- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- <iframe src="https://www.slidestalk.com/u70/distributed_platforms?embed" frame border="0" width="640" height="360" scrolling="no" allowfullscreen="true">复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
分布式计算平台介绍
展开查看详情
1 .Introduction to Distributed Platforms J. H. Wang Apr. 25, 2017
2 .Outline Motivation Why Distribution? Distributed Computing Popular distributed platforms Hadoop Spark
3 .Motivation Why distribution? Big data: volume, velocity, variety We need more storage space Space efficiency We need more computing power Time efficiency
4 .Distributed Computing Distributed computing is the study of distributed systems A distributed system is a collection of autonomous computing elements that appears to its users as a single coherent system A distributed system is a model in which components located on networked computers communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages
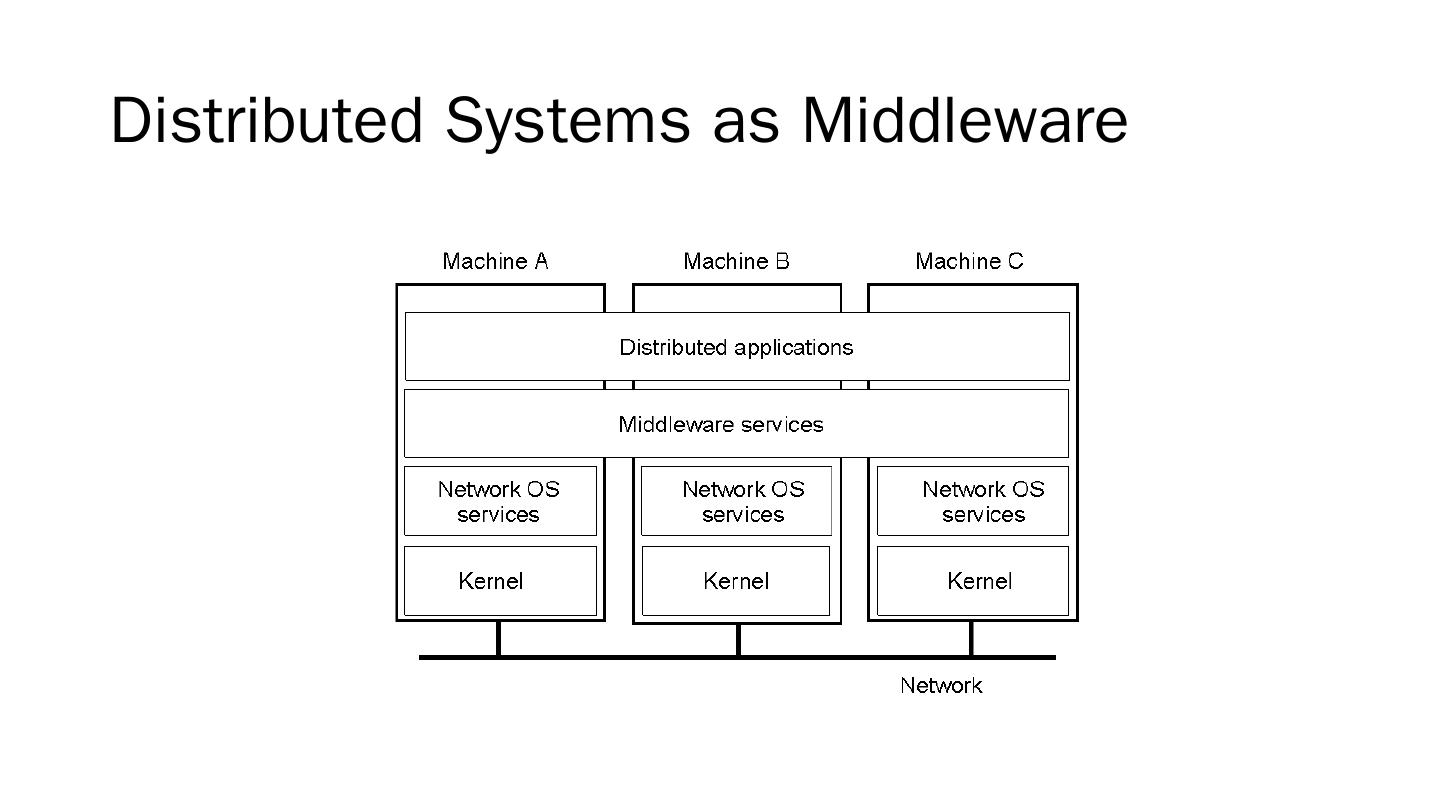
5 .Distributed Systems as Middleware
6 .Three characteristics Concurrency of components Lack of a global clock: synchronization Independent failure of components: fault tolerance Goals Resource availability Distribution transparency Openness Scalability
