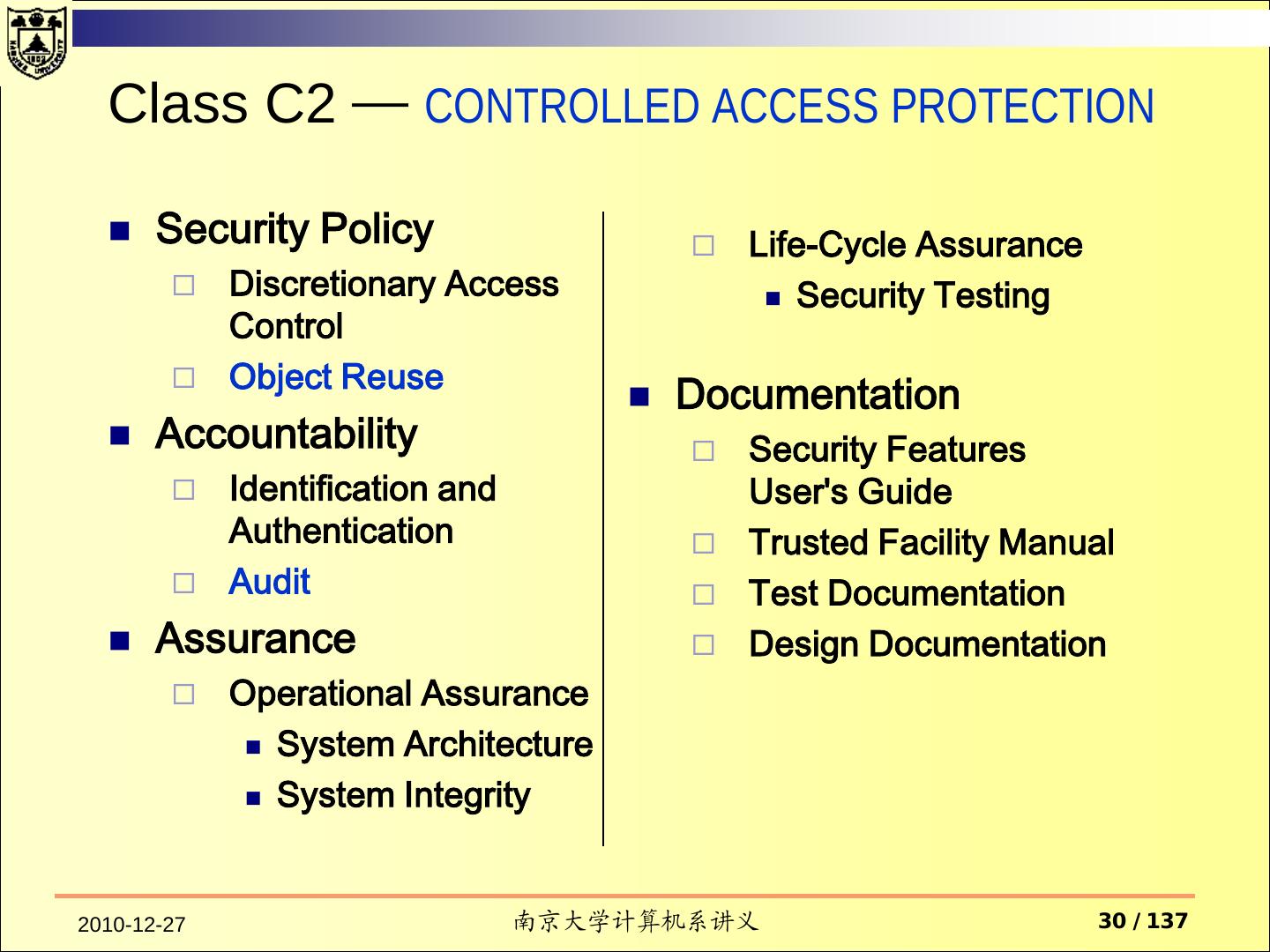
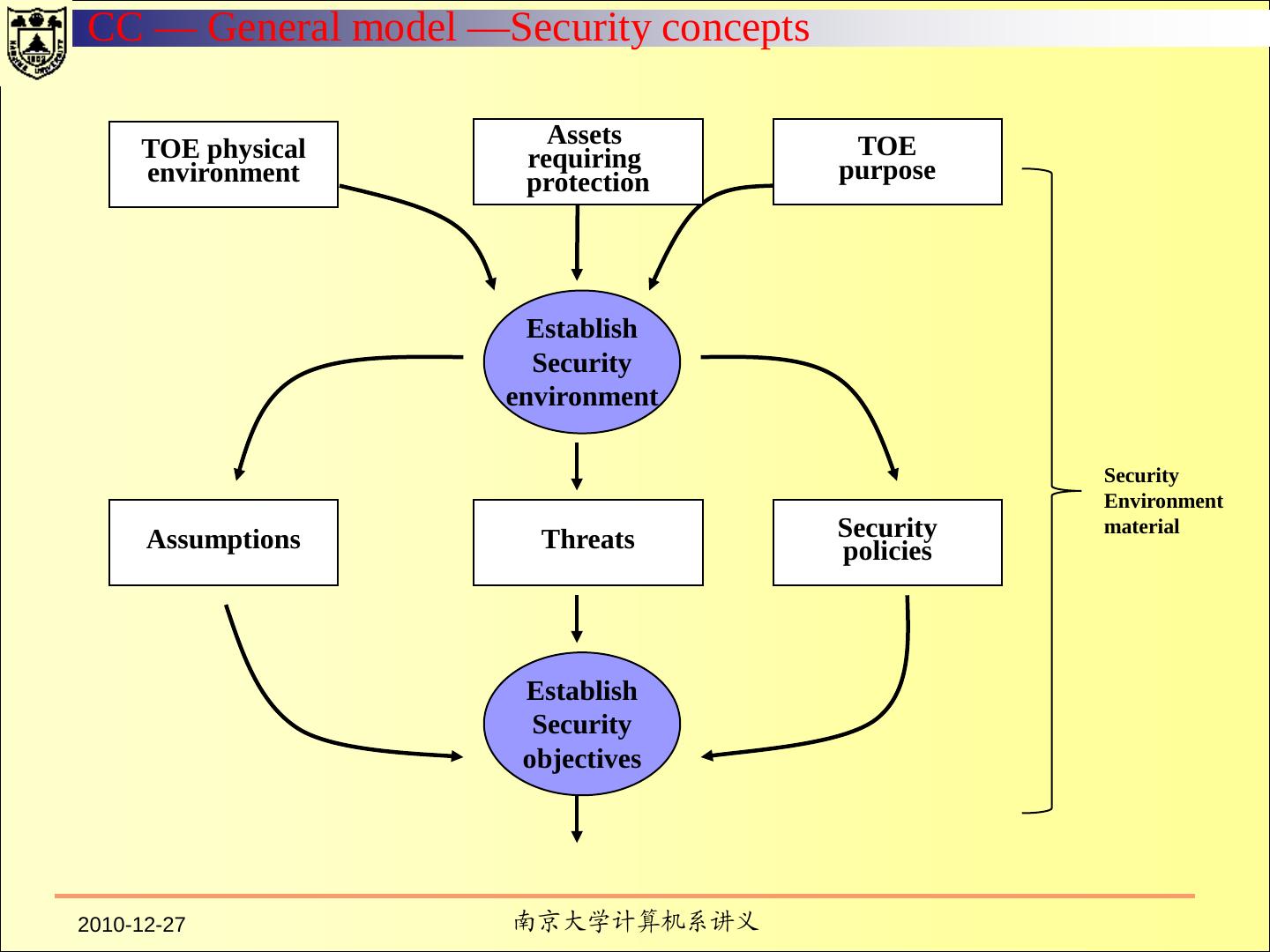
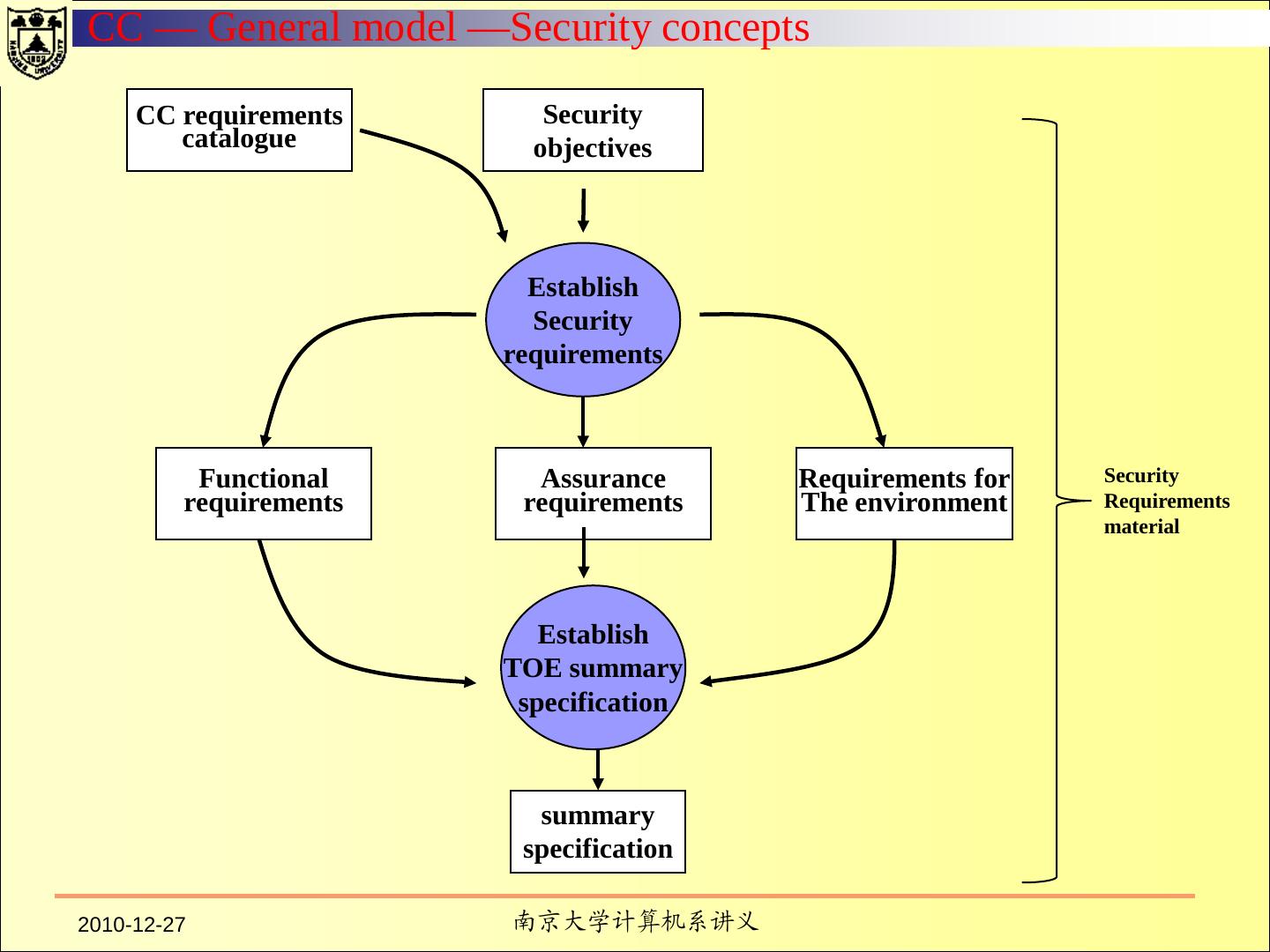
7 . Fundamental Computer Security Requirements Policy Accountability Assurance Documentation 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 7 / 137
8 . Security Policy There must be an explicit and well-defined security policy enforced by the system. Security Policy Discretionary Access Control Object Reuse Labels Label Integrity Exportation of Labeled Information Exportation to Multilevel Devices Exportation to Single-Level Devices Labeling Human-Readable Output Subject Sensitivity Labels Device Labels Mandatory Access Control 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 8 / 137
9 . Accountability — IDENTIFICATION Individual subjects must be identified. Each access to information must be mediated based on who is accessing the information and what classes of information they are authorized to deal with. This identification and authorization information must be securely maintained by the computer system and be associated with every active element that performs some security-relevant action in the system. