- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
PHP数组使用
展开查看详情
1 .Chapter - 3 Arrays PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor
2 .Outline What is an array ? Indexed array Associative array Multidimensional array
3 .What is an Array? An array is a special variable, which can store multiple values in one single variable. An array can hold many values under a single name, and you can access the values by referring to an index number.
4 .What is an array? However, what if you want to loop through the cars and find a specific one? And what if you had not 3 cars, but 300? The best solution here is to use an array! An array can hold all your variable values under a single name. And you can access the values by referring to the array name. Each element in the array has its own index so that it can be easily accessed.
5 .What is an array? In PHP, the array() function is used to create an array: array ();
6 .Kind of arrays in PHP Indexed array - An array with a numeric index Associative array - An array where each ID key is associated with a value Multidimensional array - An array containing one or more arrays
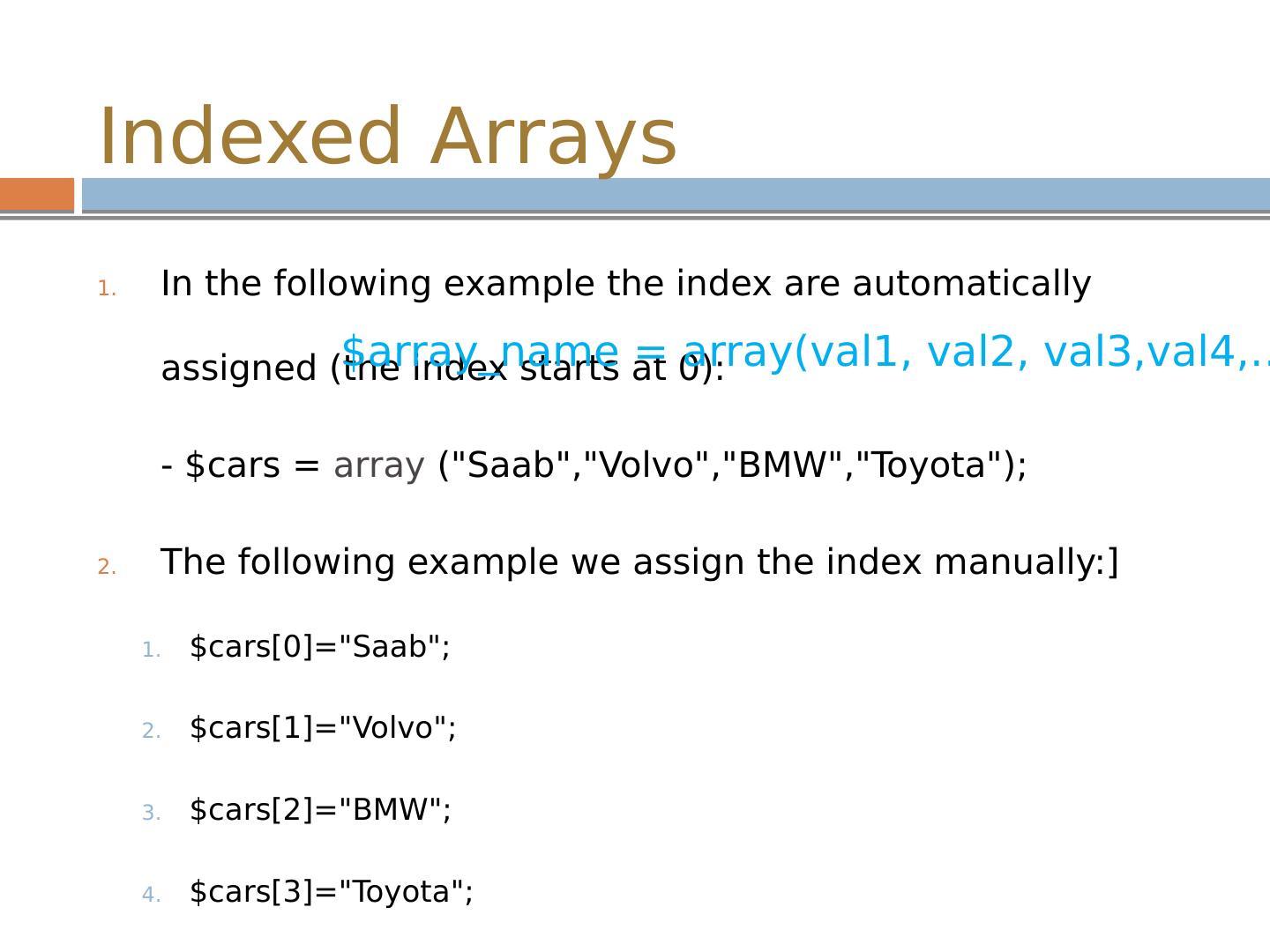
7 .Indexed Arrays A numeric array stores each array element with a numeric index. There are two ways to create indexed arrays:
8 .Indexed Arrays In the following example the index are automatically assigned (the index starts at 0 ): - $cars = array (" Saab","Volvo","BMW","Toyota "); The following example we assign the index manually :] $ cars[0]="Saab "; $ cars[1]="Volvo "; $ cars[2]="BMW "; $ cars[3]="Toyota"; $ array_name = array(val1, val2, val3,val4 ,……);
