- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
Firewall - UCCS
展开查看详情
1 .C. Edward Chow Firewall Chapter 18, Sec. 18.3.2 of Security Engineering Page 451, Section 7.4 of Security in Computing Linux Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2 by Oskar Andreasson
2 .Outline of The Talk Definition Perimeter Defense and Firewall Implement Firewall using Linux iptables
3 .Outline of The Talk Definition Perimeter Defense and Firewall Implement Firewall using Linux iptables
4 .Perimeter Defense and Firewall Intra1 (XP) Internet Outer Firewall Router Firewall Inner Firewall Router Firewall SW DNS Server Web Server Intranet SW Mail Server Intra2(win2003) DMZ SW IDS IDS IDS Honeypot
5 .Intrusion Prevent System (IPS) combining Firewall with IDS IPS Outer Intra1 (XP) Internet SW DNS Server Web Server Intranet SW Mail Server Intra2(win2003) DMZ SW Firewall IPS Inner IDS IDS Honeypot Firewall
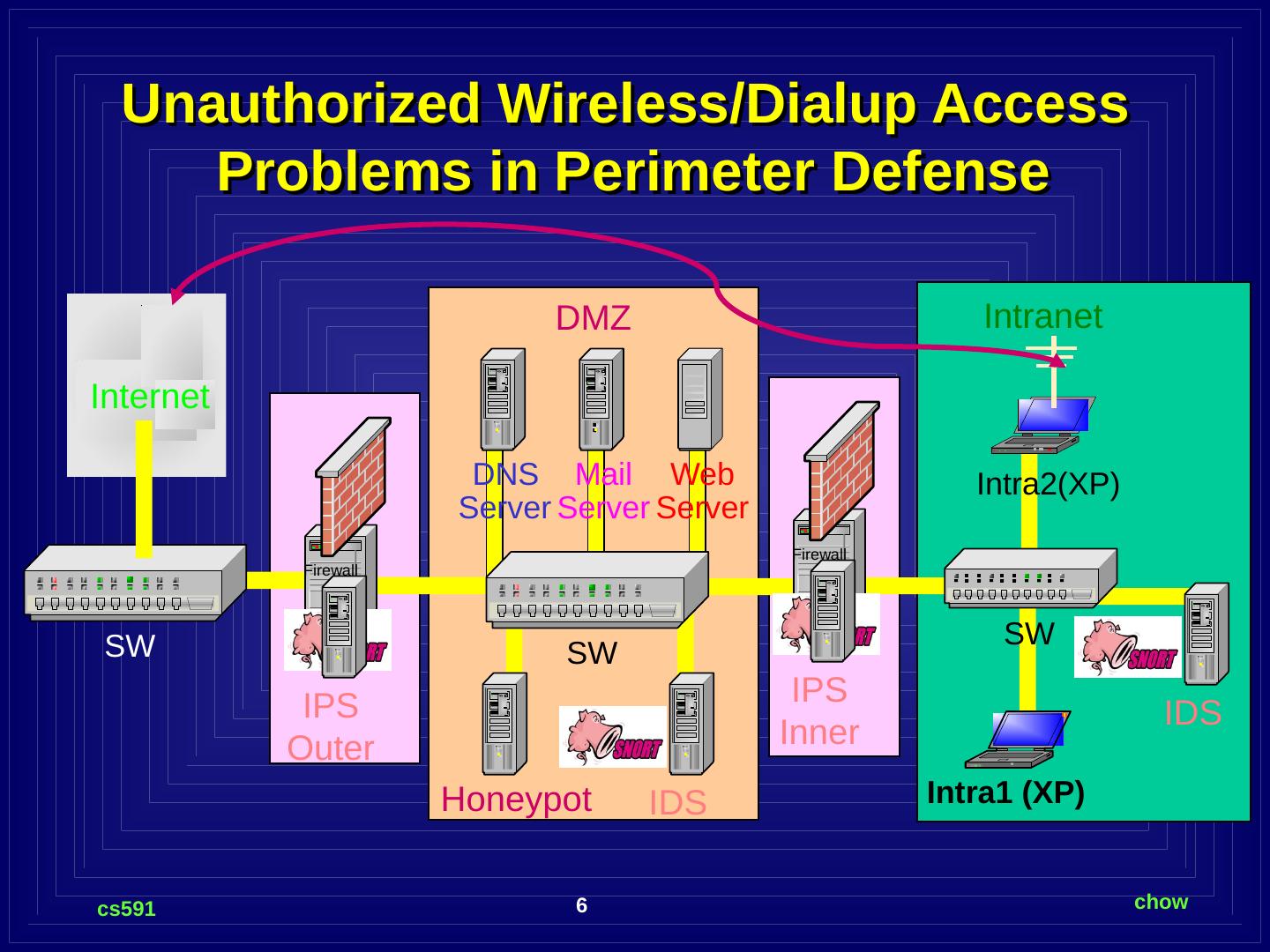
6 .IPS Outer Unauthorized Wireless/Dialup Access Problems in Perimeter Defense Intra1 (XP) Internet SW DNS Server Web Server Intranet SW Mail Server Intra2(XP) DMZ SW Firewall IPS Inner IDS IDS Honeypot Firewall
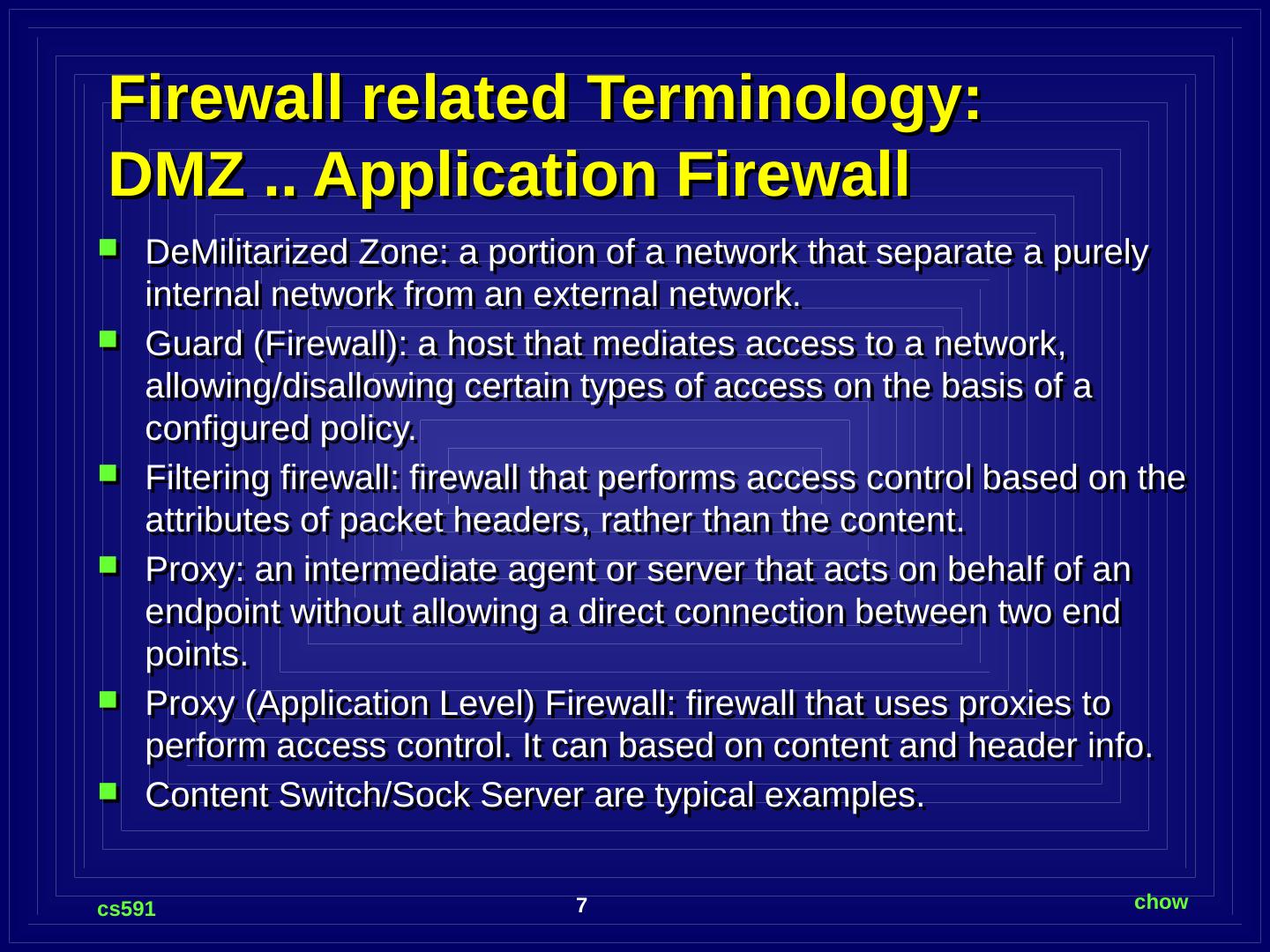
7 .Firewall related Terminology: DMZ .. Application Firewall DeMilitarized Zone: a portion of a network that separate a purely internal network from an external network. Guard (Firewall): a host that mediates access to a network, allowing/disallowing certain types of access on the basis of a configured policy. Filtering firewall: firewall that performs access control based on the attributes of packet headers, rather than the