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 9 / 137
10 . Accountability — Audit Audit information must be selectively kept and protected so that actions affecting security can be traced to the responsible party. A trusted system must be able to record the occurrences of security-relevant events in an audit log. The capability to select the audit events to be recorded is necessary to minimize the expense of auditing and to allow efficient analysis. Audit data must be protected from modification and unauthorized destruction to permit detection and after-the-fact investigations of security violations. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 10 / 137
11 . Accountability Identification and Au2.thentication Trusted Path Audit
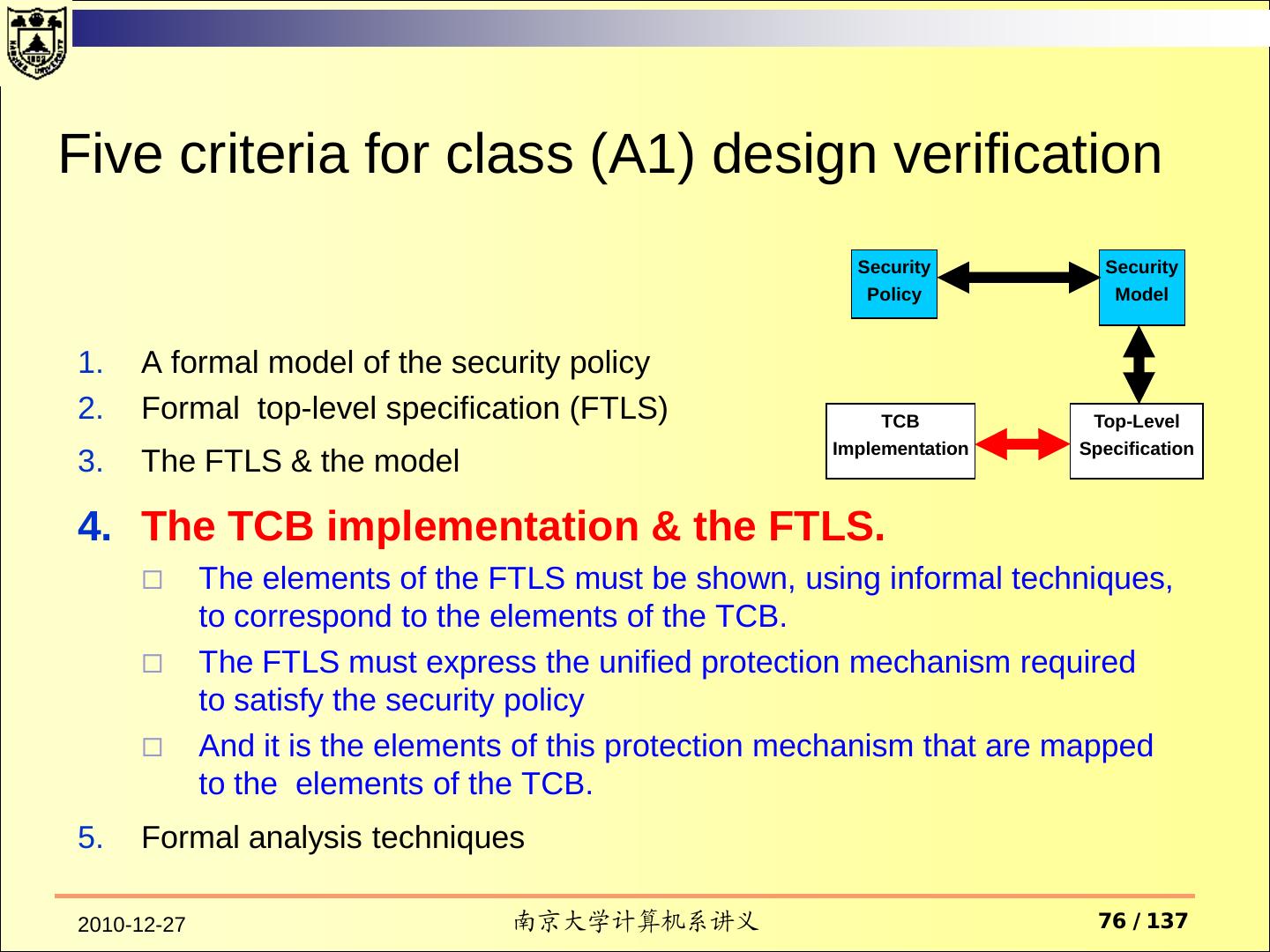
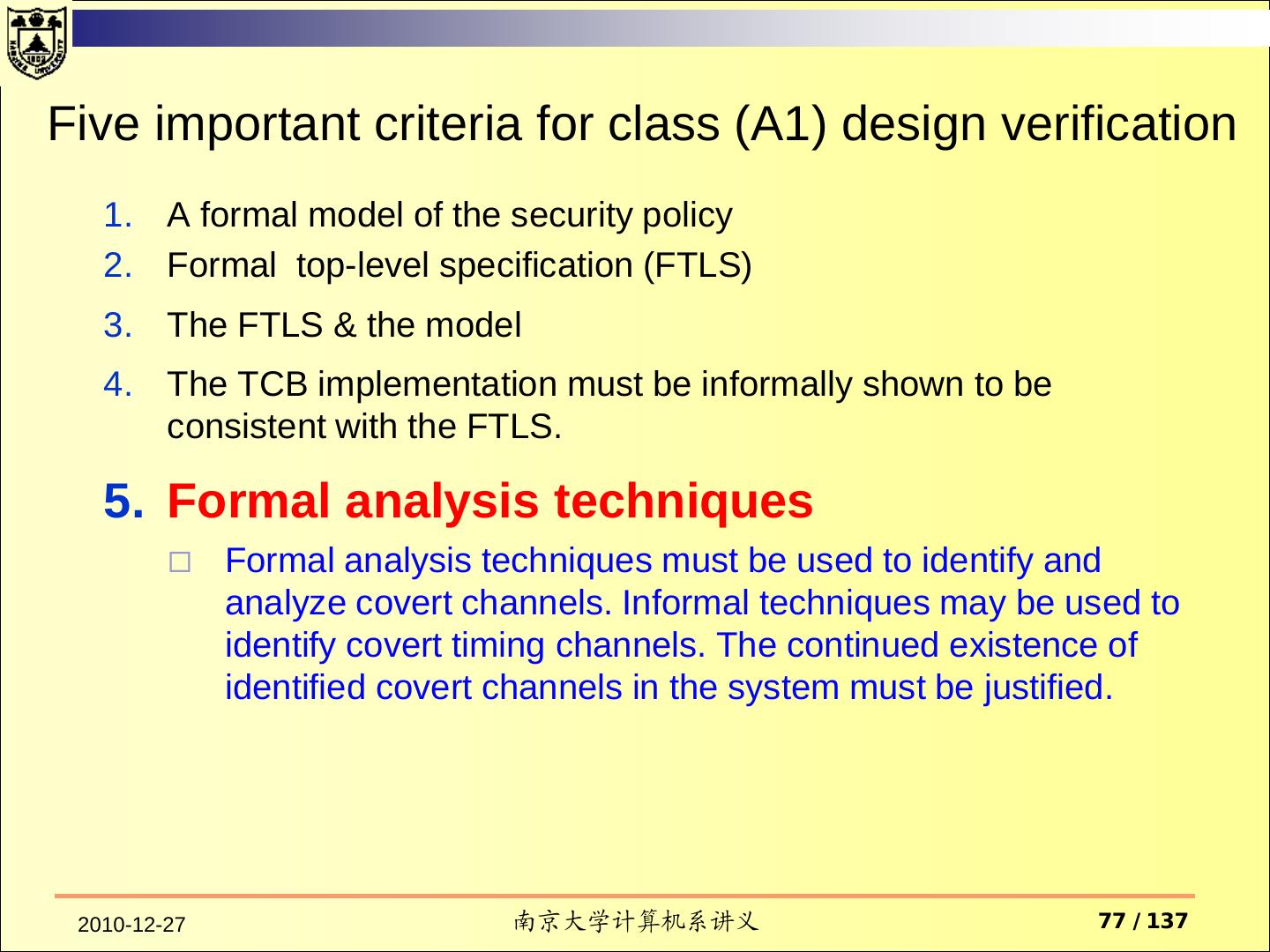