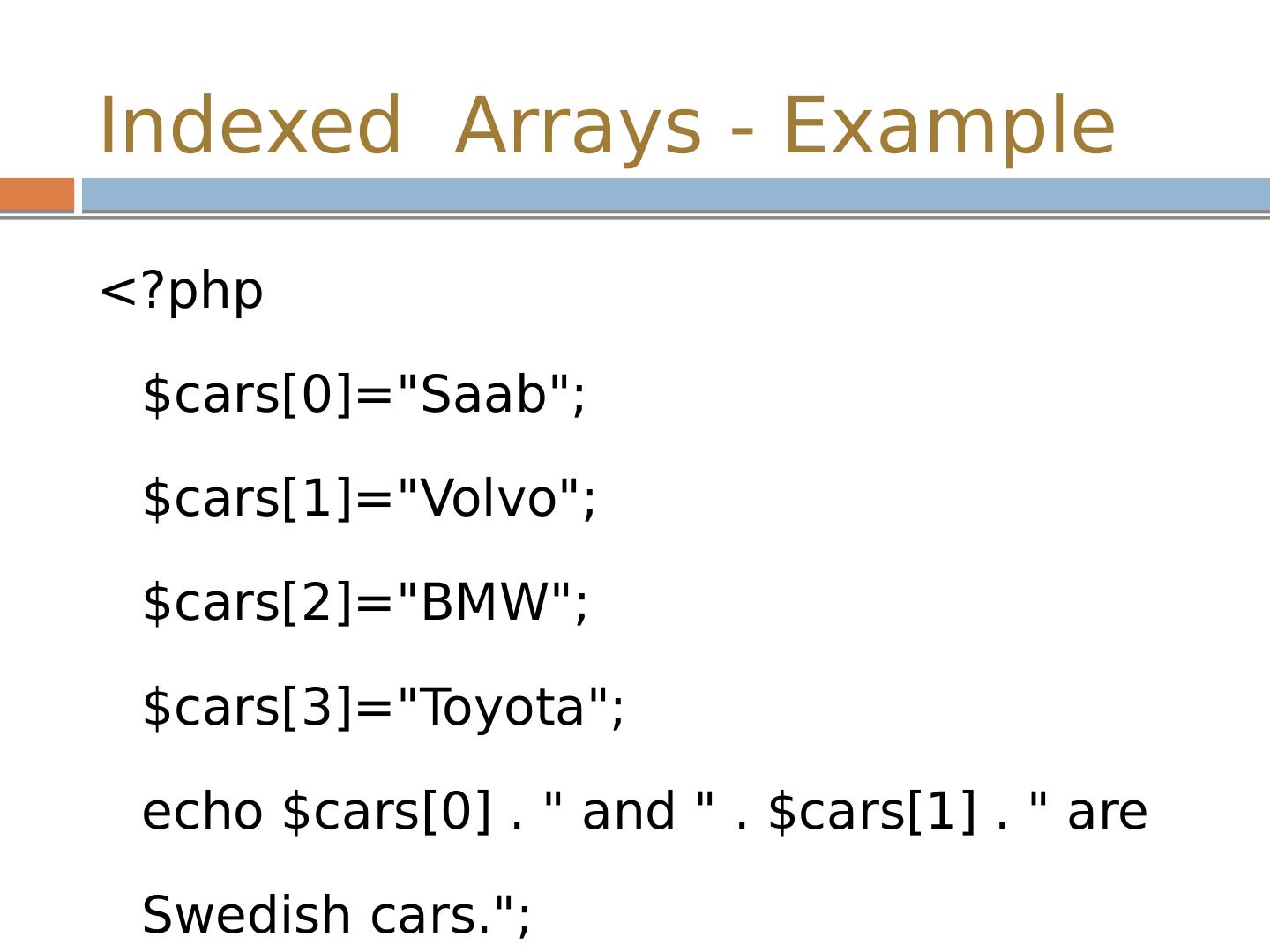
9 .Indexed Arrays - Example <? php $cars[0]="Saab"; $cars[1]="Volvo"; $cars[2]="BMW"; $cars[3]="Toyota"; echo $cars[0] . " and " . $cars[1] . " are Swedish cars."; ?>
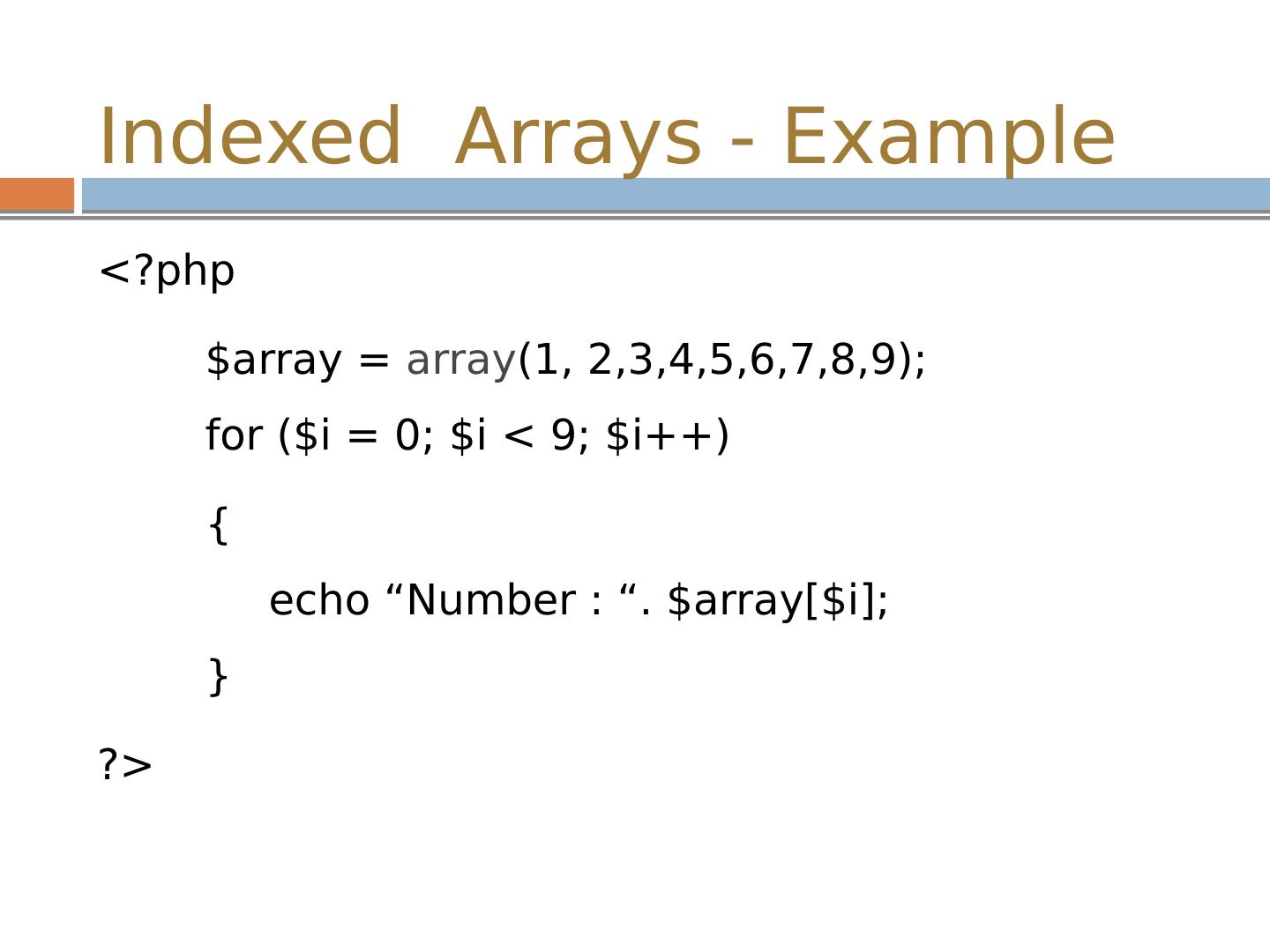
10 .Indexed Arrays - Example <? php $array = array (1, 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9); for ($ i = 0; $ i < 9; $ i ++) { echo “Number : “. $array[$ i ]; } ?>
11 .Print_r () Function Print construction of array as group of locations and the value stored in it print_r ($ expression [, bool $return = false ] )
12 .Print_r () <? php $ arr = array(1,2,3,4,5); Print_r ($ arr ); ?> Array ( [0] => 1 [1] => 2 [2] => 3 [3] => 4 [4] => 5 )