content. Proxy: an intermediate agent or server that acts on behalf of an endpoint without allowing a direct connection between two end points. Proxy (Application Level) Firewall: firewall that uses proxies to perform access control. It can based on content and header info. Content Switch/Sock Server are typical examples.
8 .Design Principles for Secure Mechanisms Least Privileges Fail-Safe Defaults Economy of Mechanism Complete Mediation Open Design Separation of Privilege Least Common Mechanism Psychological Acceptability
9 .Security Policies The DMZ servers are typically not allowed to make connections to the intranet. Systems in Internet not allowed to directly contact any systems in the intranet. Systems in Intranet not allowed to directly contact any systems in the Internet. Systems in DMZ serve as mediator (go-between). Password/certificate/credential are presented for allowing mediating services. No dual interface from DMZ servers directly to systems Intranet except the inner firewall. Intranet system typically uses Private LAN addresses: 10.x.y.z/8; 172.a.x.z (16<=a<32)/16; 192.168.x.y/24.
10 .Security Policy Complete Mediation Principle: inner firewall mediate every access involves with DMZ and Intranet. Separation of privileges; with different DMZ server running different network functions; firewall machines are different entities than the DMZ servers; inner firewall and outer firewall enforce different security policies. It is also related to least common mechanism principle. The outer firewall allows HTTP/HTTPS and SMTP access to DMZ server. Need to detect virus, malicious logic (how about inner firewall?)