12 . ASSURANCE In order to assure that the four requirements are enforced by a computer system, there must be some identified and unified collection of hardware and software controls that perform those functions. The basis for trusting such system mechanisms in their operational setting must be clearly documented such that it is possible to independently examine the evidence to evaluate their sufficiency. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 12 / 137
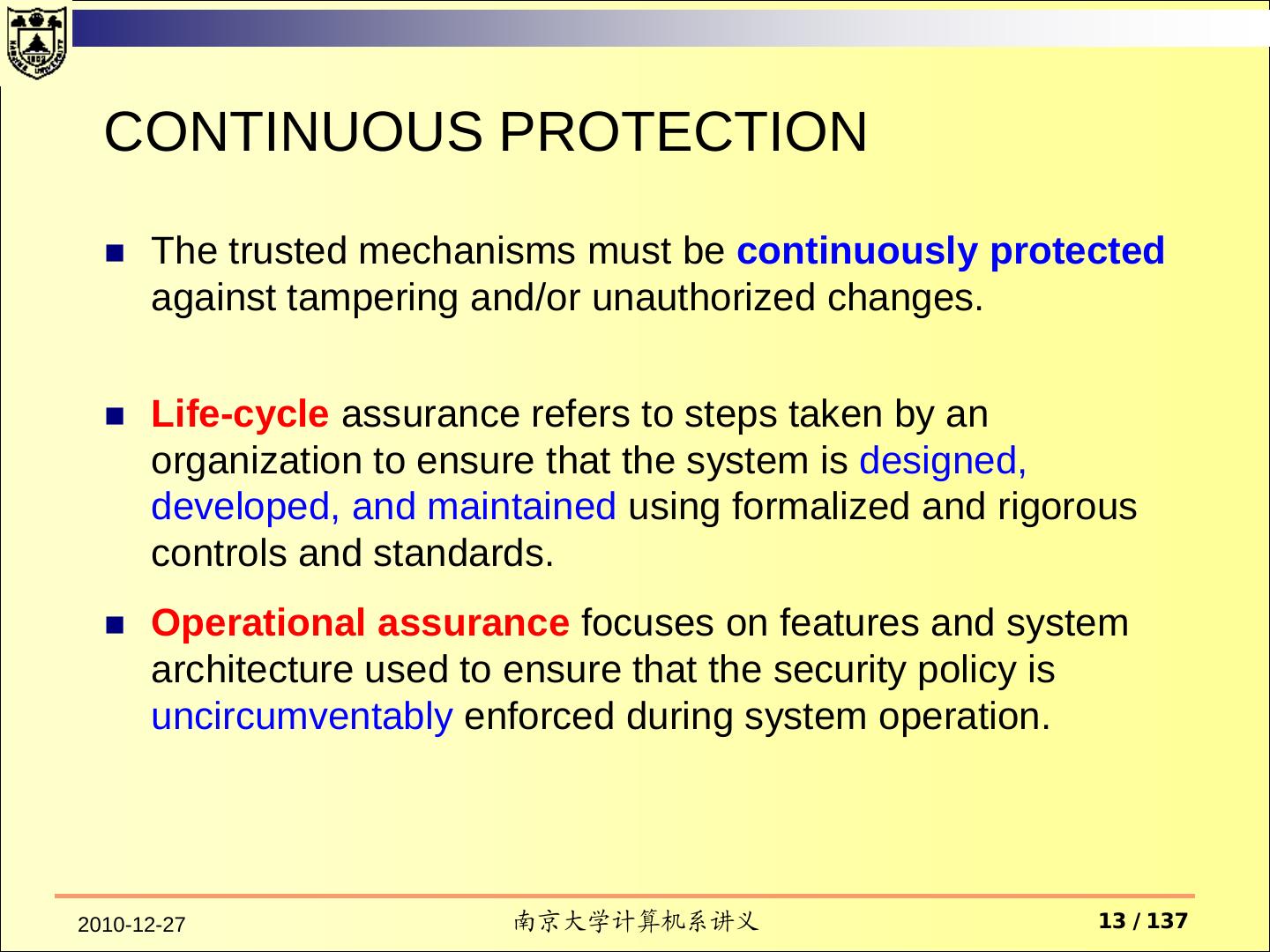
13 . CONTINUOUS PROTECTION The trusted mechanisms must be continuously protected against tampering and/or unauthorized changes. Life-cycle assurance refers to steps taken by an organization to ensure that the system is designed, developed, and maintained using formalized and rigorous controls and standards. Operational assurance focuses on features and system architecture used to ensure that the security policy is uncircumventably enforced during system operation. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 13 / 137
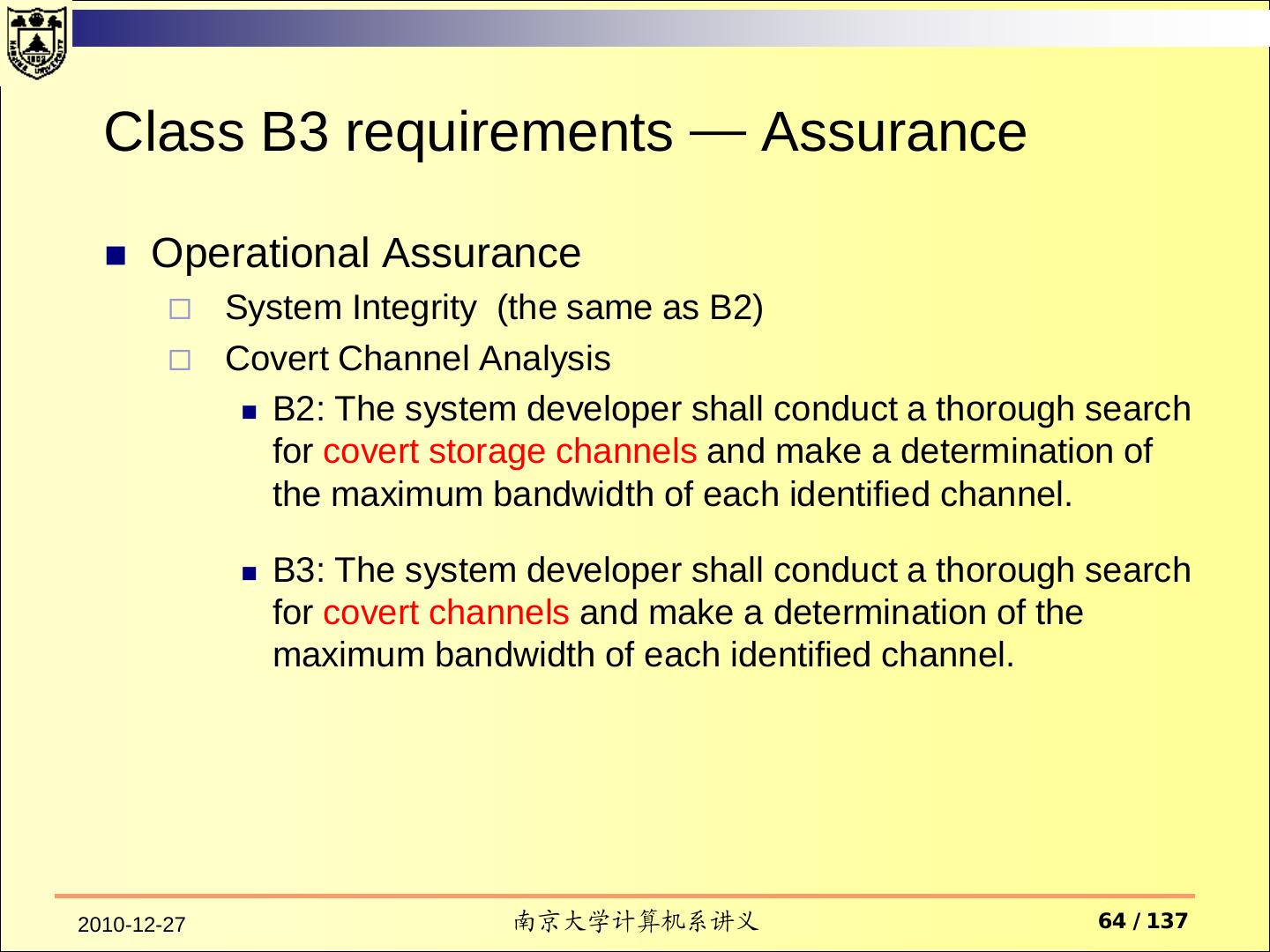
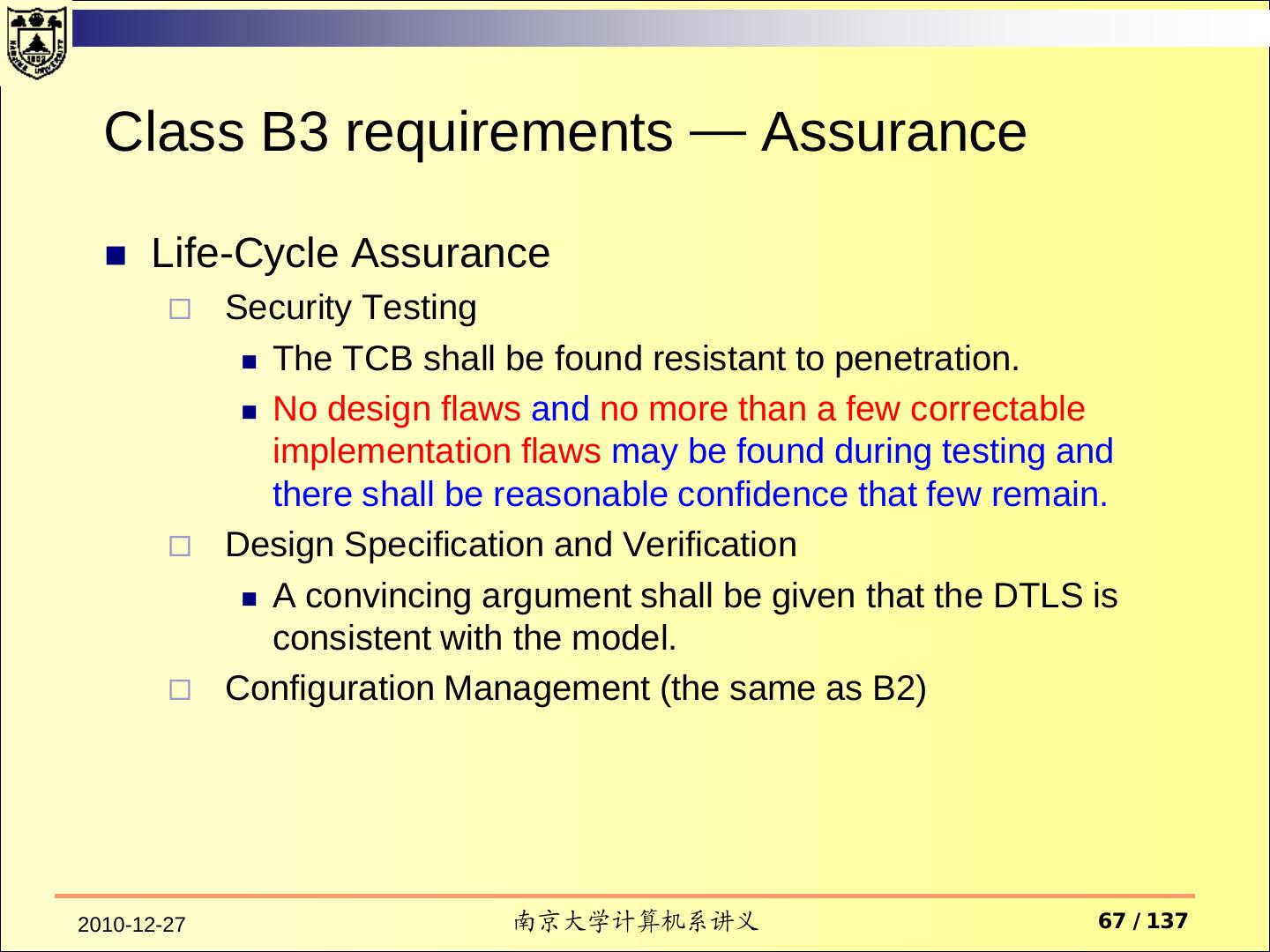