13 .Count() Function This is build in function ,counts all elements in an array, or something in an object . int count ($ var [, int $mode = COUNT_NORMAL ] )
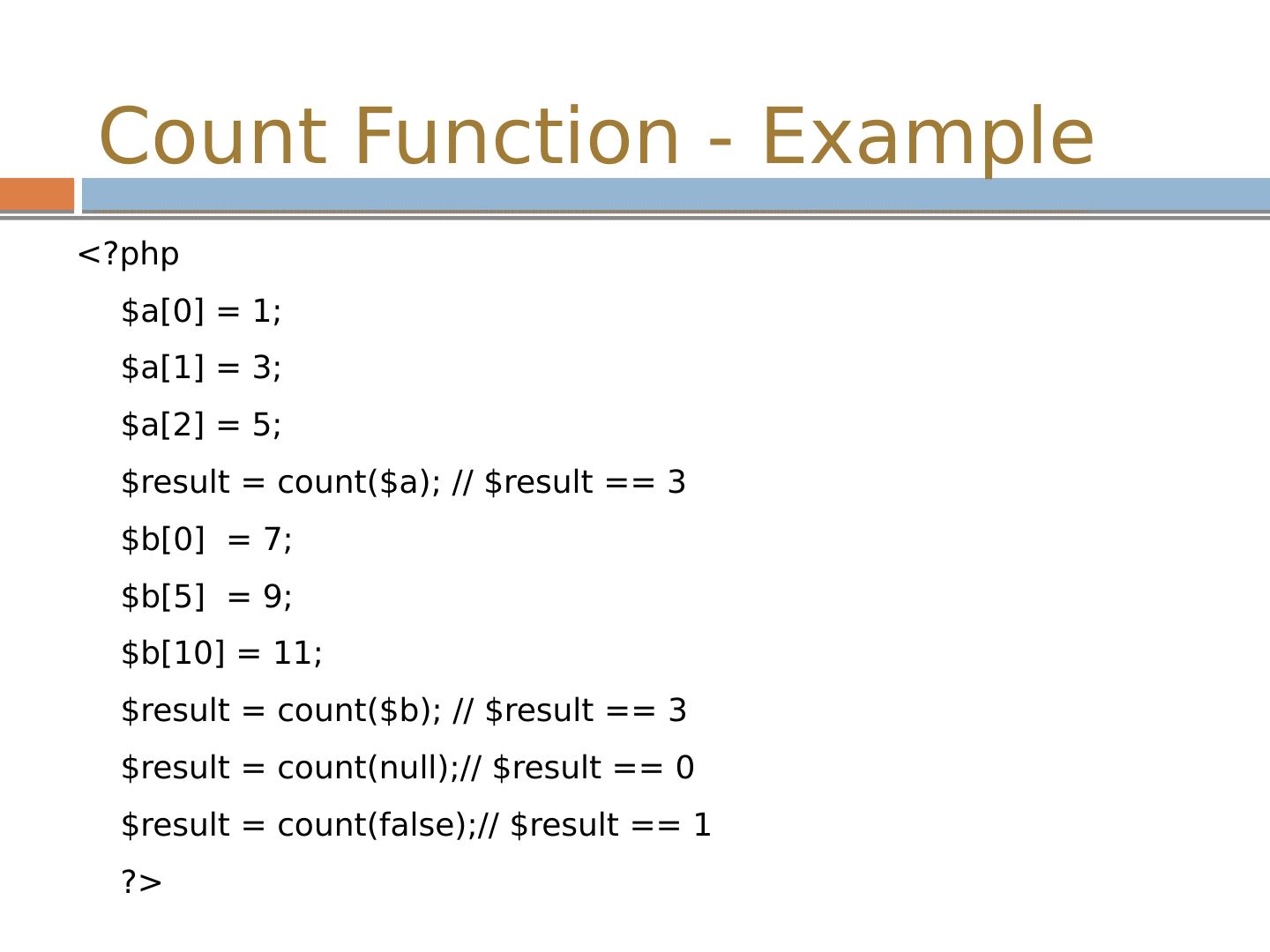
14 .Count Function - Example <? php $a[0] = 1; $a[1] = 3; $a[2] = 5; $result = count($a ); // $result == 3 $b[0] = 7; $b[5] = 9; $b[10] = 11; $result = count($b ); // $result == 3 $result = count(null );// $result == 0 $result = count(false );// $result == 1 ?>
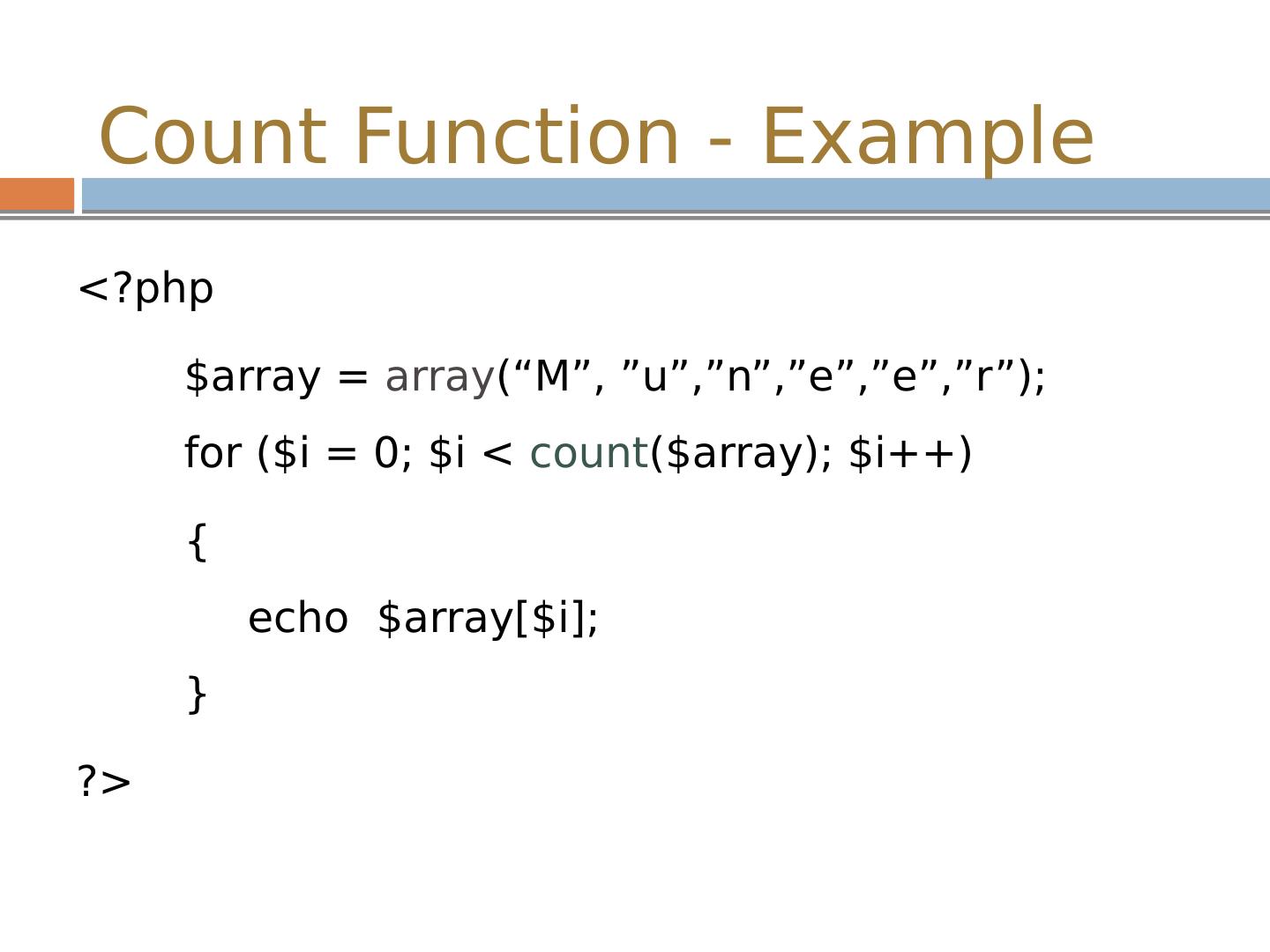
15 .Count Function - Example <? php $array = array (“M”, ” u”,”n”,”e”,”e”,”r ”); for ($ i = 0; $ i < count ($array); $ i ++) { echo $array[$ i ]; } ?>
16 .Count Function - Example <? php $array = array (“M”, ” u”,”n”,”e”,”e”,”r ”); for ($ i = 0; $ i < count ($array); $ i ++) { echo $array[$ i ]; } ?>
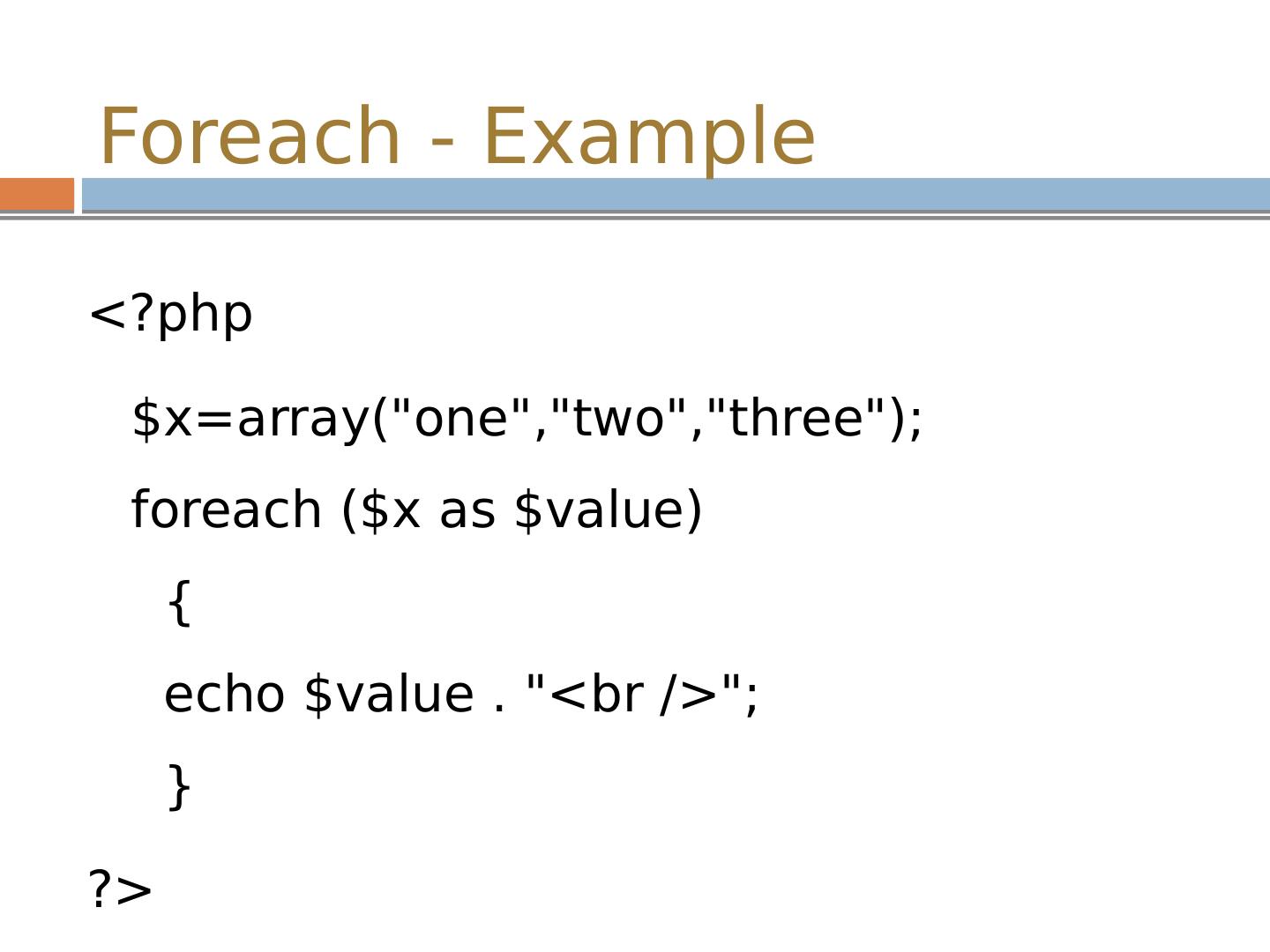
