- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
16 计算机组成--高速缓冲存储器
展开查看详情
1 . Cache Memory Bus P Cache Memory Cache is a small high-speed memory. Stores data from some frequently used addresses (of main memory). Cache hit Data found in cache. Results in data transfer at maximum speed. Cache miss Data not found in cache. Processor loads data from M and copies into cache. This results in extra delay, called miss penalty. Hit ratio = percentage of memory accesses satisfied by the cache. Miss ratio = 1-hit ratio
2 .Cache Line Cache is partitioned into lines (also called blocks). Each line has 4-64 bytes in it. During data transfer, a whole line is read or written. Each line has a tag that indicates the address in M from which the line has been copied. Index Tag Data Index Data 0 2 ABC 0 DEF 1 0 DEF 1 PQR 2 ABC 3 XYZ Cache Main Memory Cache hit is detected through an associative search of all the tags. Associative search provides a fast response to the query: “Does this key match with any of the tags?” Data is read only if a match is found.
3 . Types of Cache 1. Fully Associative 2. Direct Mapped 3. Set Associative Fully Associative Cache tag data M-addr key C M “No restriction on mapping from M to C.” Associative search of tags is expensive. Feasible for very small size caches only.
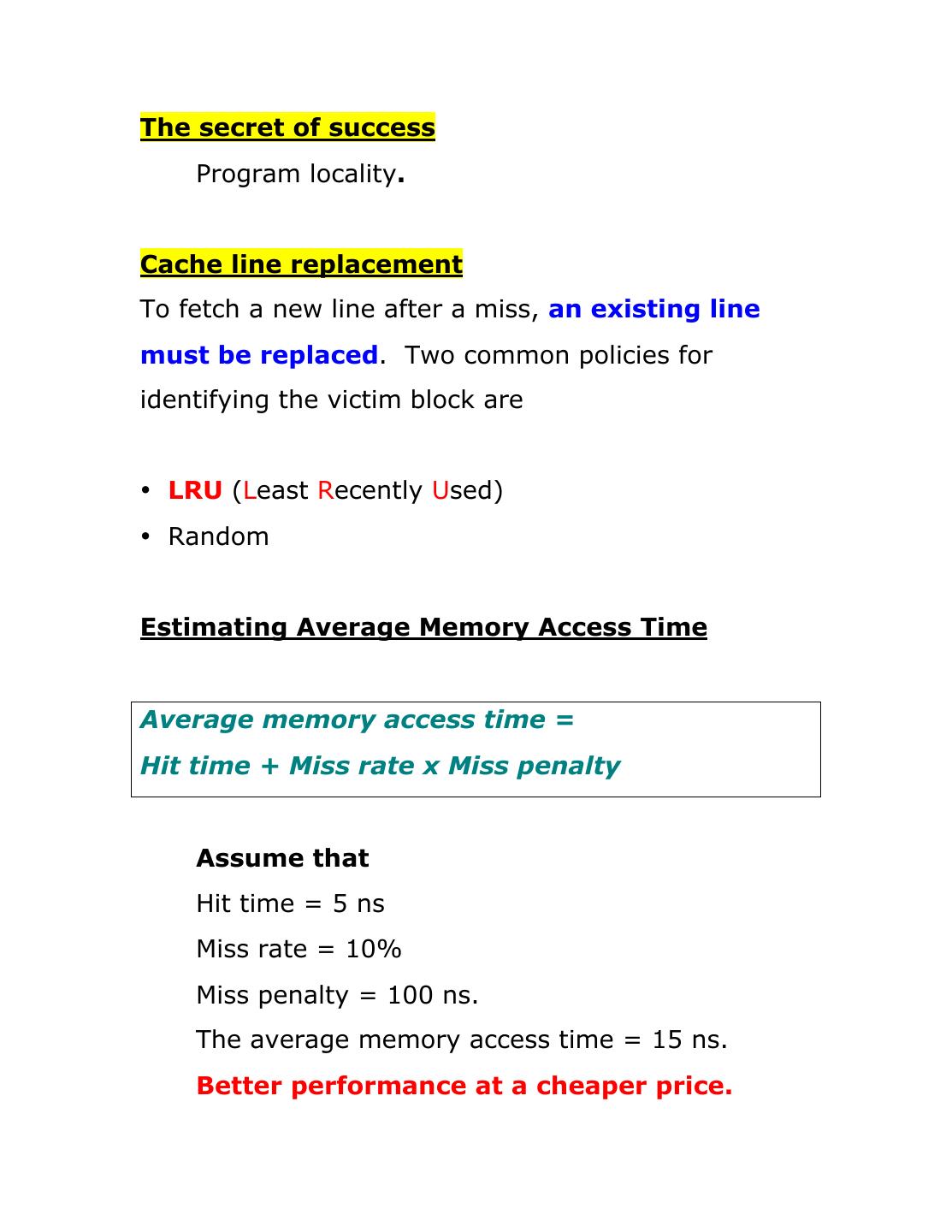
4 .The secret of success Program locality. Cache line replacement To fetch a new line after a miss, an existing line must be replaced. Two common policies for identifying the victim block are • LRU (Least Recently Used) • Random Estimating Average Memory Access Time Average memory access time = Hit time + Miss rate x Miss penalty Assume that Hit time = 5 ns Miss rate = 10% Miss penalty = 100 ns. The average memory access time = 15 ns. Better performance at a cheaper price.