7 .Example architectures Centralized: client-server Multi-tiered Decentralized: peer-to-peer Hybrid
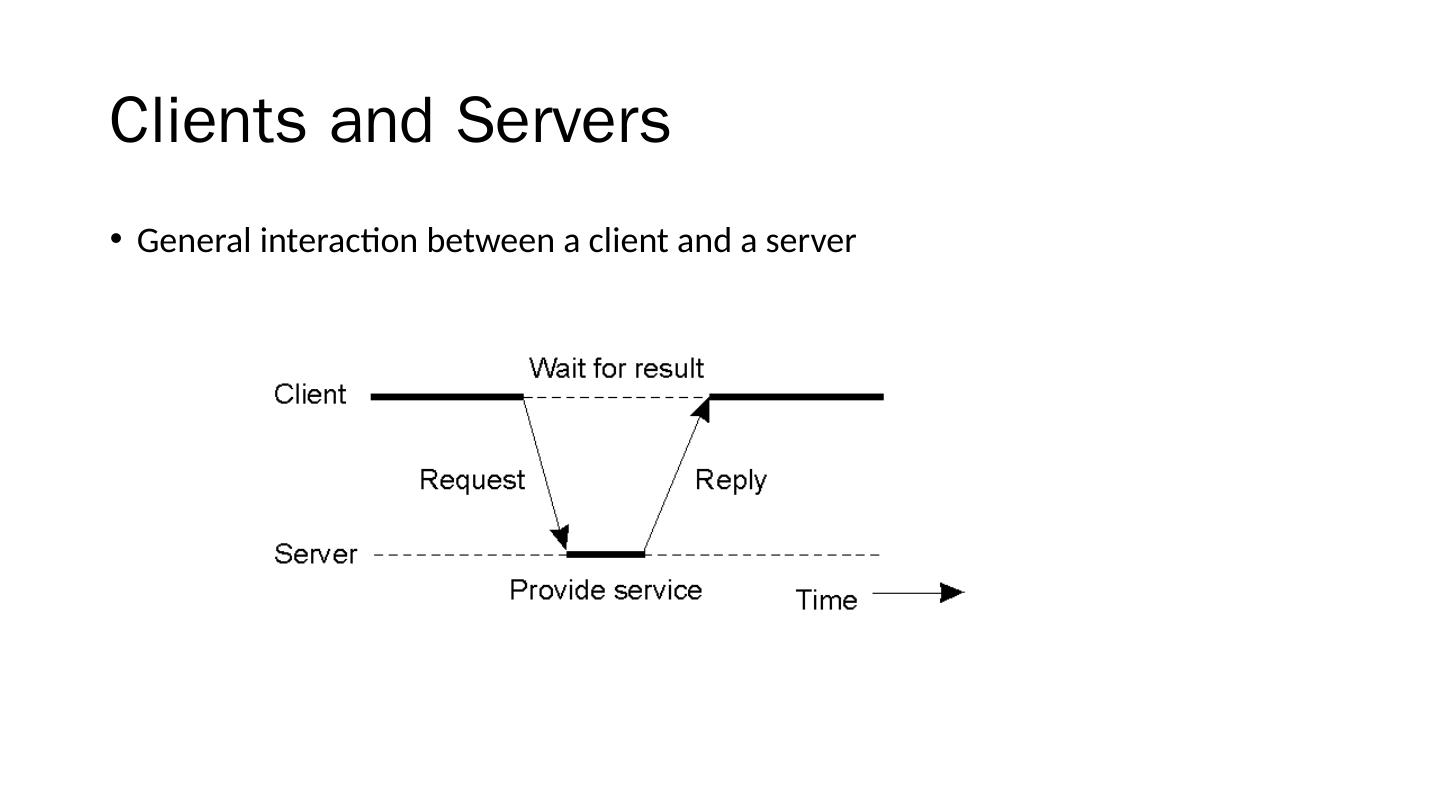
8 .Clients and Servers General interaction between a client and a server
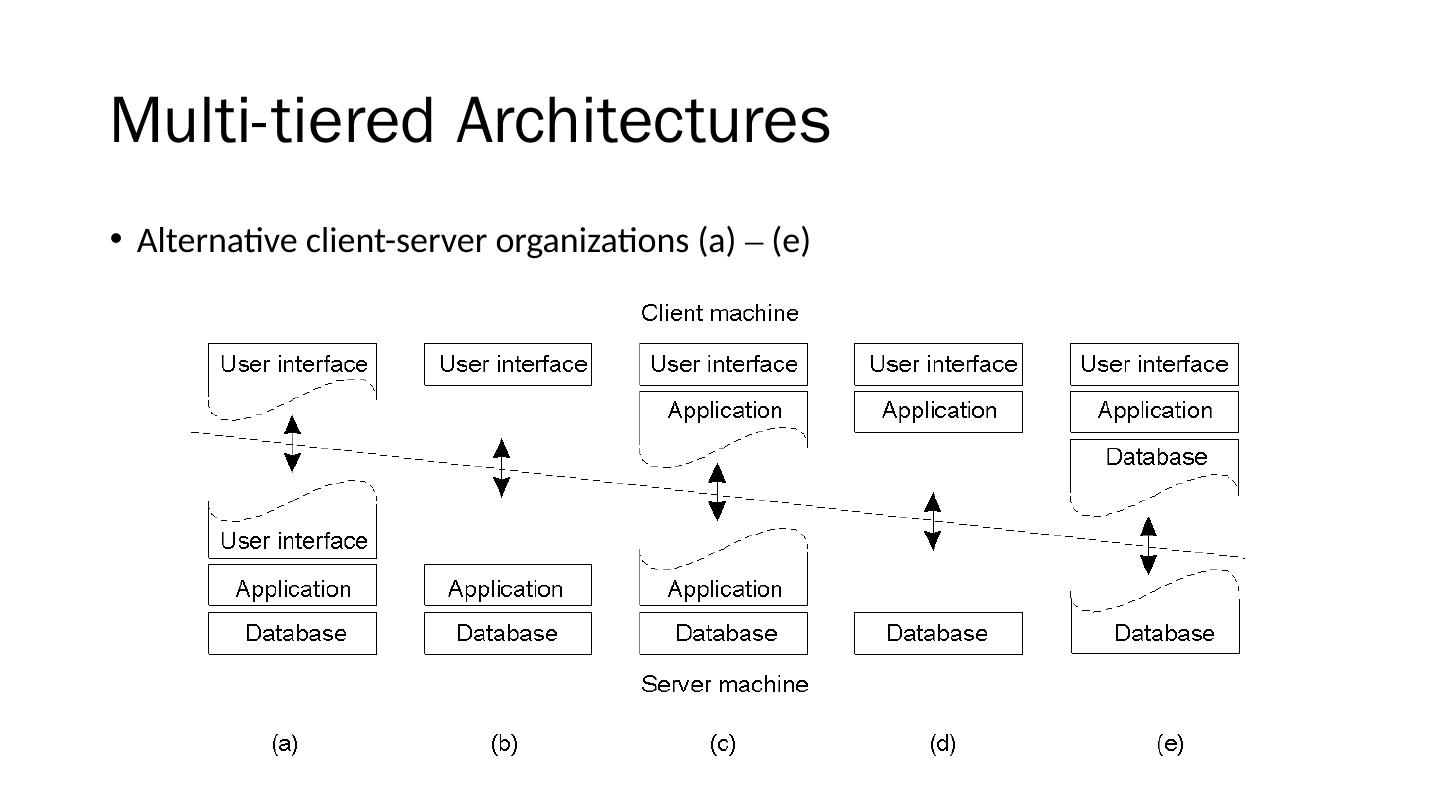
9 .Multi-tiered Architectures Alternative client-server organizations (a) – (e) 1-29
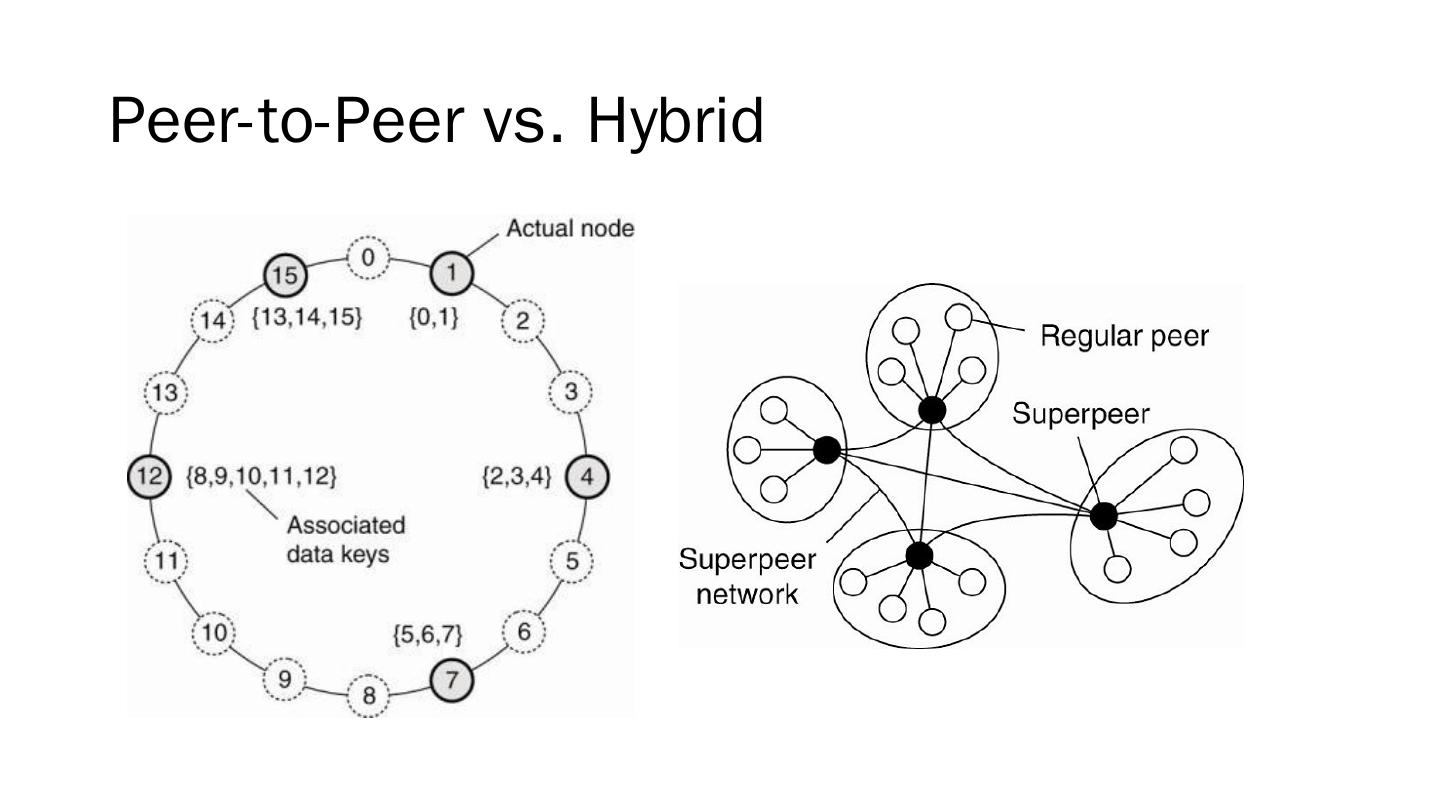
10 .Peer-to-Peer vs. Hybrid