14 . Assurance Operational Assurance System Architecture System Integrity Covert Channel Analysis Trusted Facility Management Trusted Recovery Life-Cycle Assurance Security Testing Design Specification and Verification Configuration Management Trusted Distribution
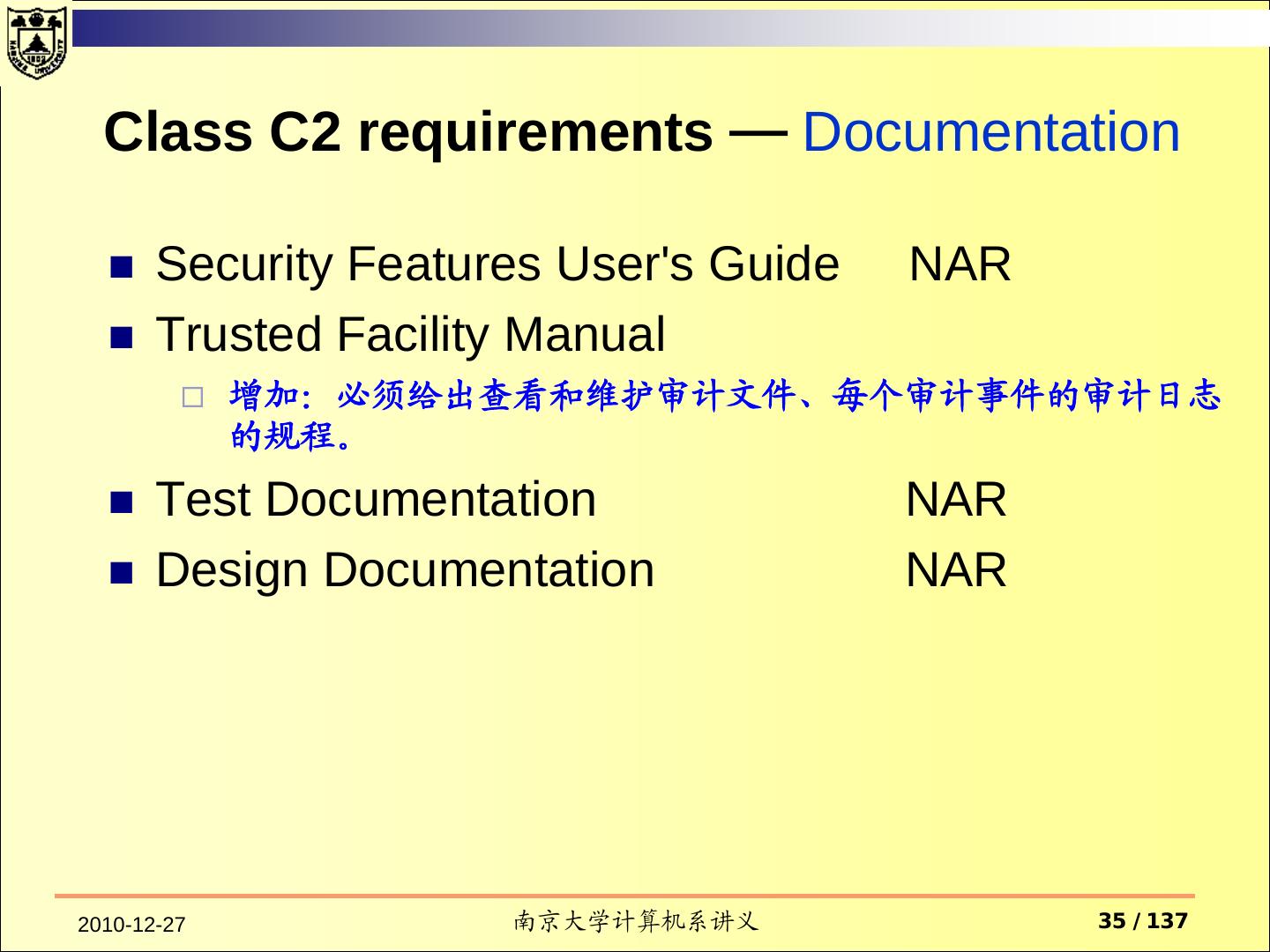
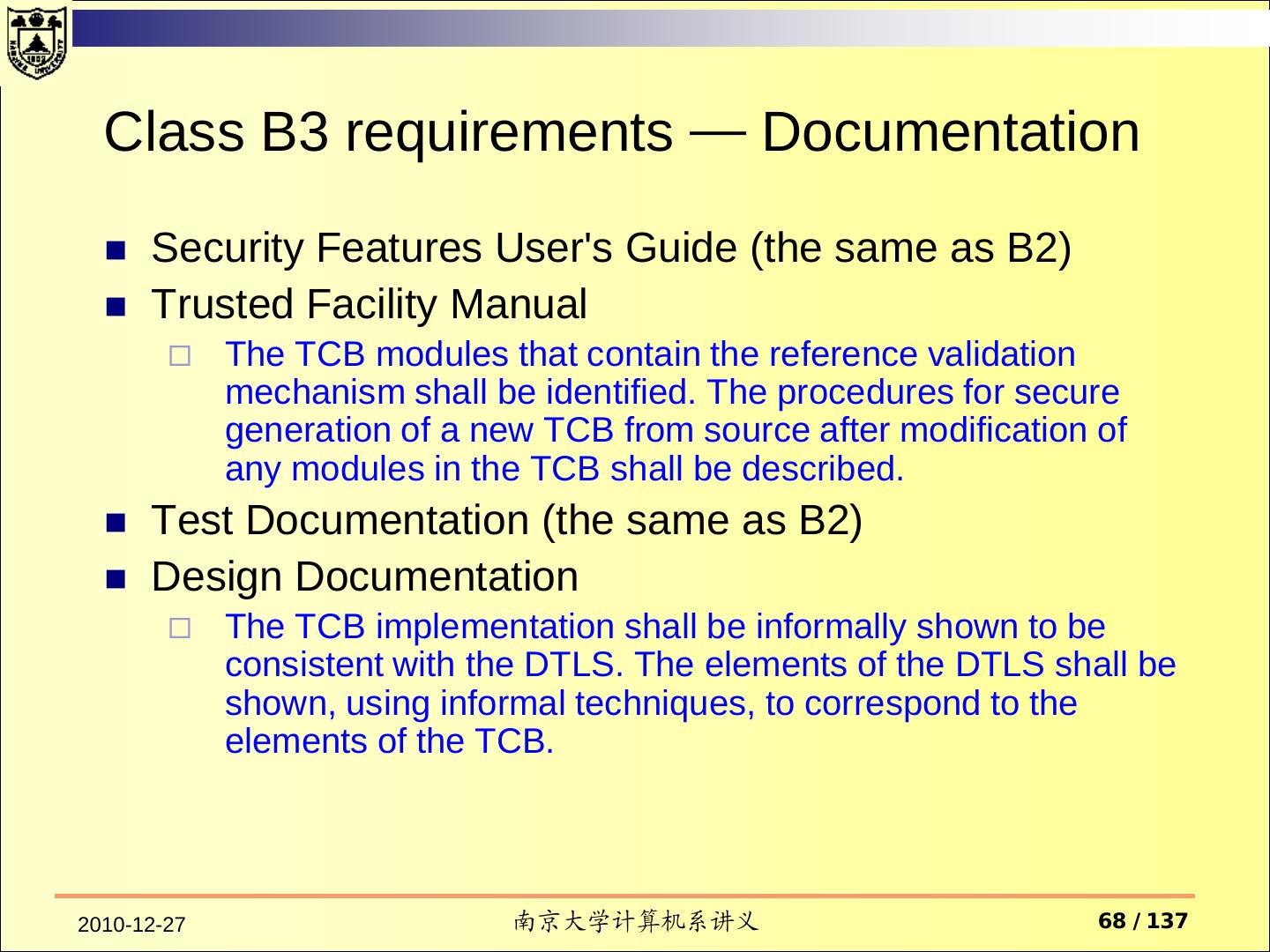
15 . Documentation Security Features User's Guide Trusted Facility Manual Test Documentation Design Documentation
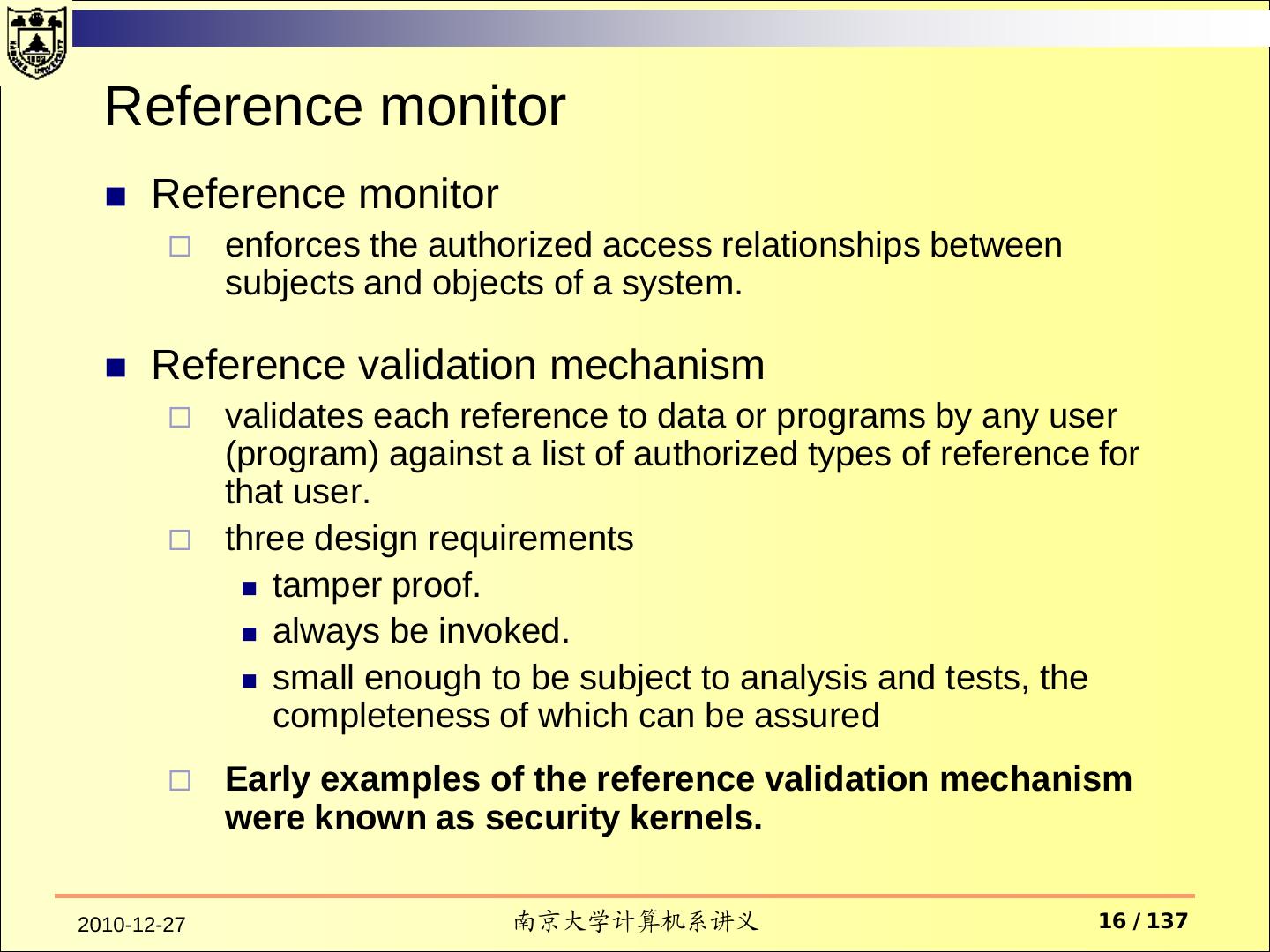
16 . Reference monitor Reference monitor enforces the authorized access relationships between subjects and objects of a system. Reference validation mechanism validates each reference to data or programs by any user (program) against a list of authorized types of reference for that user. three design requirements tamper proof. always be invoked. small enough to be subject to analysis and tests, the completeness of which can be assured Early examples of the reference validation mechanism were known as security kernels. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 16 / 137
