- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- <iframe src="https://www.slidestalk.com/u229/computerandnetworksecurity19?embed" frame border="0" width="640" height="360" scrolling="no" allowfullscreen="true">复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
19computer and network security-Mobile Device,Platform Security
展开查看详情
1 .Mobile Device and Platform Security – Part II John Mitchell CS 155 Spring 2018
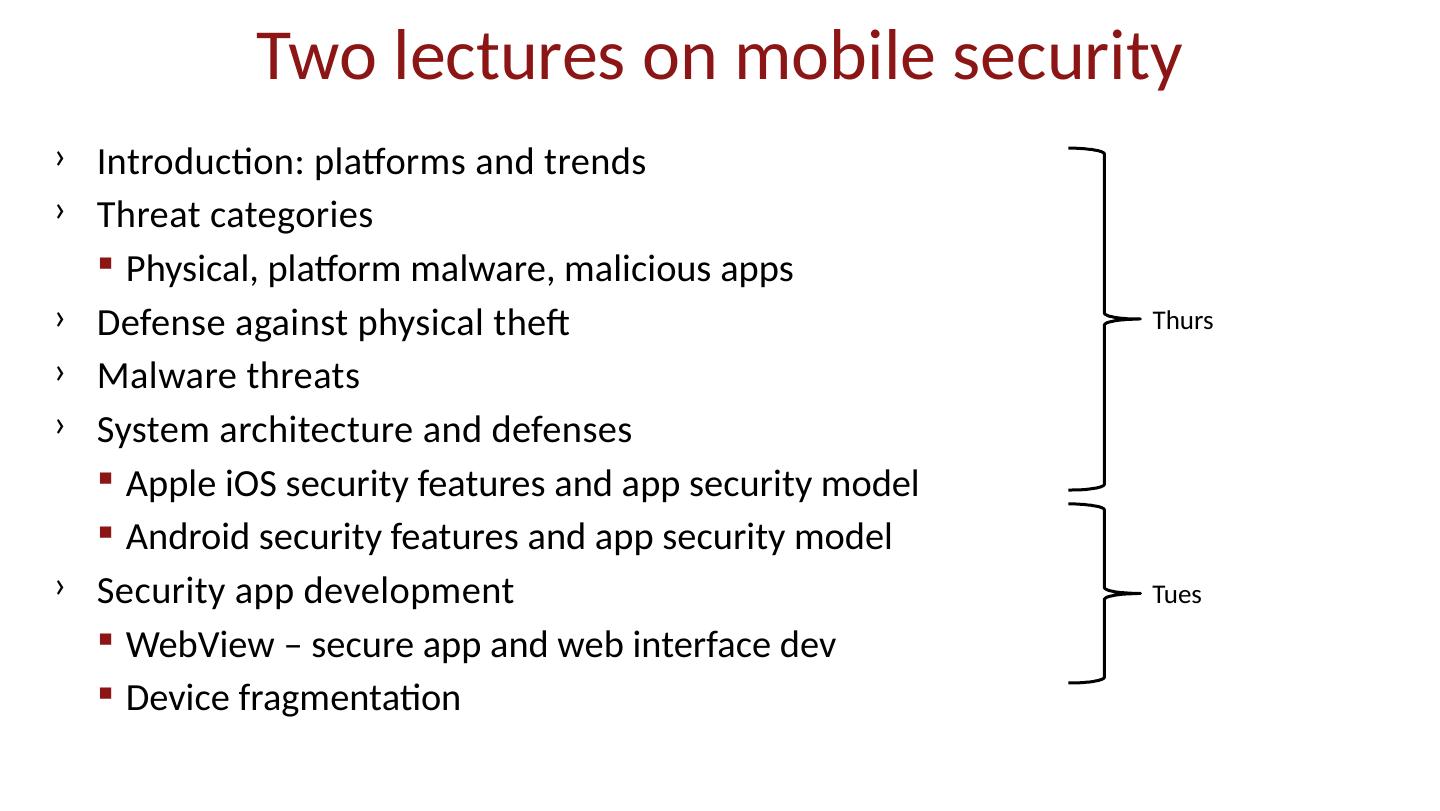
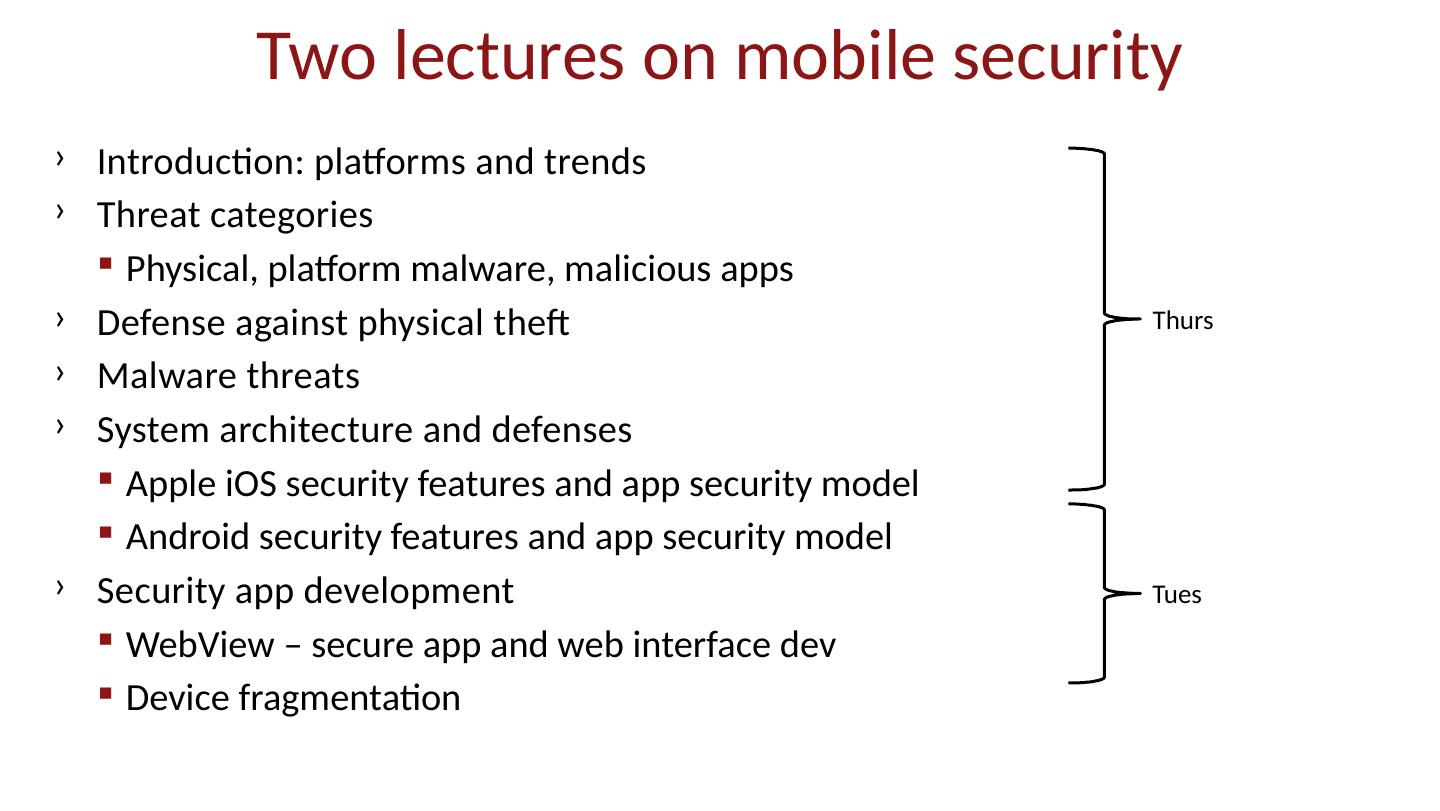
2 .Two lectures on mobile security Introduction: platforms and trends Threat categories Physical, platform malware, malicious apps Defense against physical theft Malware threats System architecture and defenses Apple iOS security features and app security model Android security features and app security model Security app development WebView – secure app and web interface dev Device fragmentation Thurs Tues
3 .Android History and early decisions
4 .Android history Android, Inc founded by Andy Rubin around 2005 Worked with HTC-built device with a physical keyboard Scrapped Blackberry-like phone when iPhone came out First Android phone HTC Dream, Oct 2008 (T-Mobile G1): touchscreen and keyboard Open-source software project Backed and acquired by Google