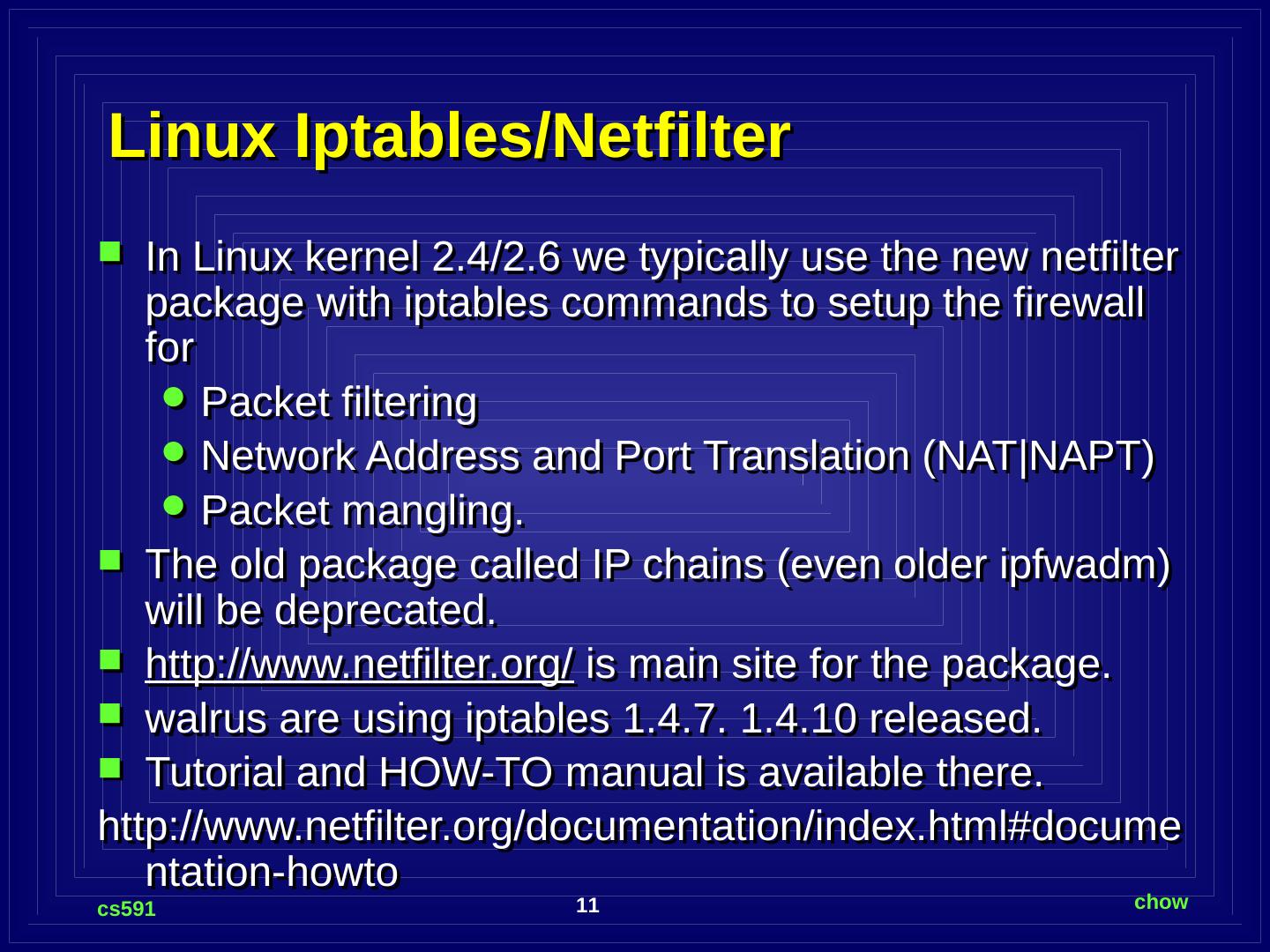
11 .Linux Iptables/Netfilter In Linux kernel 2.4/2.6 we typically use the new netfilter package with iptables commands to setup the firewall for Packet filtering Network Address and Port Translation (NAT|NAPT) Packet mangling. The old package called IP chains (even older ipfwadm ) will be deprecated. http://www.netfilter.org/ is main site for the package. walrus are using iptables 1.4.7. 1.4.10 released. Tutorial and HOW-TO manual is available there. http://www.netfilter.org/documentation/index.html#documentation-howto
12 .Netfilter and Iptables netfilter is a set of hooks inside the Linux kernel that allows kernel modules to register callback functions with the network stack. A registered callback function is then called back for every packet that traverses the respective hook within the network stack. iptables is a generic table structure for the definition of rulesets . Each rule within an IP table consists of a number of classifiers ( iptables matches) and one connected action ( iptables target/jump). Tables ; commands ; classifiers ; actions netfilter , ip_tables , connection tracking ( ip_conntrack , nf_conntrack ) and the NAT subsystem together build the major parts of the firewall framework.
13 .Netfilter and Iptables netfilter is a set of hooks inside the Linux kernel that allows kernel modules to register callback functions with the network stack. A registered callback function is then called back for every packet that traverses the respective hook within the network stack. iptables is a generic table structure for the definition of rulesets . Each rule within an IP table consists of a number of classifiers ( iptables matches) and one connected action ( iptables target/jump). Tables ; commands ; classifiers ; actions netfilter , ip_tables , connection tracking ( ip_conntrack , nf_conntrack ) and the NAT subsystem together build the major parts of the firewall framework.