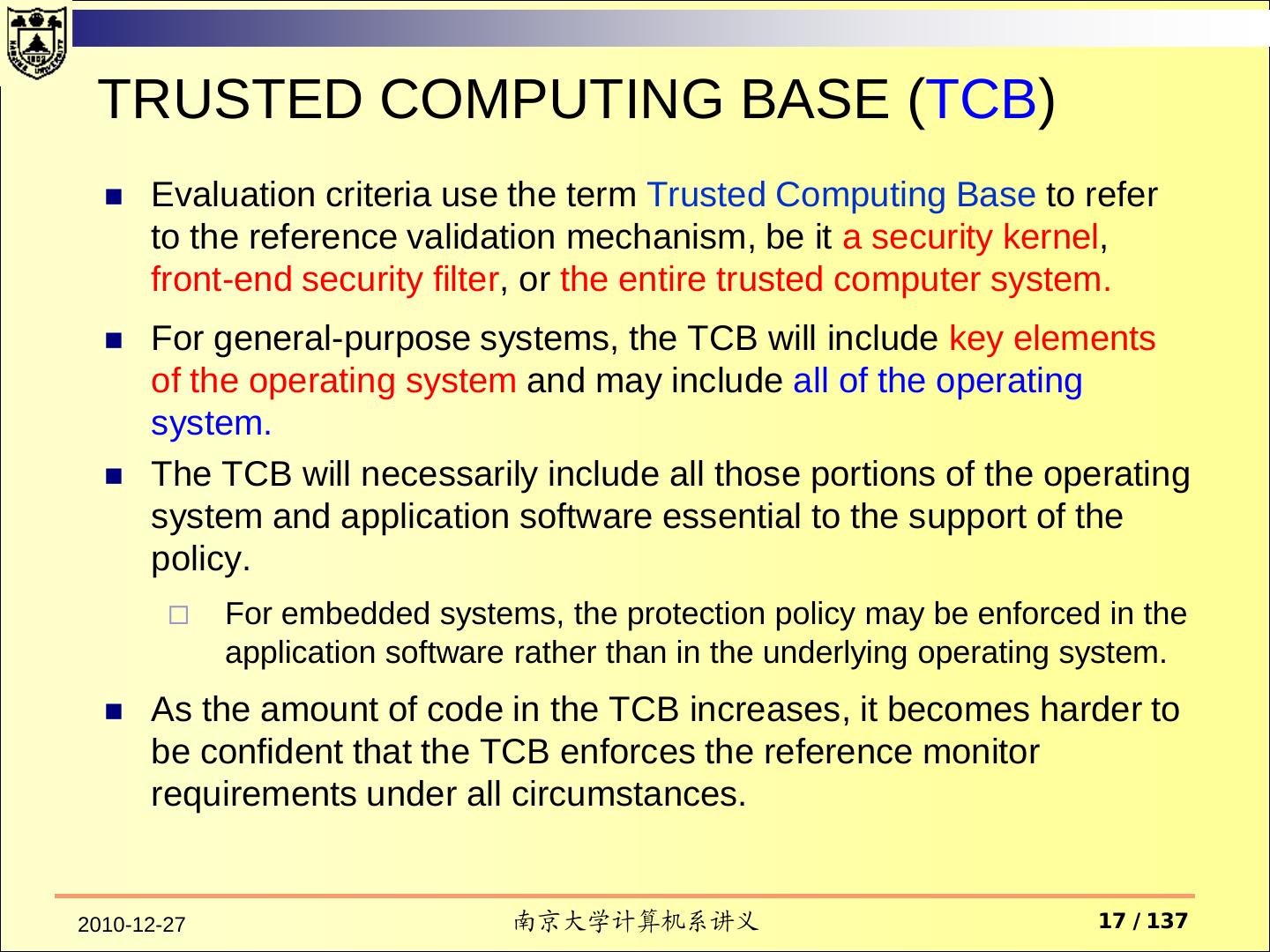
17 . TRUSTED COMPUTING BASE (TCB) Evaluation criteria use the term Trusted Computing Base to refer to the reference validation mechanism, be it a security kernel, front-end security filter, or the entire trusted computer system. For general-purpose systems, the TCB will include key elements of the operating system and may include all of the operating system. The TCB will necessarily include all those portions of the operating system and application software essential to the support of the policy. For embedded systems, the protection policy may be enforced in the application software rather than in the underlying operating system. As the amount of code in the TCB increases, it becomes harder to be confident that the TCB enforces the reference monitor requirements under all circumstances. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 17 / 137