5 .HTC Dream First phone had Android 1.6 (Donut) 3.15 megapixel rear camera with auto-focus 3.2 inch touchscreen Gmail, Google Maps, Search, Google Talk, You Tube, calendar, contacts, alarm
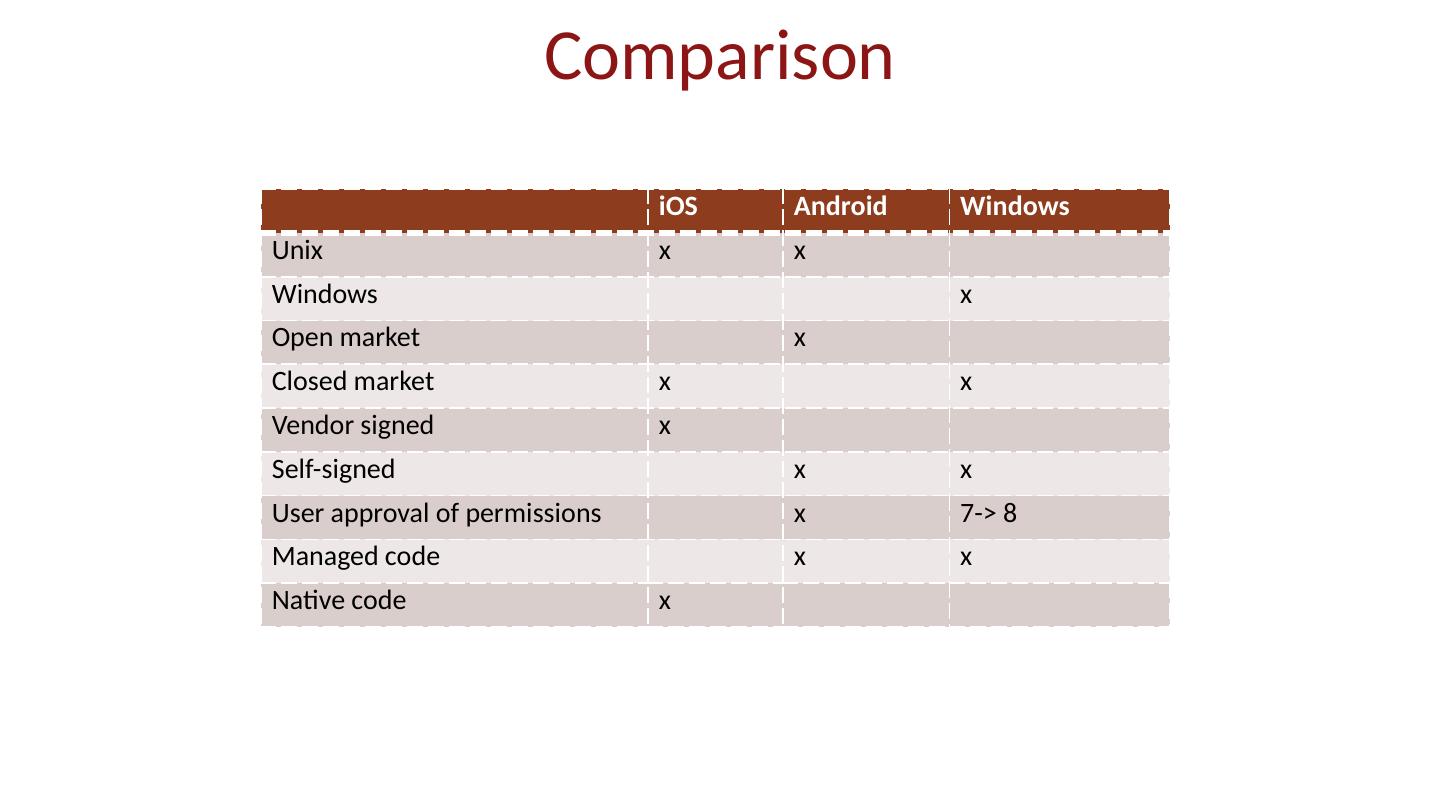
6 .Android ecosystem Open-source software distributed by Google Business goal: increase number of users and devices linked to core Google products Multiple hardware vendors Each customize software for their products Open marketplace for apps Aim for scale Aside: open-source OS successful pre-mobile
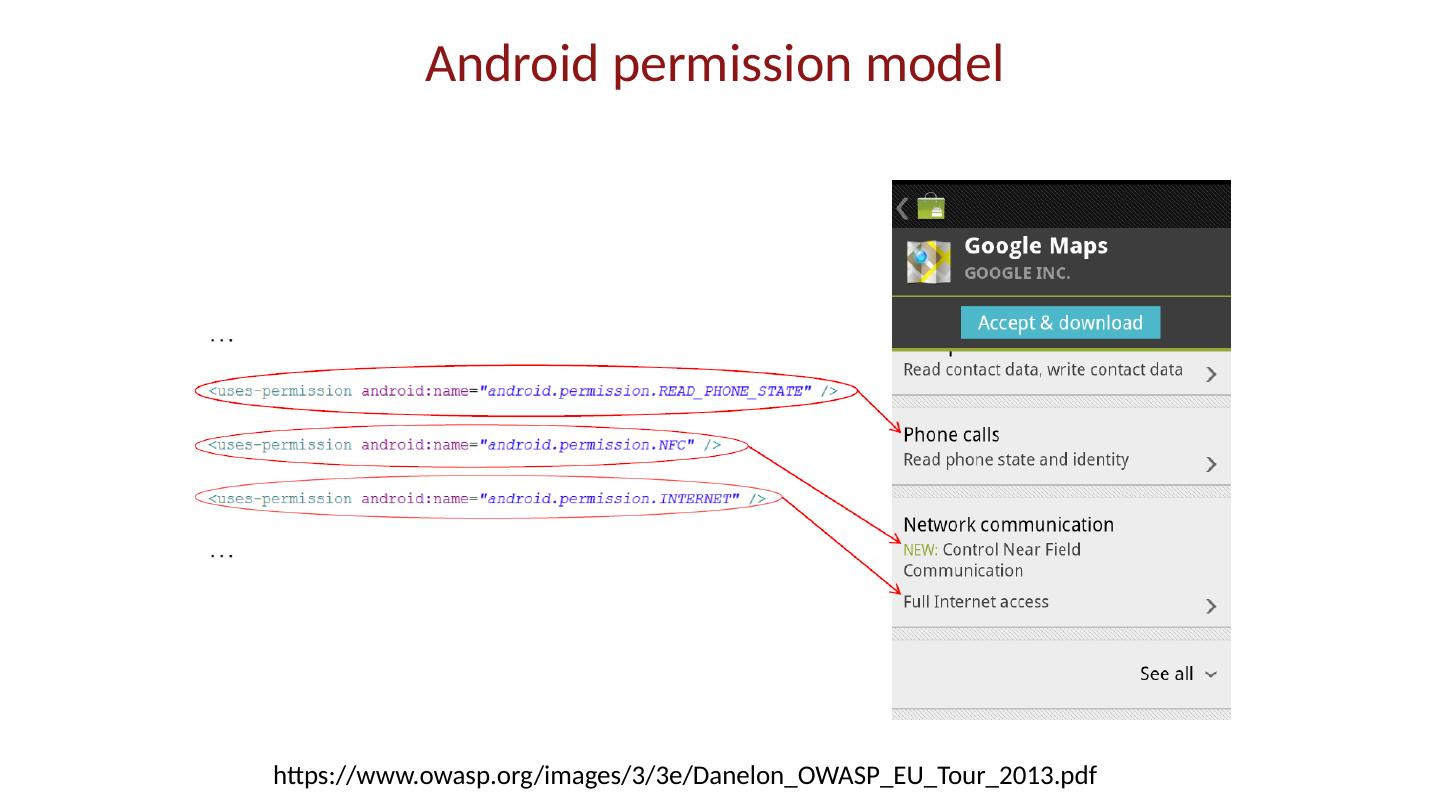
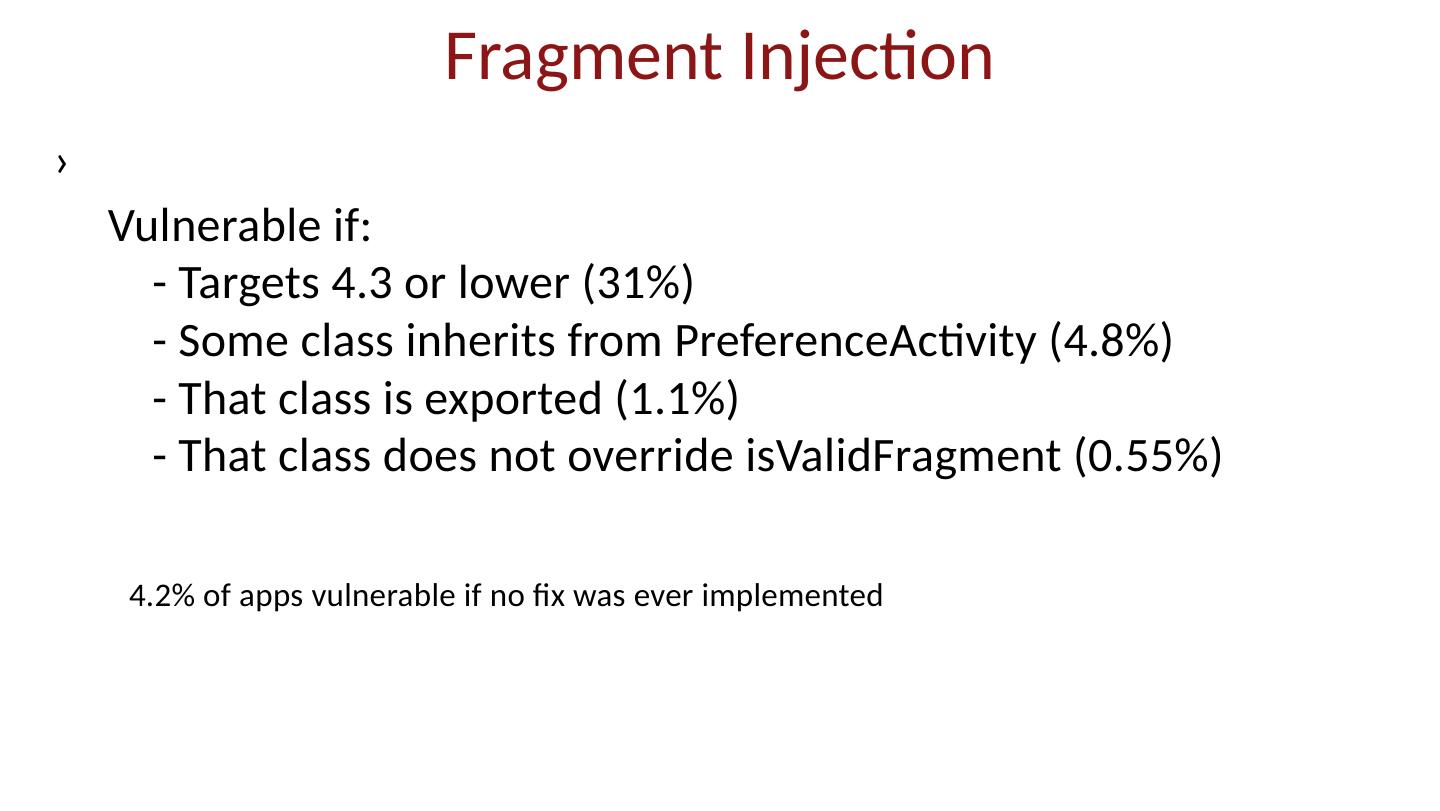
7 .App market Self-signed apps App permissions granted on user installation Open market Bad apps may show up on market Shifts focus from remote exploit to privilege escalation
8 .Android Platform Theft and loss protection
9 .Predictive security Look for malicious code in apps Privacy advisor See if app can access private information Locate lost phone Map location and make a sound Lock and wipe Web interface to remotely remove data Data backup Store and retrieve from cloud https://www.lookout.com/android