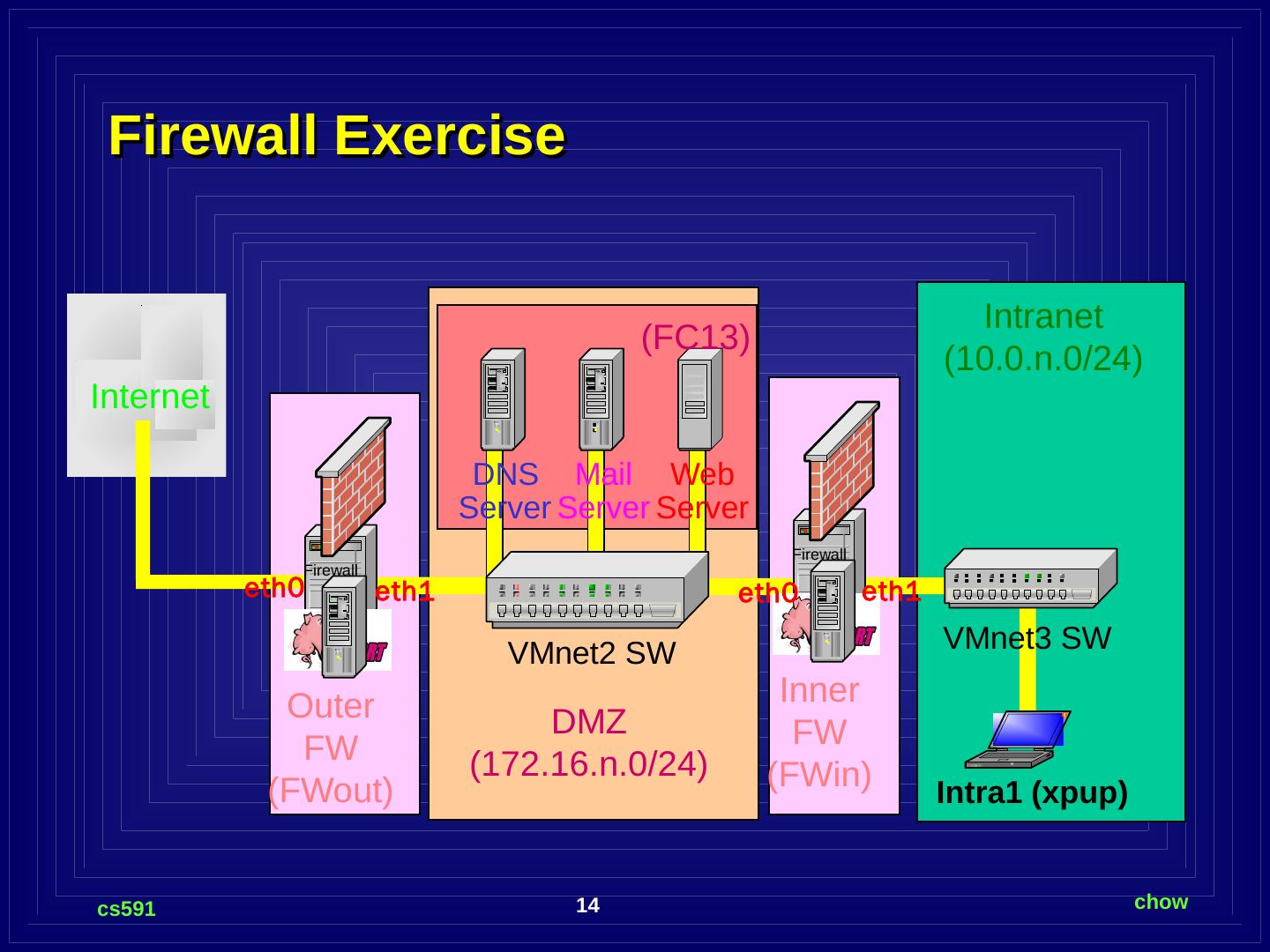
14 .Firewall Exercise Outer FW ( FWout ) Intra1 ( xpup ) Internet VMnet3 SW DNS Server Web Server Intranet ( 10.0.n.0/24) VMnet2 SW Mail Server DMZ ( 172.16.n.0/24) Firewall Inner FW ( FWin ) Firewall ( FC13) eth0 eth1 eth0 eth1
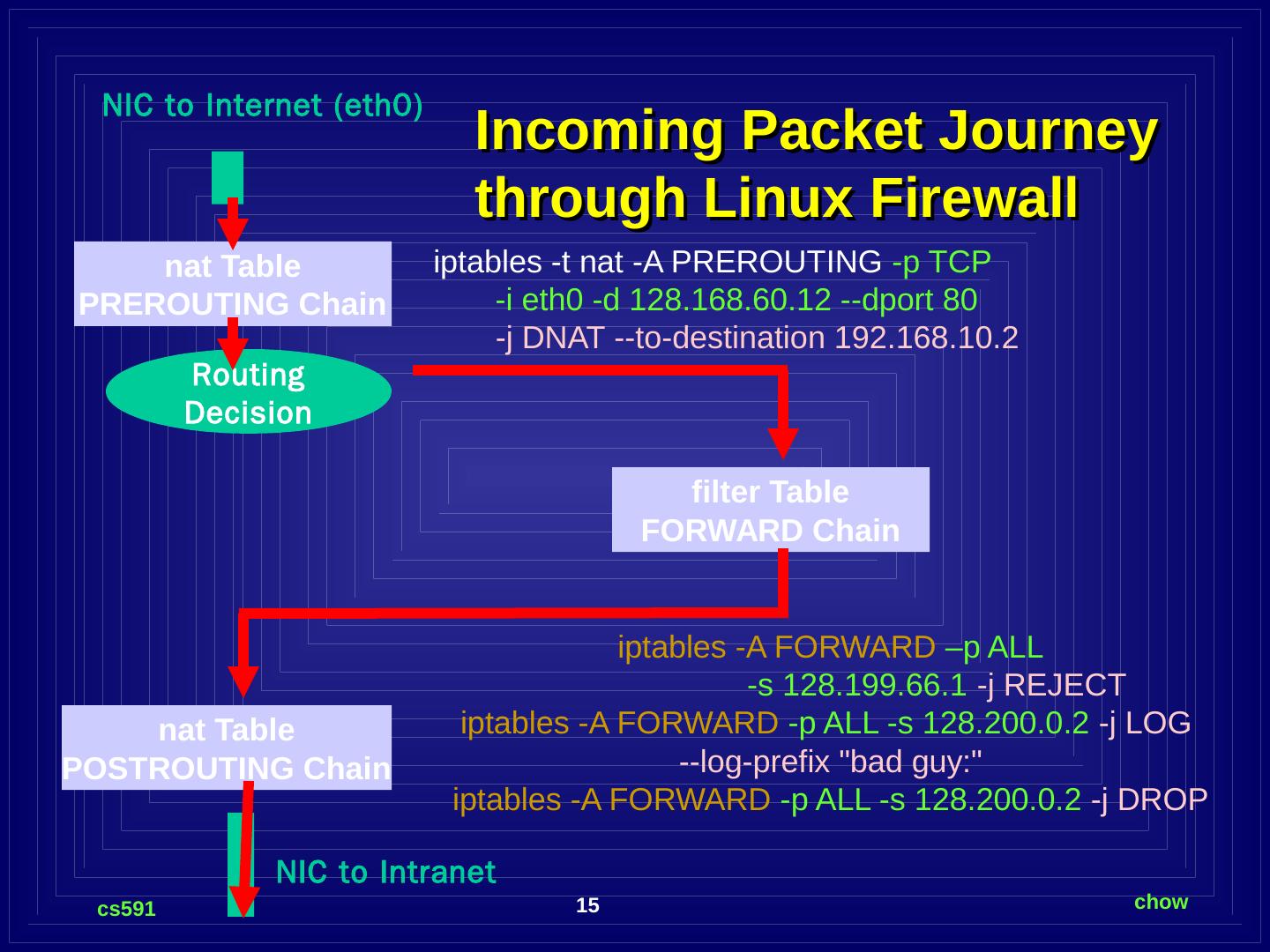
15 .Incoming Packet Journey through Linux Firewall NIC to Internet (eth0) nat Table PREROUTING Chain Routing Decision filter Table FORWARD Chain nat Table POSTROUTING Chain NIC to Intranet iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p TCP -i eth0 -d 128.168.60.12 --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.10.2 iptables - A FORWARD –p ALL -s 128.199.66.1 -j REJECT iptables -A FORWARD -p ALL -s 128.200.0.2 -j LOG --log-prefix "bad guy:" iptables -A FORWARD -p ALL -s 128.200.0.2 -j DROP
16 .DNAT and Iptables command DNAT: Destination Network Address Translation. Deal with packets from Internet to our Internet exposed servers. It translates the destination (external) IP addresses to the corresponding internal IP address of DMZ servers. iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p TCP -i eth0 -d 128.168.60.12 --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.10.2 -t specify the type of tables -A Append to a specific chain -p specify the protocol -i specify the incoming interface -d specify the matched destination IP address in packet -j specify the “target” or operation to be performed. --to-destination substitute the destination IP address.