17 .Foreach - Example <? php $x=array(" one","two","three "); foreach ($x as $value) { echo $value . "< br />"; } ?>
18 .Foreach - Example <? php $colors = array (red, blue, green, yellow); foreach ($colors as $color) { echo "Do you like $color?
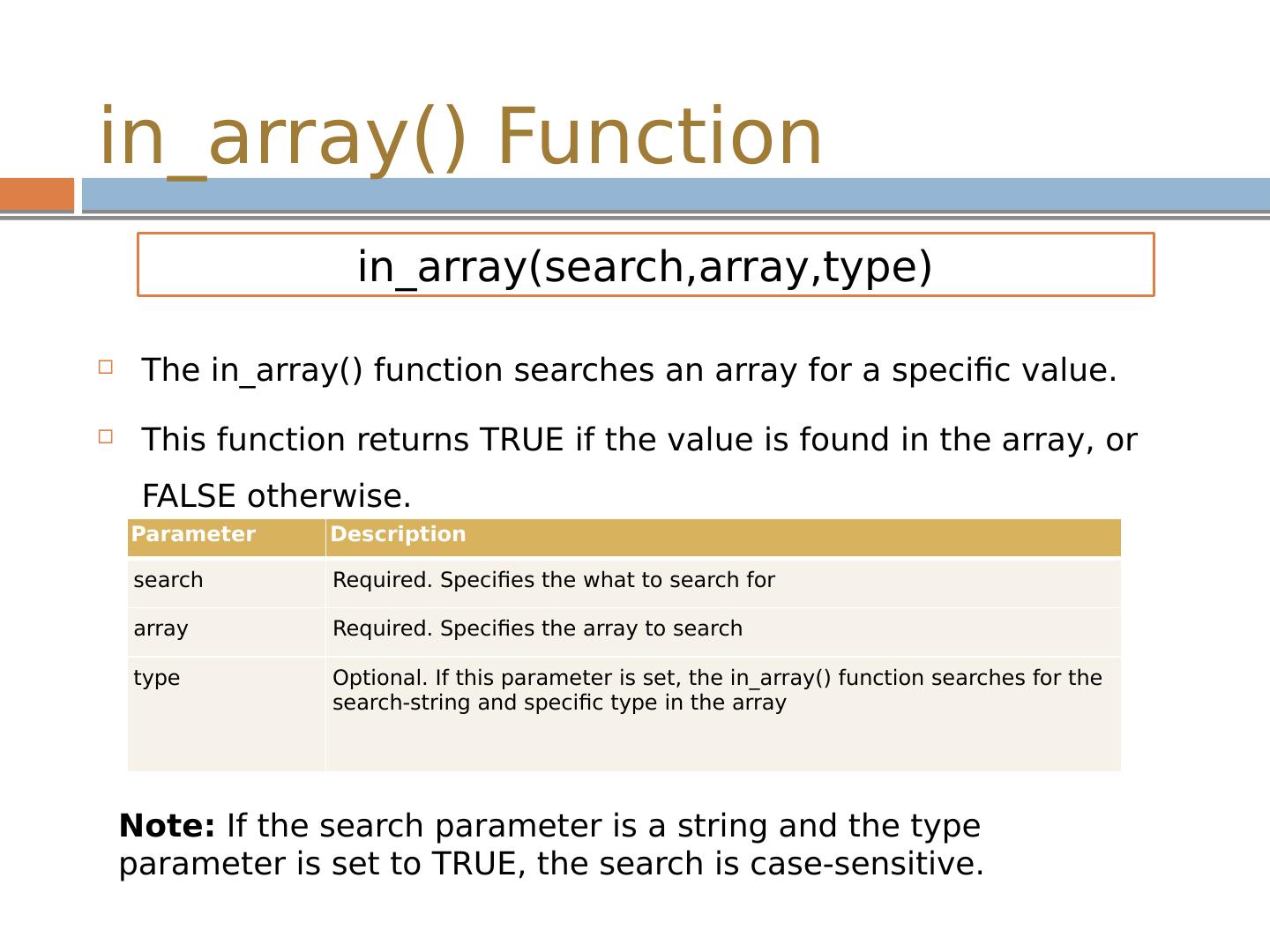
19 .in_array () Function The in_array () function searches an array for a specific value . This function returns TRUE if the value is found in the array, or FALSE otherwise. in_array ( search,array,type ) Parameter Description search Required. Specifies the what to search for array Required. Specifies the array to search type Optional. If this parameter is set, the in_array () function searches for the search-string and specific type in the array Note : If the search parameter is a string and the type parameter is set to TRUE, the search is case-sensitive.