10 .Device lock and unlock Similar PIN and fingerprint Fingerprint API lets users Unlock device Securely sign in to apps Use Android Pay Purchase on Play Store
11 .Android Platform Managed code
12 .Managed code overview Java programming language Bytecode execution environment Verifier Run-time checks Memory safety Permission checking Stack inspection
13 .Java language overview Classes and Inheritance Object features Encapsulation Inheritance Types and Subtyping Primitive and ref types Interfaces; arrays Exception hierarchy Generics Subtype polymorphism. generic programming Virtual machine Loader and initialization Linker and verifier Bytecode interpreter Security Java “sandbox” Type safety Stack inspection
14 .Java language overview Classes and Inheritance Object features Encapsulation Inheritance Types and Subtyping Primitive and ref types Interfaces; arrays Exception hierarchy Generics Subtype polymorphism. generic programming Virtual machine Loader and initialization Linker and verifier Bytecode interpreter Security Java “sandbox” Type safety Stack inspection
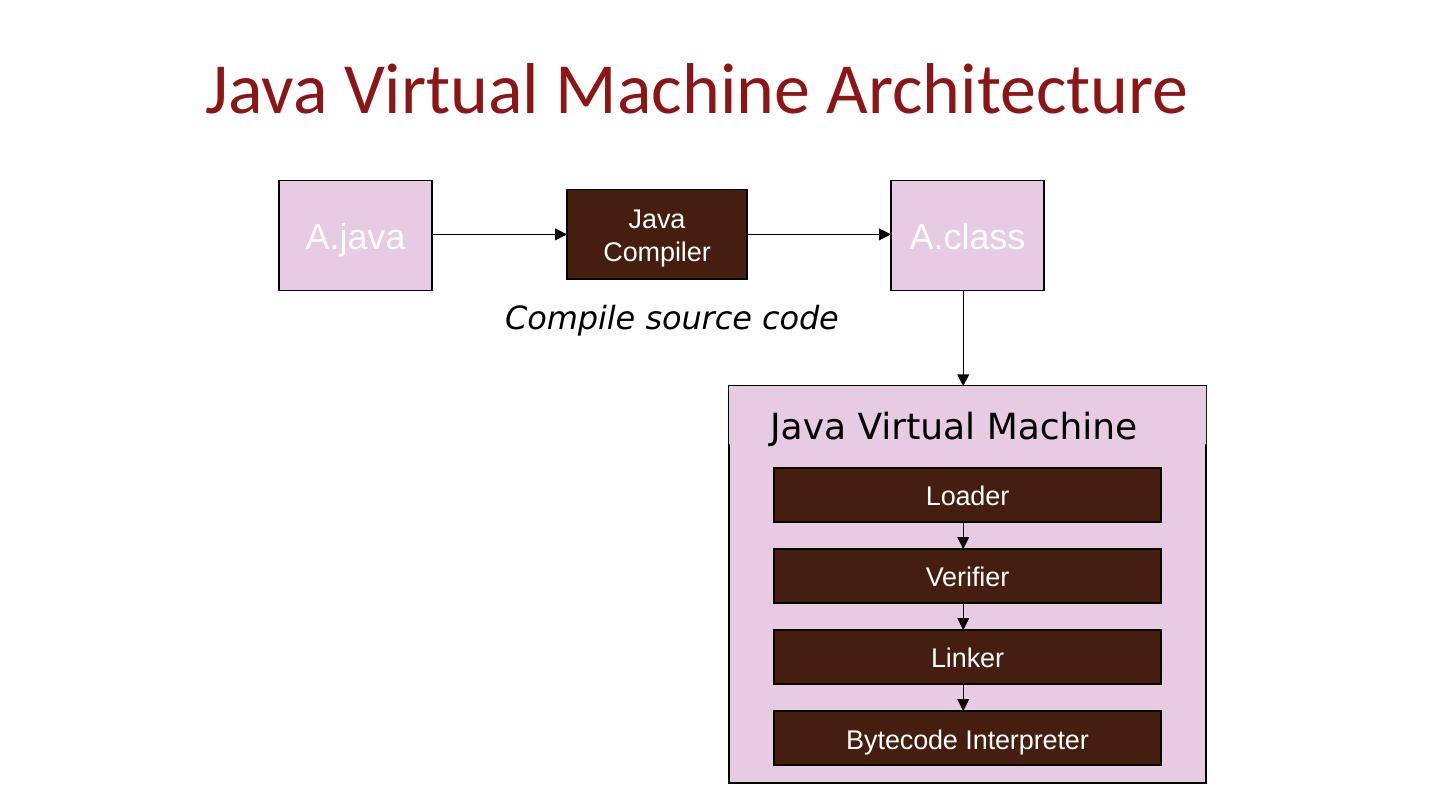