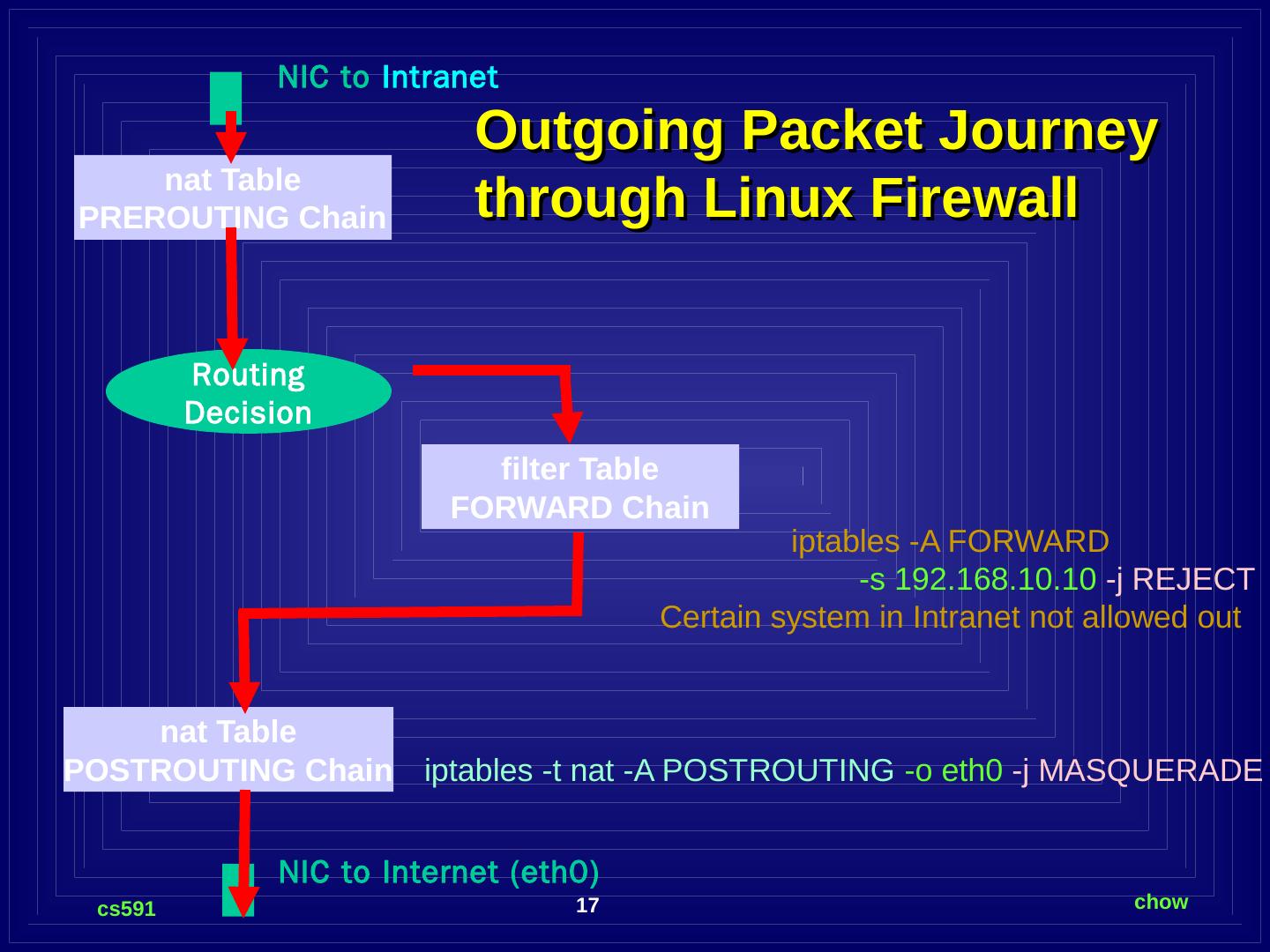
17 .Outgoing Packet Journey through Linux Firewall NIC to Intranet nat Table PREROUTING Chain Routing Decision filter Table FORWARD Chain nat Table POSTROUTING Chain NIC to Internet (eth0) iptables - A FORWARD -s 192.168.10.10 -j REJECT Certain system in Intranet not allowed out iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
18 .SNAT vs. MASQUERADE SNAT which translates only the IP addresses, the port number is preserved unchanged. However, it requires that you have the equal number of outgoing IP addresses as IP address in your intranet that are carrying in the source address field of the outgoing packets. Since it does not have to search for the available port or available IP address, SNAT is faster than MASQUERADE. For smaller organization which only have a few static IP addresses, MASQUERADE is the typically method.