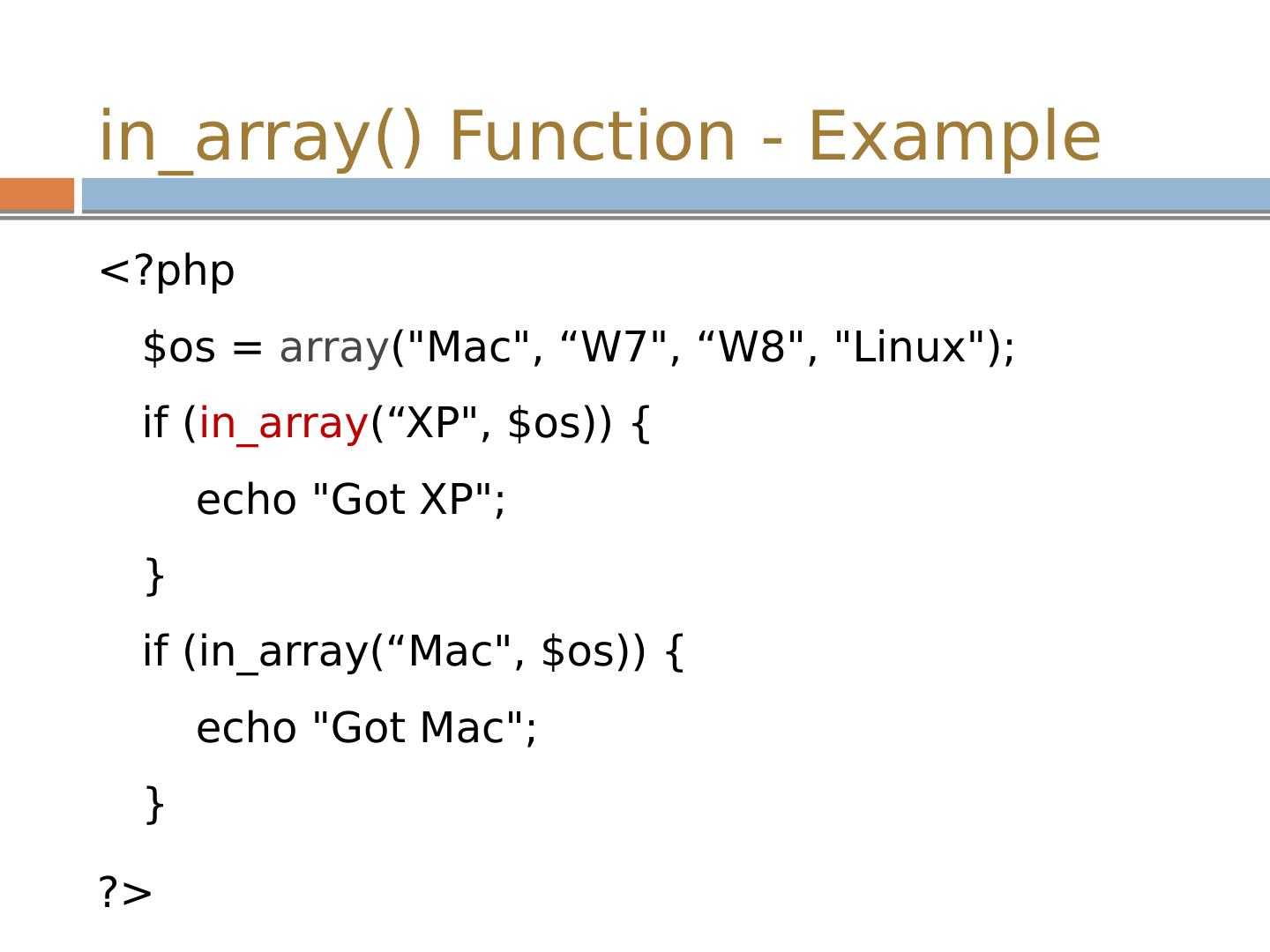
20 .in_array () Function - Example <? php $ os = array ("Mac", “W7", “W8", "Linux"); if ( in_array (“XP", $ os )) { echo "Got XP"; } if ( in_array (“Mac", $ os )) { echo "Got Mac"; } ?>
21 .Associative Arrays An associative array, each ID key is associated with a value. When storing data about specific named values, a numerical array is not always the best way to do it. With associative arrays we can use the values as keys and assign values to them.