15 .Java Implementation Compiler and Virtual Machine Compiler produces bytecode Virtual machine loads classes on demand, verifies bytecode properties, interprets bytecode Why this design? Bytecode interpreter “manages” code execution safely Minimize machine-dependent part of implementation
16 .A.class A.java Java Compiler Loader Verifier Linker Bytecode Interpreter Java Virtual Machine Compile source code Java Virtual Machine Architecture
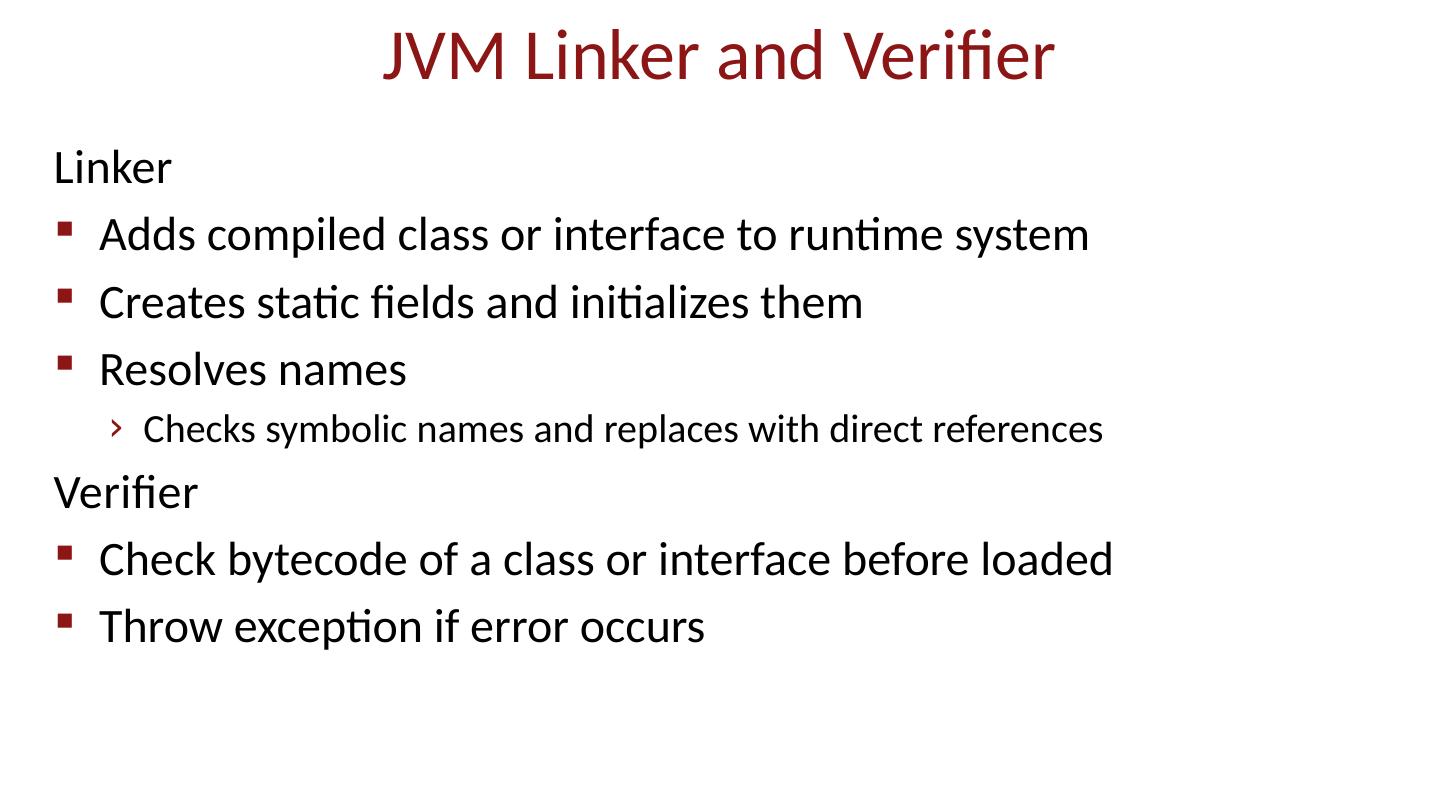
17 .JVM Linker and Verifier Linker Adds compiled class or interface to runtime system Creates static fields and initializes them Resolves names Checks symbolic names and replaces with direct references Verifier Check bytecode of a class or interface before loaded Throw exception if error occurs
18 .Verifier Bytecode may not come from standard compiler Evil hacker may write dangerous bytecode Verifier checks correctness of bytecode Every instruction must have a valid operation code Every branch instruction must branch to the start of some other instruction, not middle of instruction Every method must have a structurally correct signature Every instruction obeys the Java type discipline Last condition is fairly complicated .