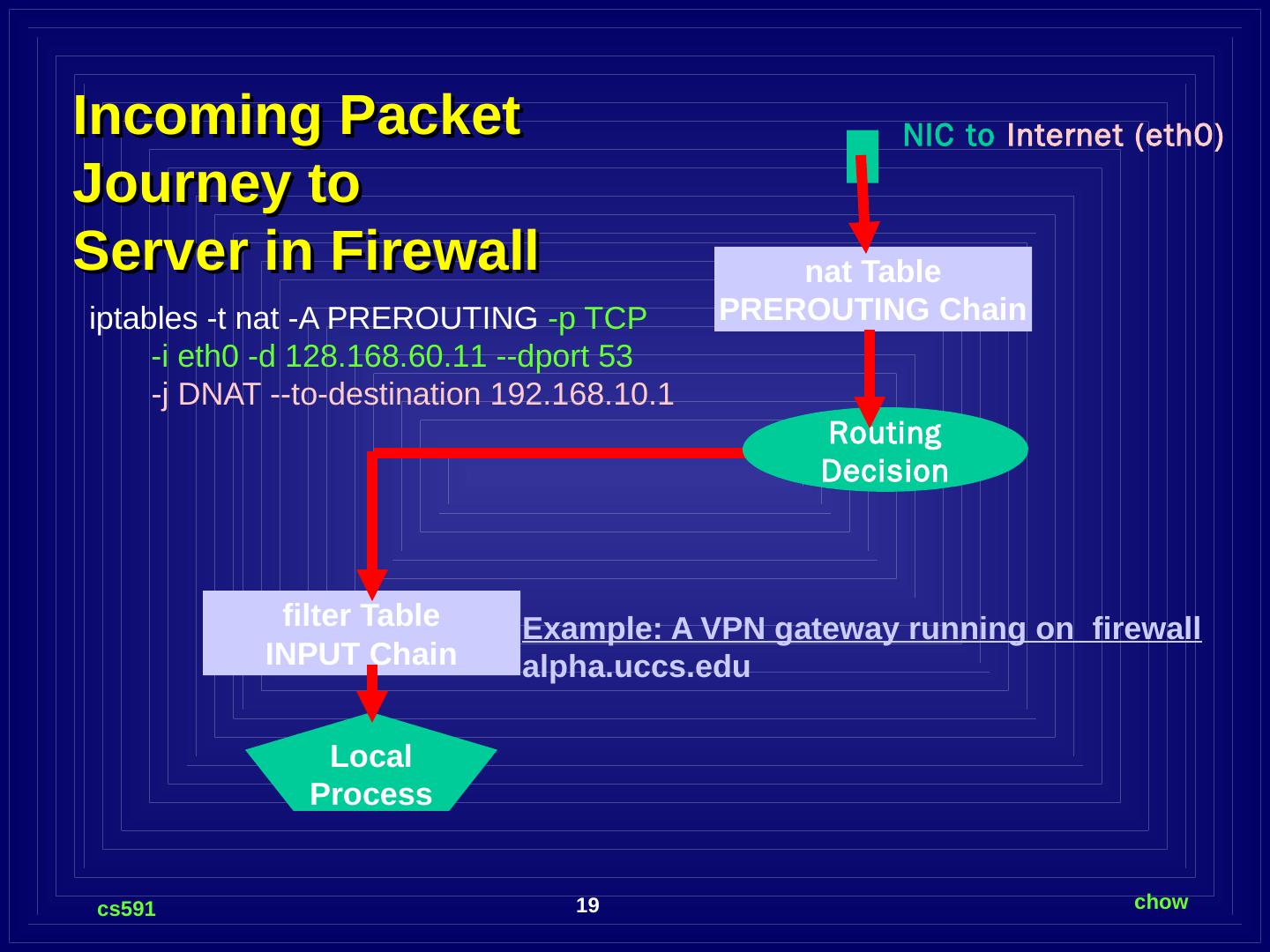
19 .Incoming Packet Journey to Server in Firewall filter Table INPUT Chain NIC to Internet (eth0) nat Table PREROUTING Chain Routing Decision iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p TCP -i eth0 -d 128.168.60.11 --dport 53 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.10.1 Local Process Example: A VPN gateway running on firewall alpha.uccs.edu
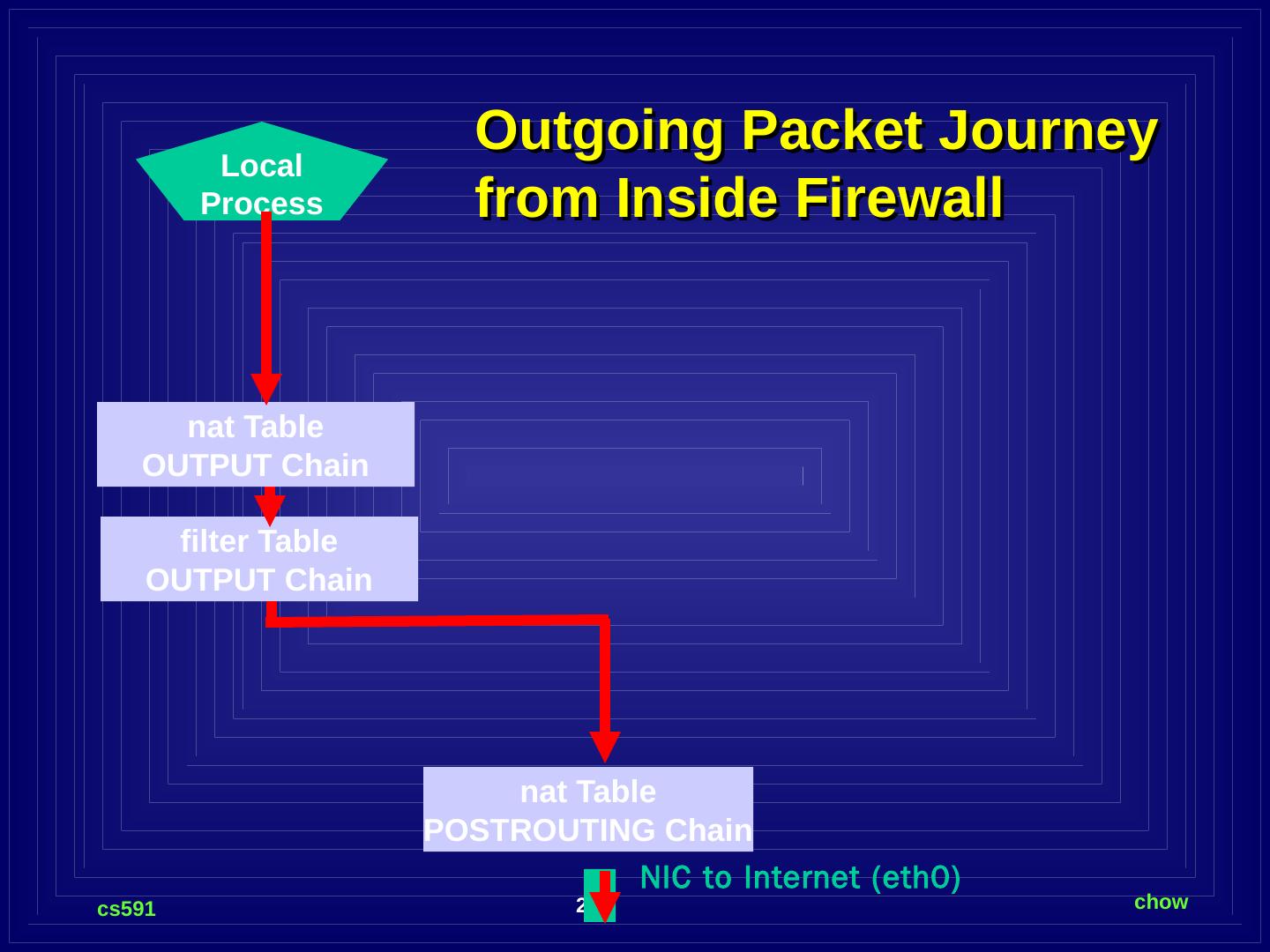
20 .Outgoing Packet Journey from Inside Firewall filter Table OUTPUT Chain nat Table POSTROUTING Chain NIC to Internet (eth0) nat Table OUTPUT Chain Local Process
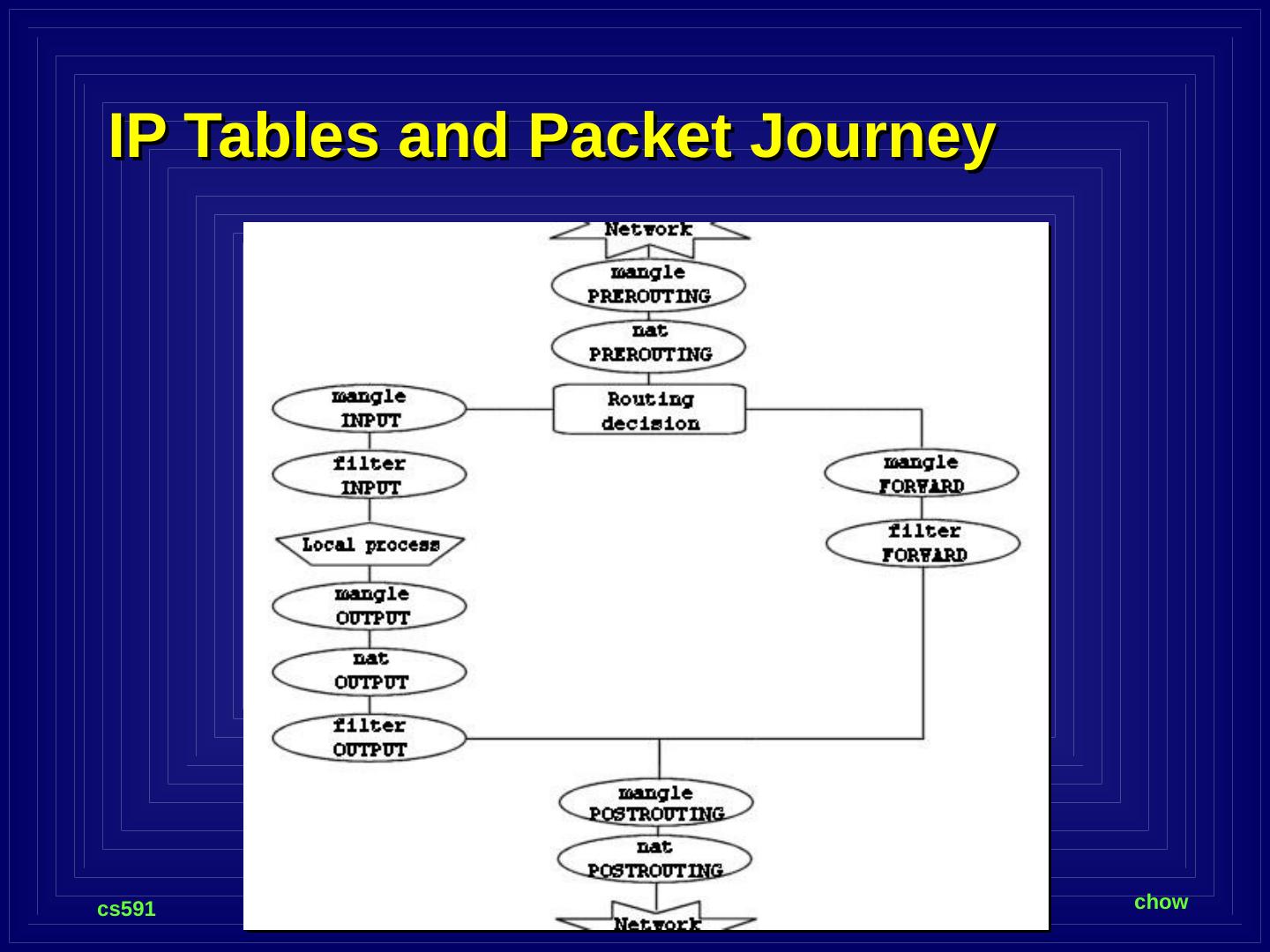
21 .IP Tables and Packet Journey
22 .DMZ Example See http://iptables-tutorial.frozentux.net/iptables-tutorial.html#RCDMZFIREWALLTXT
23 .DMZ Example See http://iptables-tutorial.frozentux.net/iptables-tutorial.html#RCDMZFIREWALLTXT
24 .SmoothWall SmoothWall Express is an open source firewall distribution based on the GNU/Linux operating system. “SmoothWall is configured via a web-based GUI, and requires absolutely no knowledge of Linux to install or use” (scary statement!) It integrates with firewall, DHCP, VPN, IDS, Web proxy, SSH, Dynamic DNS. http://downloads.smoothwall.org/pdf/2.0/admin.pdf