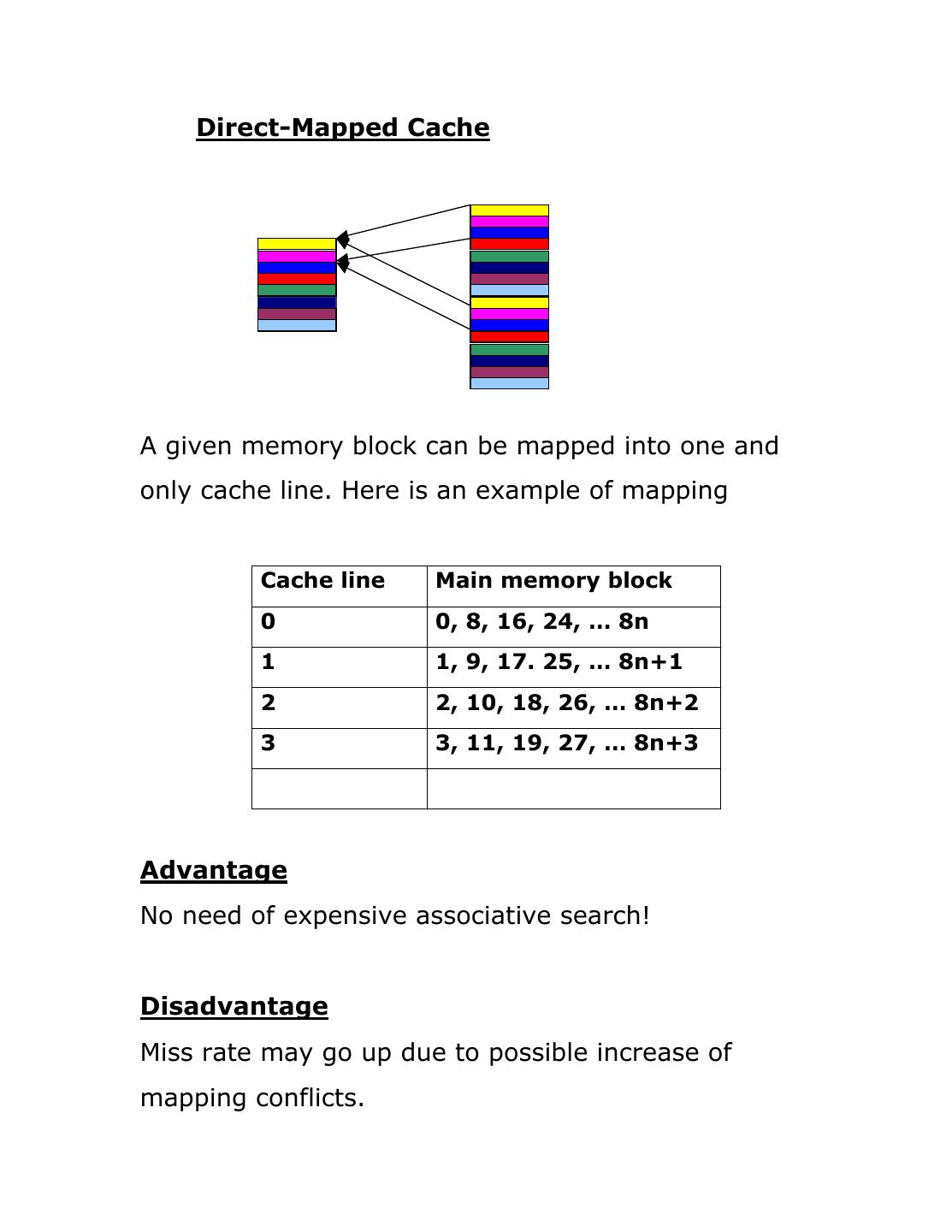
5 . Direct-Mapped Cache A given memory block can be mapped into one and only cache line. Here is an example of mapping Cache line Main memory block 0 0, 8, 16, 24, … 8n 1 1, 9, 17. 25, … 8n+1 2 2, 10, 18, 26, … 8n+2 3 3, 11, 19, 27, … 8n+3 Advantage No need of expensive associative search! Disadvantage Miss rate may go up due to possible increase of mapping conflicts.