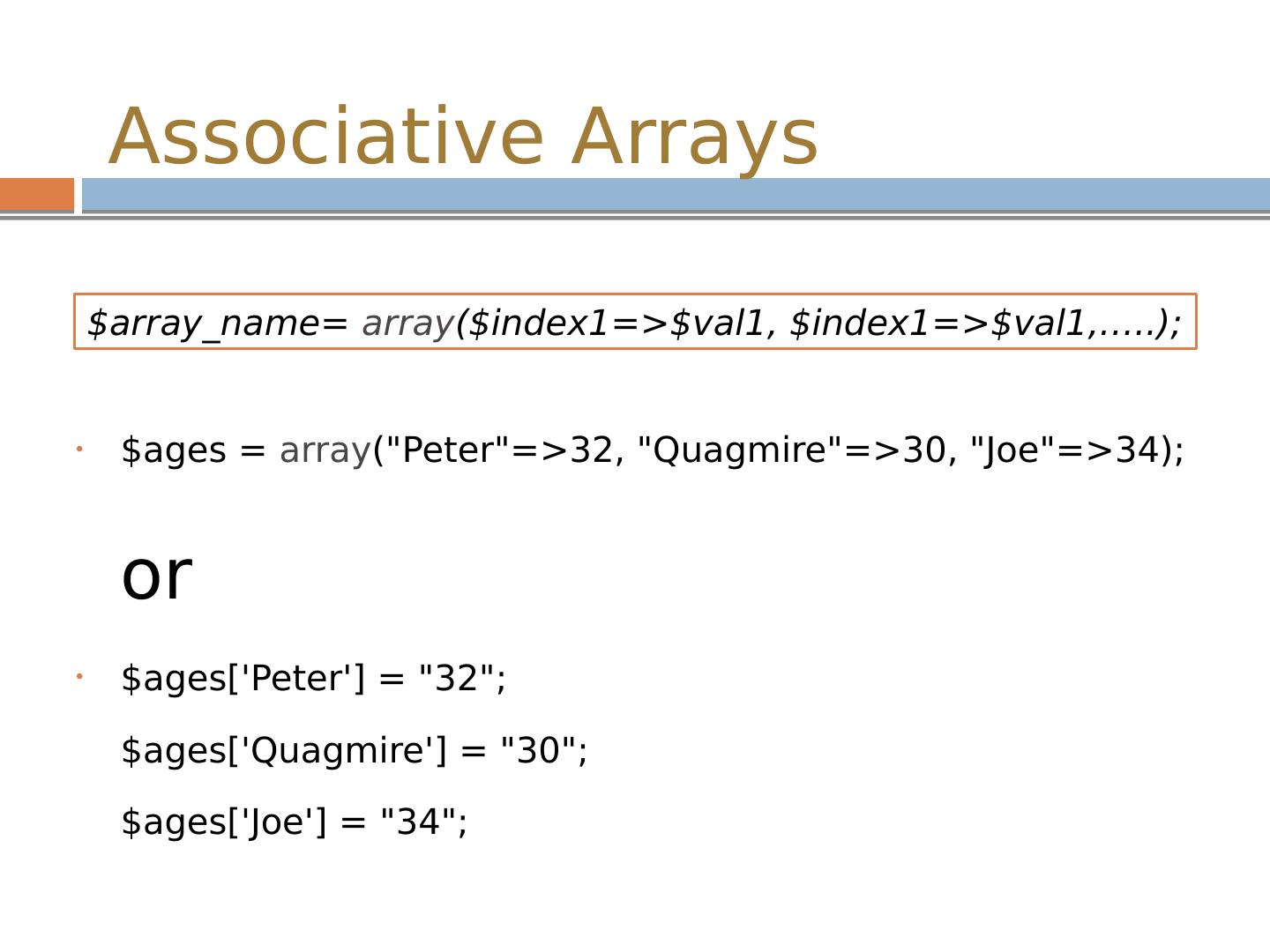
22 .Associative Arrays $ ages = array ("Peter"=>32, " Quagmire "=>30, "Joe"=>34); or $ ages [Peter] = "32"; $ ages [ Quagmire ] = "30"; $ ages [Joe] = "34"; $ array_name = array ($index1=>$val1, $index1=>$val1,…..);
23 .Associative Arrays <? php $ arr = array("foo" => "bar", 12 => true ); echo $ arr ["foo"]; // bar echo $ arr [12]; // 1 ?>
24 .Associative Arrays - example <? php // This array is the same as ... array(5 => 43, 32, 56, "b" => 12); // ...this array array (5 => 43, 6 => 32, 7 => 56, "b" => 12); ?>
25 .Associative Arrays - example <? php $ages[Peter] = "32"; $ages[Quagmire] = "30"; $ages[Joe] = "34"; echo "Peter is " . $ages[Peter] . " years old."; ?>
26 .Associative Arrays - example <? php $ arr = array (5 => 1, 12 => 2); $ arr [] = 56; // This is the same as $ arr [13] = 56; // at this point of the script $ arr ["x"] = 42; // This adds a new element to // the array with key "x" unset($ arr [5]); // This removes the element from the array unset($ arr ); // This deletes the whole array ?>