25 .Sonicwall Pro 300 Firewall A firewall device with 3 ports: Internet, DMZ, Intranet. http://www.sonicwall.com/products/pro330.html Restriction: NAT does not apply to servers on DMZ. Need to use public IP address. You can use one-to-one NAT for systems in Intranet. Support VPN. IPSec VPN, compatible with other IPSec-compliant VPN gateways Bundled with 200 VPN clients for remote users Supports up to 1,000 VPN Security Associations* 3 DES (168-Bit) Performance: 45 Mbps ICSA Certified, Stateful Packet Inspection firewall Unlimited number of users Concurrent connections: 128,000 Firewall performance: 190 Mbps (bi-directional)
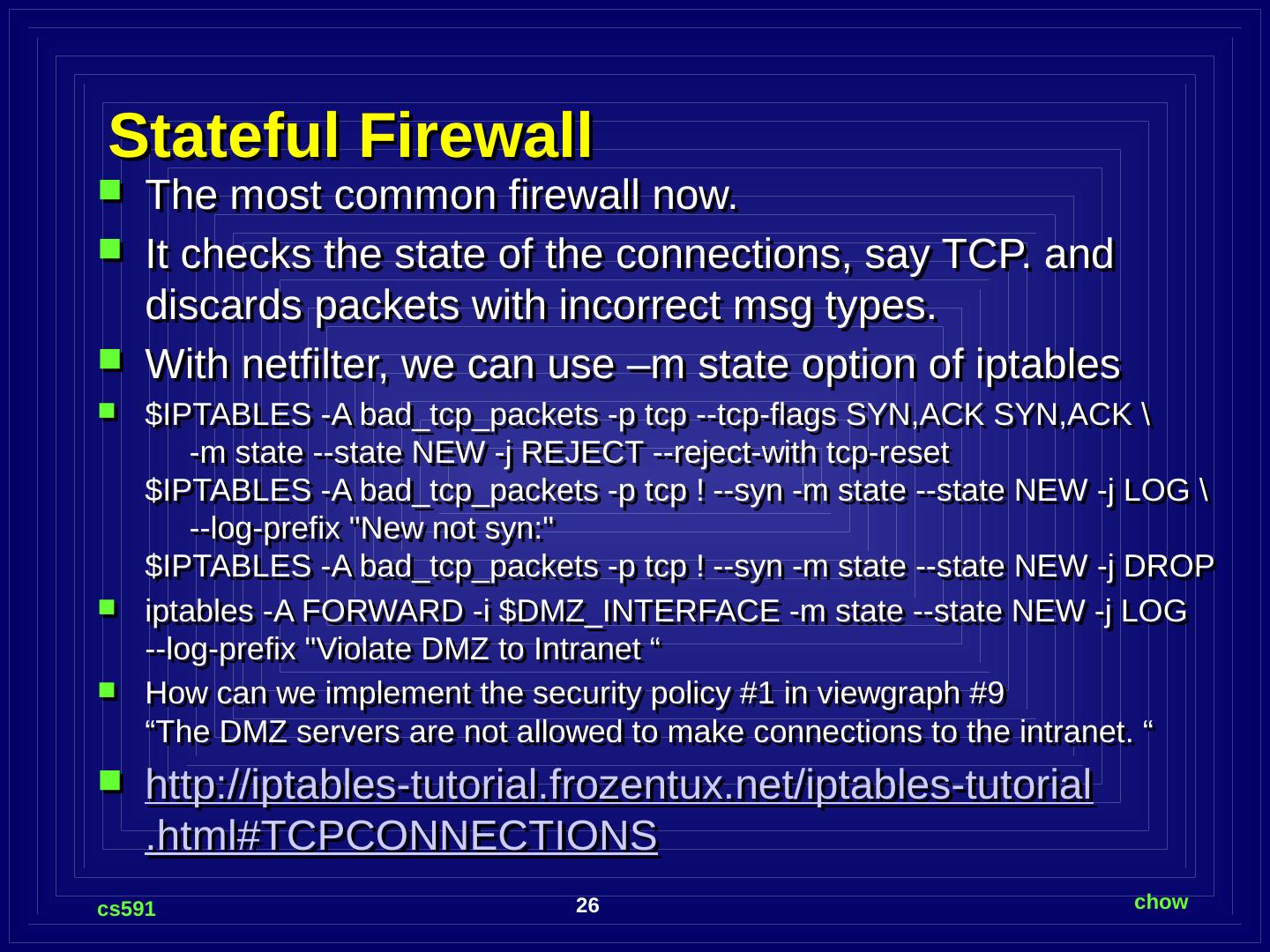
26 .Stateful Firewall The most common firewall now. It checks the state of the connections, say TCP. and discards packets with incorrect msg types. With netfilter , we can use –m state option of iptables $IPTABLES -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp -- tcp -flags SYN,ACK SYN,ACK \ -m state --state NEW -j REJECT --reject-with tcp -reset $IPTABLES -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp ! -- syn -m state --state NEW -j LOG \ --log-prefix "New not syn :" $IPTABLES -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp ! -- syn -m state --state NEW -j DROP iptables -A FORWARD - i $DMZ_INTERFACE -m state --state NEW -j LOG -- log-prefix "Violate DMZ to Intranet “ How can we implement the security policy #1 in viewgraph #9 “The DMZ servers are not allowed to make connections to the intranet. “ http://iptables-tutorial.frozentux.net/iptables-tutorial.html#TCPCONNECTIONS