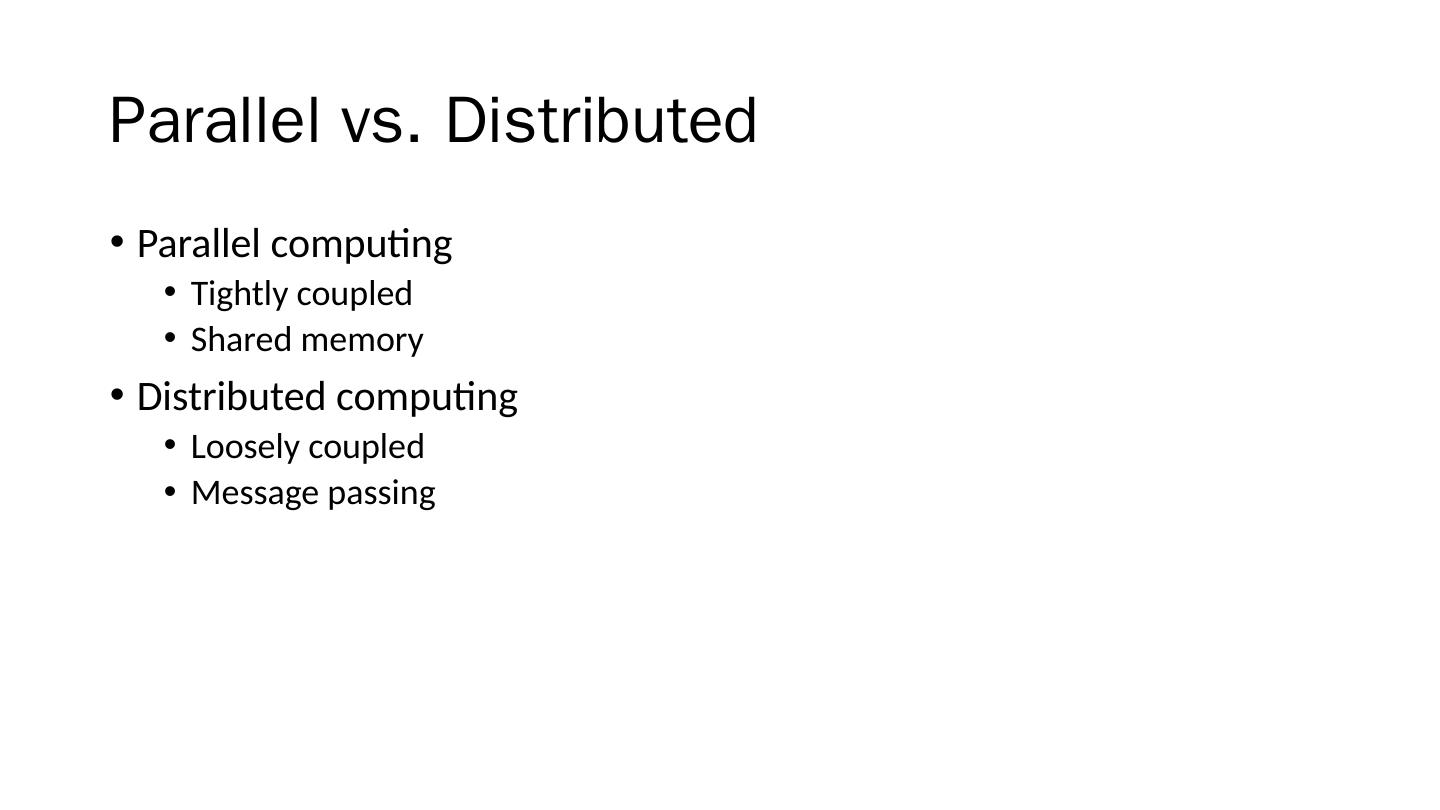
11 .Parallel vs. Distributed Parallel computing Tightly coupled Shared memory Distributed computing Loosely coupled Message passing
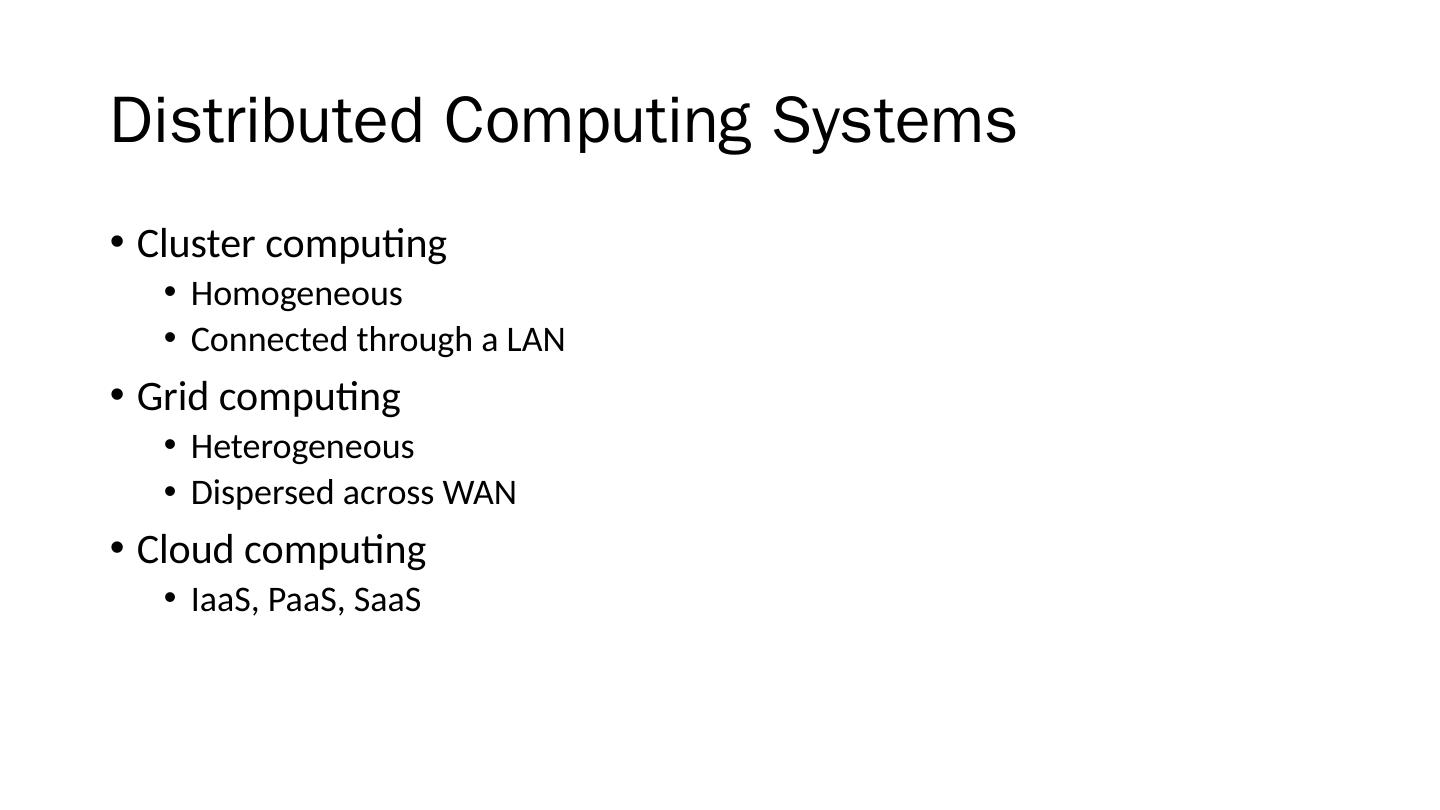
12 .Distributed Computing Systems Cluster computing Homogeneous Connected through a LAN Grid computing Heterogeneous Dispersed across WAN Cloud computing IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