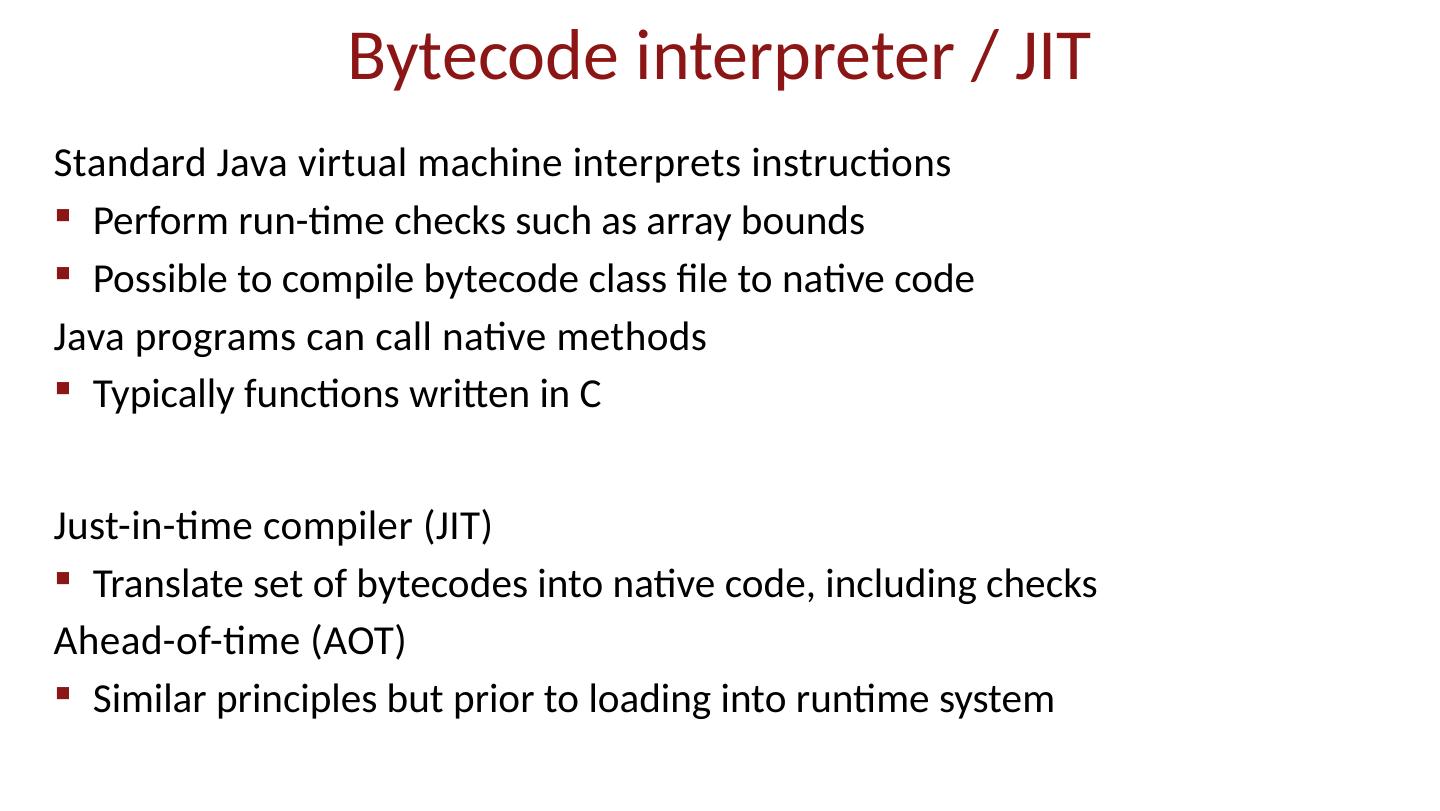
19 .Bytecode interpreter / JIT Standard Java virtual machine interprets instructions Perform run-time checks such as array bounds Possible to compile bytecode class file to native code Java programs can call native methods Typically functions written in C Just-in-time compiler (JIT) Translate set of bytecodes into native code, including checks Ahead-of-time (AOT) Similar principles but prior to loading into runtime system
20 .Type Safety of Java Run-time type checking All casts are checked to make sure type safe All array references are checked to make sure the array index is within the array bounds References are tested to make sure they are not null before they are dereferenced. Additional features Automatic garbage collection No pointer arithmetic If program accesses memory, that memory is allocated to the program and declared with correct type