27 .Lab Testbed for Exercise Outer FW (u10.10) Intra1 ( xpup ) Internet dvswitch 24 bits DNS Server Web Server Intranet (10.0.n.0/24) d vswitch 20 bits Mail Server bt4r1) DMZ ( 172.16.n.0/24 ) VLAN 36n SW Firewall Inner FW ( u10.10 ) Firewall ( fc 13 ) 172.16.n.1 172.16.n.3 172.16.n.3 10.0.n.3 10.0.n.2 10.0.n.1 128.198.161.n 128.198.161.(n+1)
28 .Firewall Facts (C) A firewall typically protects a smaller, secure network (such as a corporate LAN, or even just one host) from a larger network (such as the Internet). The firewall is installed at the point where the networks connect, and the firewall applies security policy rules to control traffic that flows in and out of the protected network. (C) A firewall is not always a single computer. For example, a firewall may consist of a pair of filtering routers and one or more proxy servers running on one or more bastion hosts, all connected to a small, dedicated LAN between the two routers. The external router blocks attacks that use IP to break security (IP address spoofing, source routing, packet fragments), while proxy servers block attacks that would exploit a vulnerability in a higher layer protocol or service. The internal router blocks traffic from leaving the protected network except through the proxy servers. The difficult part is defining criteria by which packets are denied passage through the firewall, because a firewall not only needs to keep intruders out, but usually also needs to let authorized users in and out.