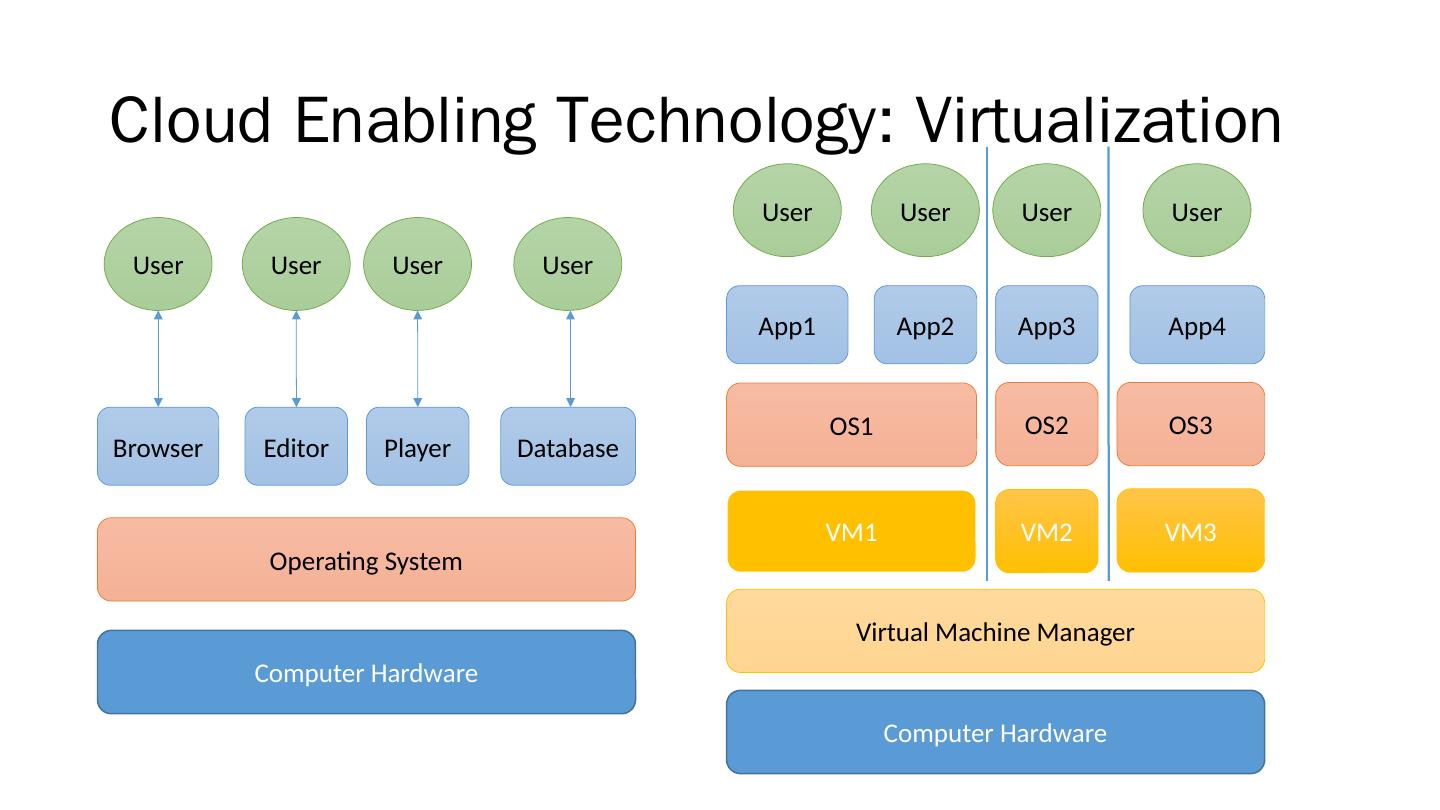
13 .Cloud Enabling Technology: Virtualization Computer Hardware OS1 App1 App2 App4 App3 User User User User Virtual Machine Manager OS2 OS3 VM1 VM2 VM3 Computer Hardware Operating System Browser Editor Database Player User User User User
14 .Popular Distributed Platforms Hadoop Spark
15 .Apache Hadoop Project For reliable, scalable, distributed computing http://Hadoop.apache.org/ Current version: 2.8.0