21 .Type Safety of Java Run-time type checking All casts are checked to make sure type safe All array references are checked to make sure the array index is within the array bounds References are tested to make sure they are not null before they are dereferenced. Additional features Automatic garbage collection No pointer arithmetic If program accesses memory, that memory is allocated to the program and declared with correct type
22 .Stack Inspection Permission depends on Permission of calling method Permission of all methods above it on stack Up to method that is trusted and asserts this trust Many details omitted here java.io.FileInputStream method f method g method h Stories: Netscape font / passwd bug; Shockwave plug-in
23 .Stack Inspection Stack frames annotated with owners, set of enabled privileges During inspection, stack searched from most to least recent: Fail if a frame belongs to owner not authorized for privilege is Succeed if enabled privilege is found in frame
24 .Example: privileged printing privPrint(f) = (* owned by system *) { checkPrivilege(PrintPriv); print(f); } foreignProg() = (* owned by Joe *) { …; privPrint(file); …; }
25 .Example: privileged printing privPrint(f) = (* owned by system *) { checkPrivilege(PrintPriv); print(f); } foreignProg() = (* owned by Joe *) { …; privPrint(file); …; }
26 .Example: privileged printing privPrint(f) = (* owned by system *) { checkPrivilege(PrintPriv); print(f); } foreignProg() = (* owned by Joe *) { …; privPrint(file); …; }
27 .Android Platform Platform security model