6 .Set-Associative Cache C M set 0 set 1 Set 3 Two-way Set-associative cache N-way set-associative cache Each M-block can now be mapped into any one of a set of N C-blocks. The sets are predefined. Let there be K blocks in the cache. Then N=1 Direct-mapped cache N=K Fully associative cache Most commercial cache have N= 2, 4, or 8. Cheaper than a fully associative cache. Lower miss ratio than a direct mapped cache. But direct-mapped cache is the fastest.
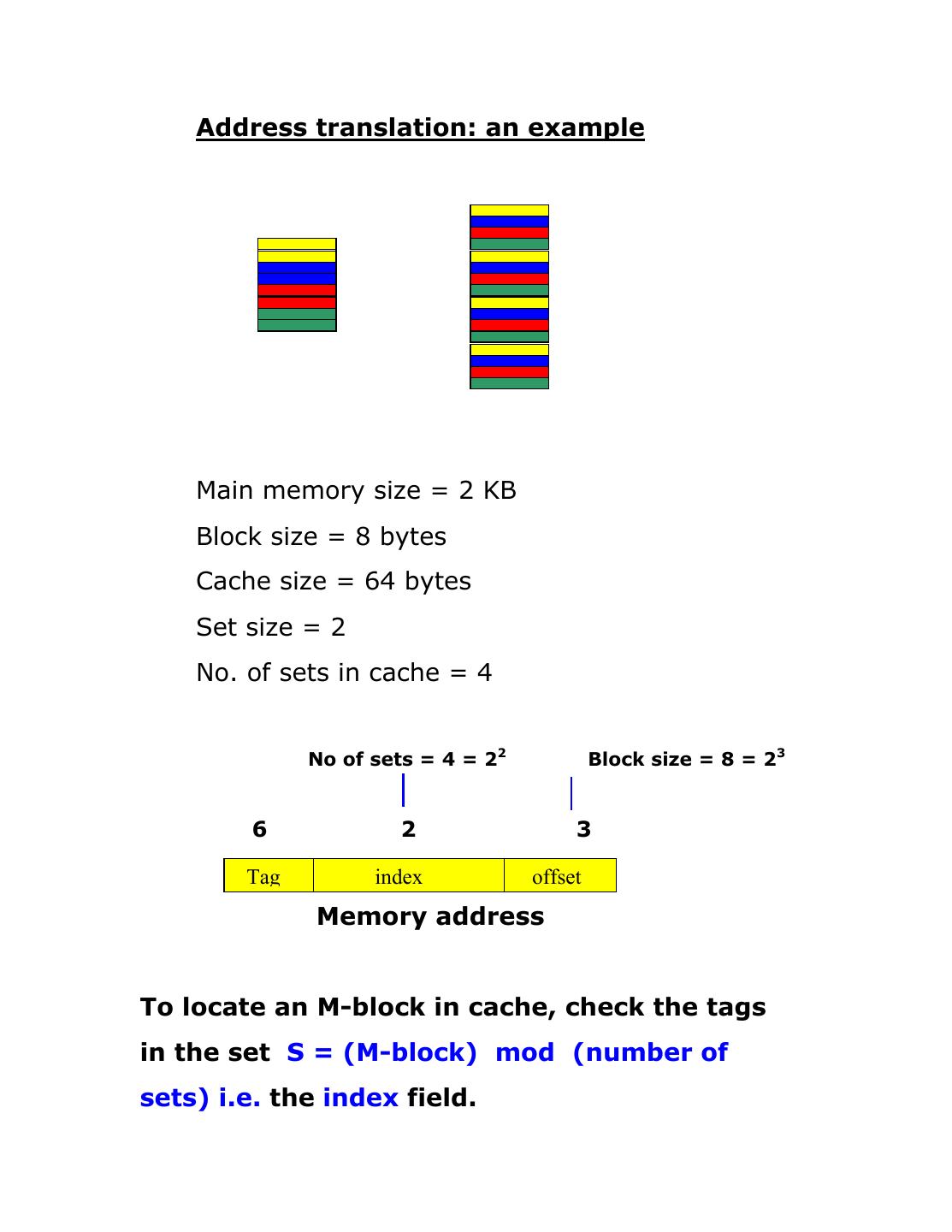
7 . Address translation: an example Main memory size = 2 KB Block size = 8 bytes Cache size = 64 bytes Set size = 2 No. of sets in cache = 4 No of sets = 4 = 22 Block size = 8 = 23 6 2 3 Tag index offset Memory address To locate an M-block in cache, check the tags in the set S = (M-block) mod (number of sets) i.e. the index field.
8 .Specification of a cache memory Block size 4-64 byte Hit time 1-2 cycle Miss penalty 8-32 cycles Access 6-10 cycles Transfer 2-22 cycles Miss rate 1-20% Cache size L1 8KB-64KB L2 128KB-2 MB Cache speed L1 0.5 ns (8 GB/sec) L2* 0.75 ns (6 GB/sec) on-chip cache What happens to the cache during a write operation?