18 . DIVISION D : MINIMAL PROTECTION This division contains only one class. It is reserved for those systems that have been evaluated but that fail to meet the requirements for a higher evaluation class. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 18 / 137
19 .DIVISION C: DISCRETIONARY PROTECTION Classes in this division provide for discretionary protection for accountability of subjects and the actions they initiate 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 19 / 137
20 . CLASS C1 DISCRETIONARY SECURITY PROTECTION The class (C1) environment is expected to be one of cooperating users processing data at the same level(s) of sensitivity. 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 20 / 137
21 . Class C1 requirements Security Policy Documentation Discretionary Access Security Features User's Guide Control Trusted Facility Manual Accountability Test Documentation Identification and Design Documentation Authentication Assurance Operational Assurance System Architecture System Integrity Life-Cycle Assurance Security Testing 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 21 / 137
22 . Class C1 requirements—Security Policy Security Policy — Discretionary Access Control TCB必须在ADP中的命名用户和客体(例如,文件、 程序)之间进行访问控制。 实施的机制采用“本人/用户组/公共”的控制方式,访 问控制列表等,允许用户来指定和控制客体由一些单 个的用户、一些用户组或者两者的组合。 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 22 / 137
23 . Class C1 requirements — Accountability Identification and Authentication TCB必须要求用户在进行任何TCB期望控制的行为之前声明自 己的身份。 TCB必须利用一个受到保护的机制(例如,口令)来认证用户 的身份。 TCB必须保护认证信息,使得任何非授权的用户无法访问认证 信息。 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 23 / 137
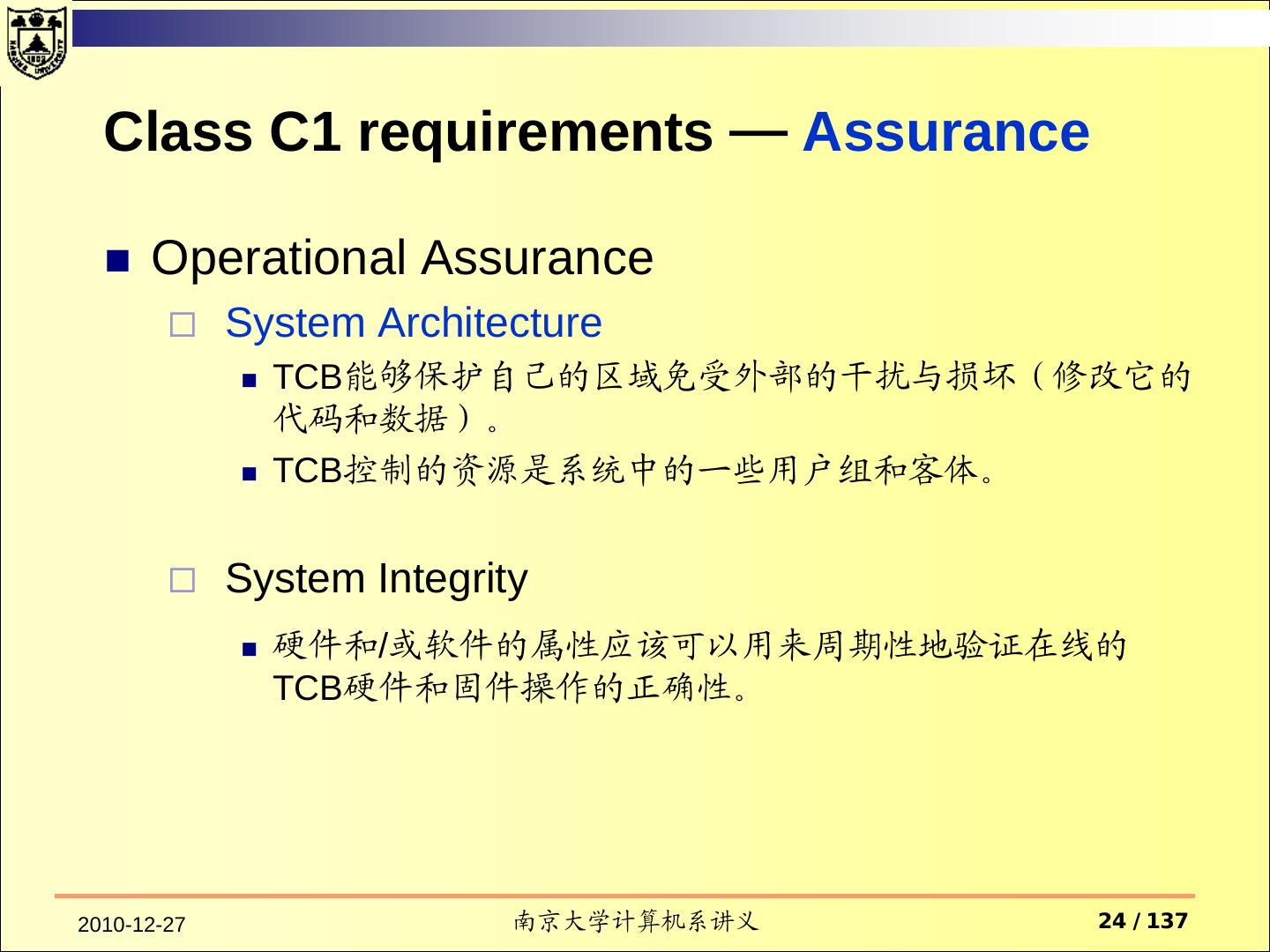
24 . Class C1 requirements — Assurance Operational Assurance System Architecture TCB能够保护自己的区域免受外部的干扰与损坏(修改它的 代码和数据)。 TCB控制的资源是系统中的一些用户组和客体。 System Integrity 硬件和/或软件的属性应该可以用来周期性地验证在线的 TCB硬件和固件操作的正确性。 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 24 / 137
25 . Class C1 requirements — Assurance Life-Cycle Assurance Security Testing 系统的安全功能必须测试过并且与系统的文档描述的一致。 测试结果应当显示系统没有明显的方式让非授权的用户绕过 或击破TCB的保护机制。 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 25 / 137
26 . Class C1 requirements — Documentation Security Features User's Guide 用户手册应有专门章节描述TCB提供的保护机制、使用指南、相 互之间的交互。 Trusted Facility Manual Test Documentation Design Documentation 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 26 / 137
27 . Class C1 requirements — Documentation Security Features User's Guide Trusted Facility Manual 给ADP系统管理员的手册必须说明在运行一个安全工具时对它 的功能与特权需要考虑的注意事项。 Test Documentation Design Documentation 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 27 / 137
28 . Class C1 requirements — Documentation Security Features User's Guide Trusted Facility Manual Test Documentation 系统开发者应该向评估者提供文档描述 测试计划 测试过程 说明安全机制和安全机制的功能是如何测试的。 Design Documentation 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 28 / 137
29 . Class C1 requirements — Documentation Security Features User's Guide Trusted Facility Manual Test Documentation Design Documentation 必 须 提 供 描 述 开 发 者 的 保 护 思 想 ( philosophy : motivating concepts and principles)。 这些保护思想如何对应到TCB中。 如果TCB由多个模块组成,需要阐述模块之间的接口。 2010-12-27 南京大学计算机系讲义 29 / 137