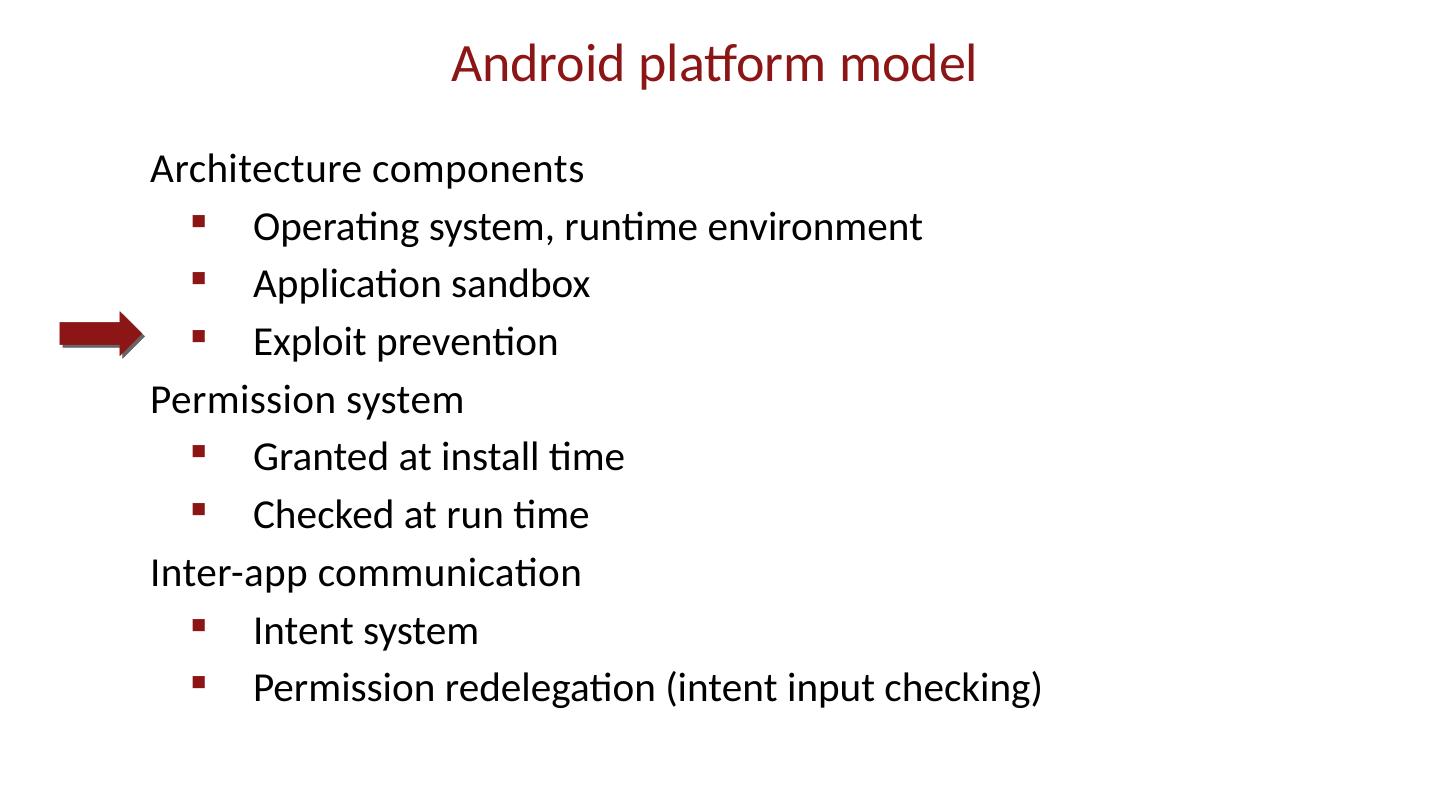
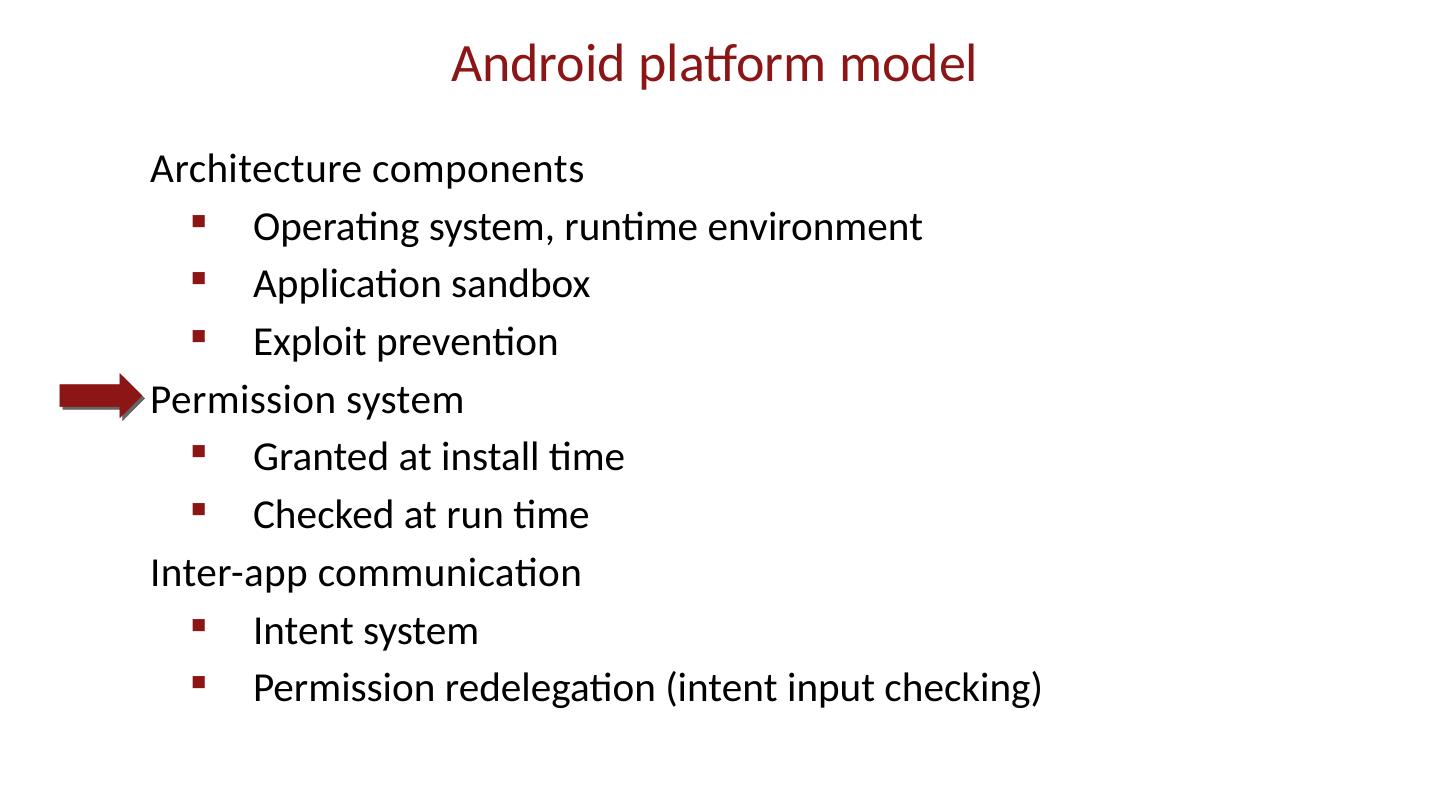
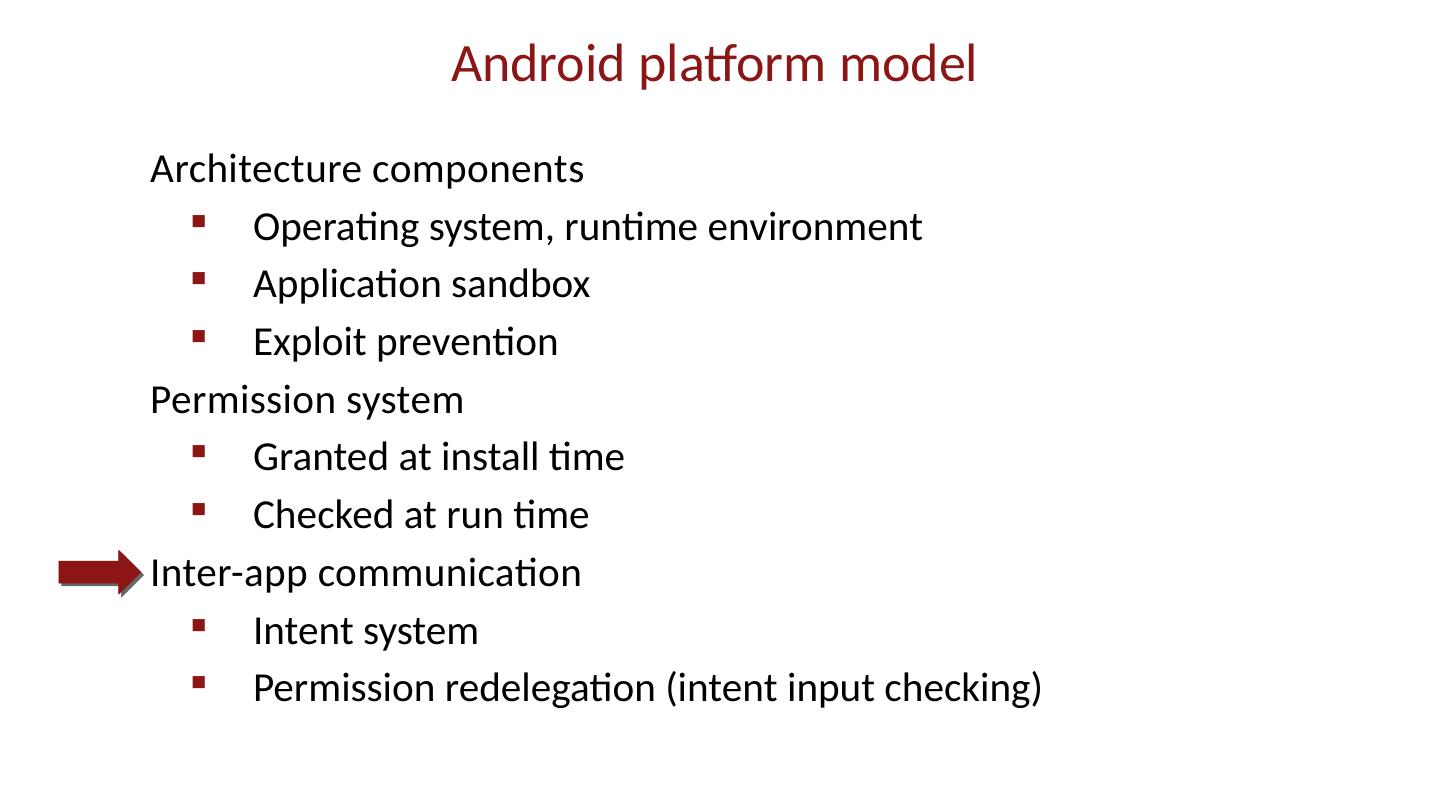
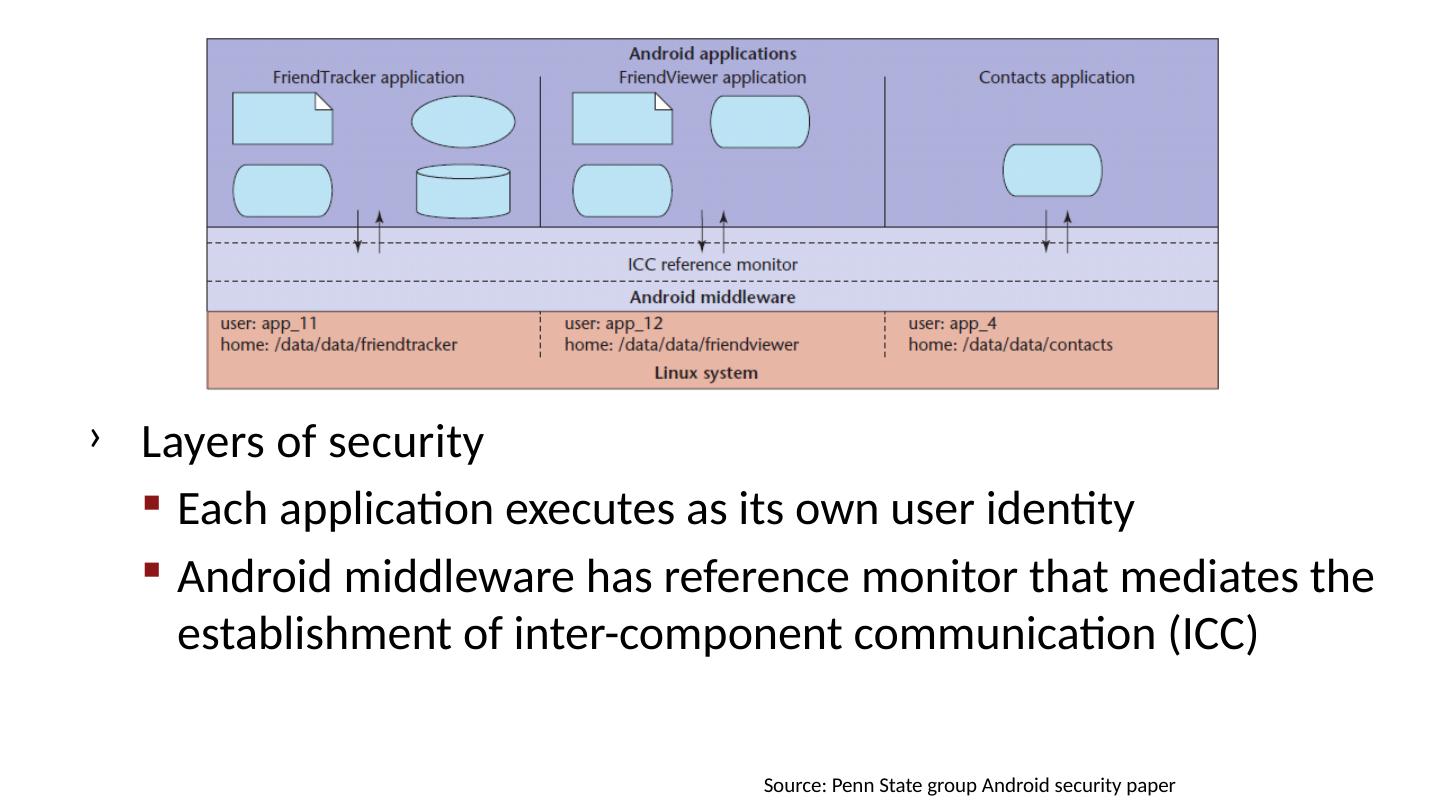
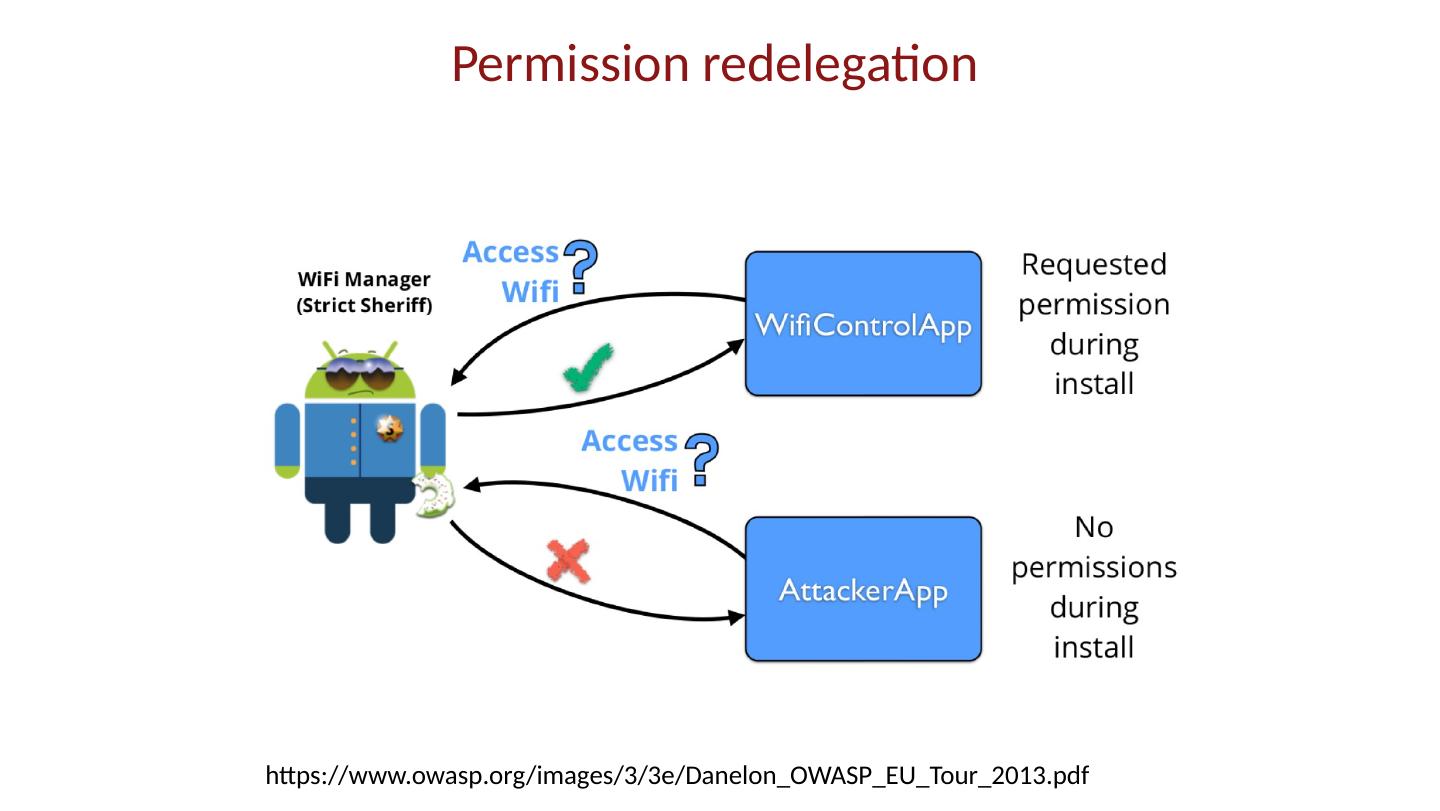
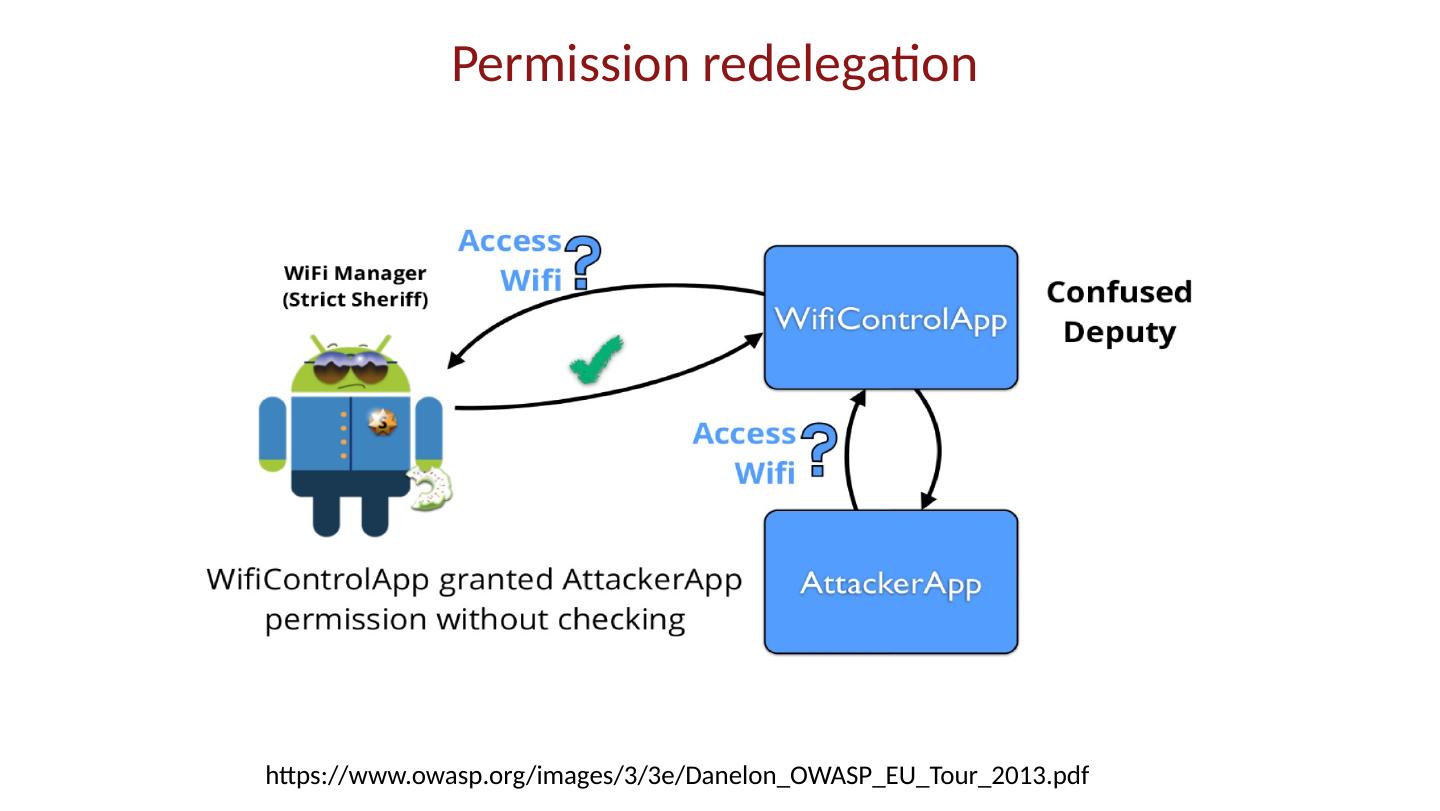
28 .Android platform model Architecture components Operating system, runtime environment Application sandbox Exploit prevention Permission system Granted at install time Checked at run time Inter-app communication Intent system Permission redelegation (intent input checking)
29 .Android platform summary Linux kernel, browser, SQL-lite database Software for secure network communication Open SSL, Bouncy Castle crypto API and Java library C language infrastructure Java platform for running applications Dalvik bytecode, virtual machine / Android runtime (ART)