27 .Associative Arrays - example <? php $ arr = array(" somearray " => array(6 => 5, 13 => 9, "a" => 42 )); echo $ arr [" somearray "][6]; // 5 echo $ arr [" somearray "][13]; // 9 echo $ arr [" somearray "]["a"]; // 42 ?>
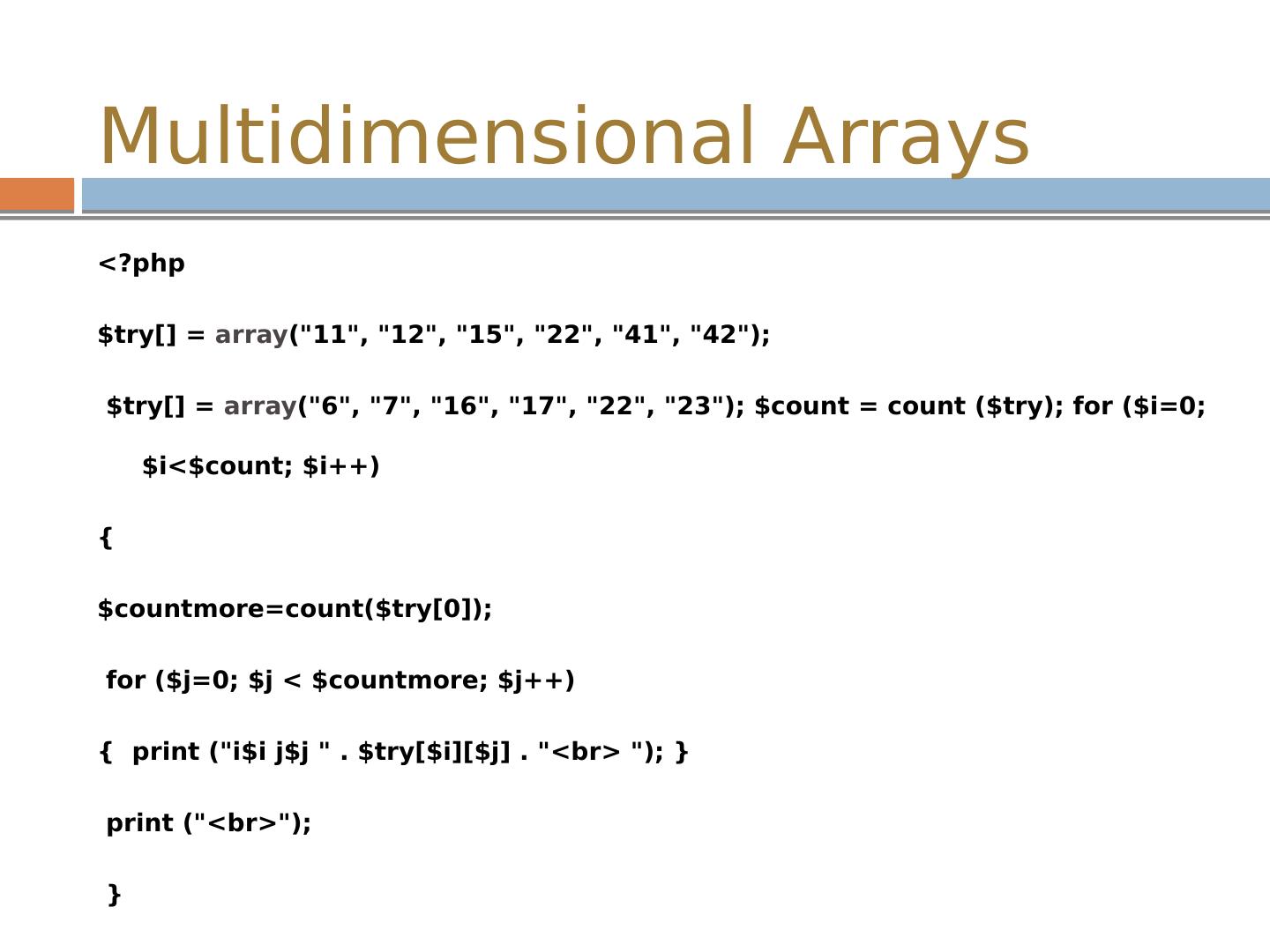
28 .Multidimensional Arrays In a multidimensional array, each element in the main array can also be an array. And each element in the sub-array can be an array, $ myArray = array ( array( value1, value2, value3 ), array( value4, value5, value6 ), array( value7, value8, value9 ) );
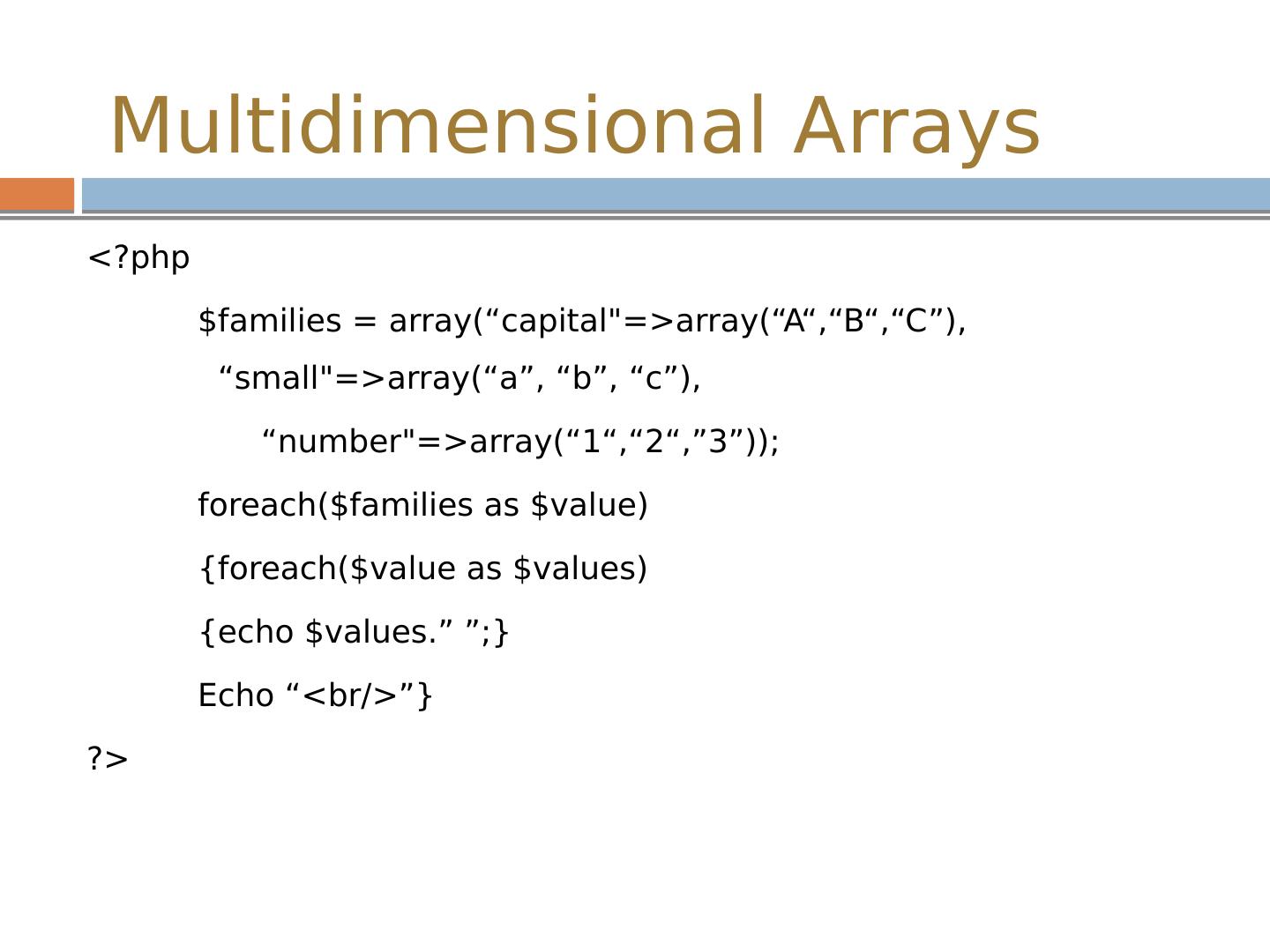
29 .Multidimensional Arrays <? php $fruits = array ( "fruits" => array ( "a" => "orange", "b" => " banana“,"c " => "apple”),"numbers" => array ( 1, 2,3,4,5,6), "holes" => array ("first“,5 => " second“,"third ”)); echo $fruits["holes"][5]; // prints "second" echo $fruits["fruits"]["a"]; // prints "orange" ?>