16 .Hadoop Architecture
17 .MapReduce Software framework for easily writing applications which process vast amounts of data in-parallel on large clusters of commodity hardware in a reliable, fault-tolerant manner HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System A distributed file system designed to run on commodity hardware Fault-tolerant Low-cost High throughput
18 .Assumptions and Goals of HDFS Hardware failure Detection of faults and quick, automatic recovery from them is a core architectural goal Streaming data access Batch processing, high throughput Large data sets Simple coherency model Write-once-read-many access model Moving computation is cheaper than moving data Portability across heterogeneous hardware and software platforms
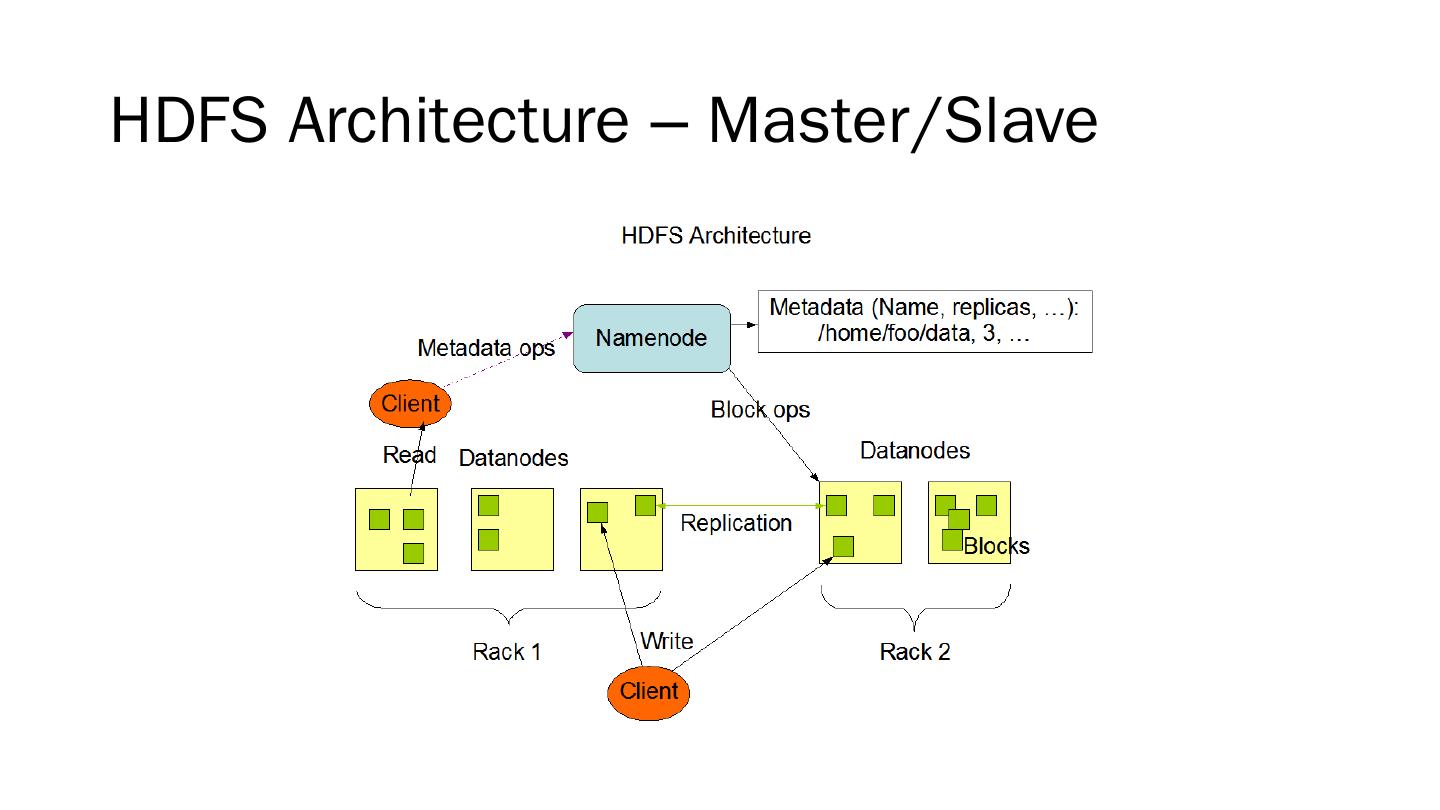
19 .HDFS Architecture – Master/Slave
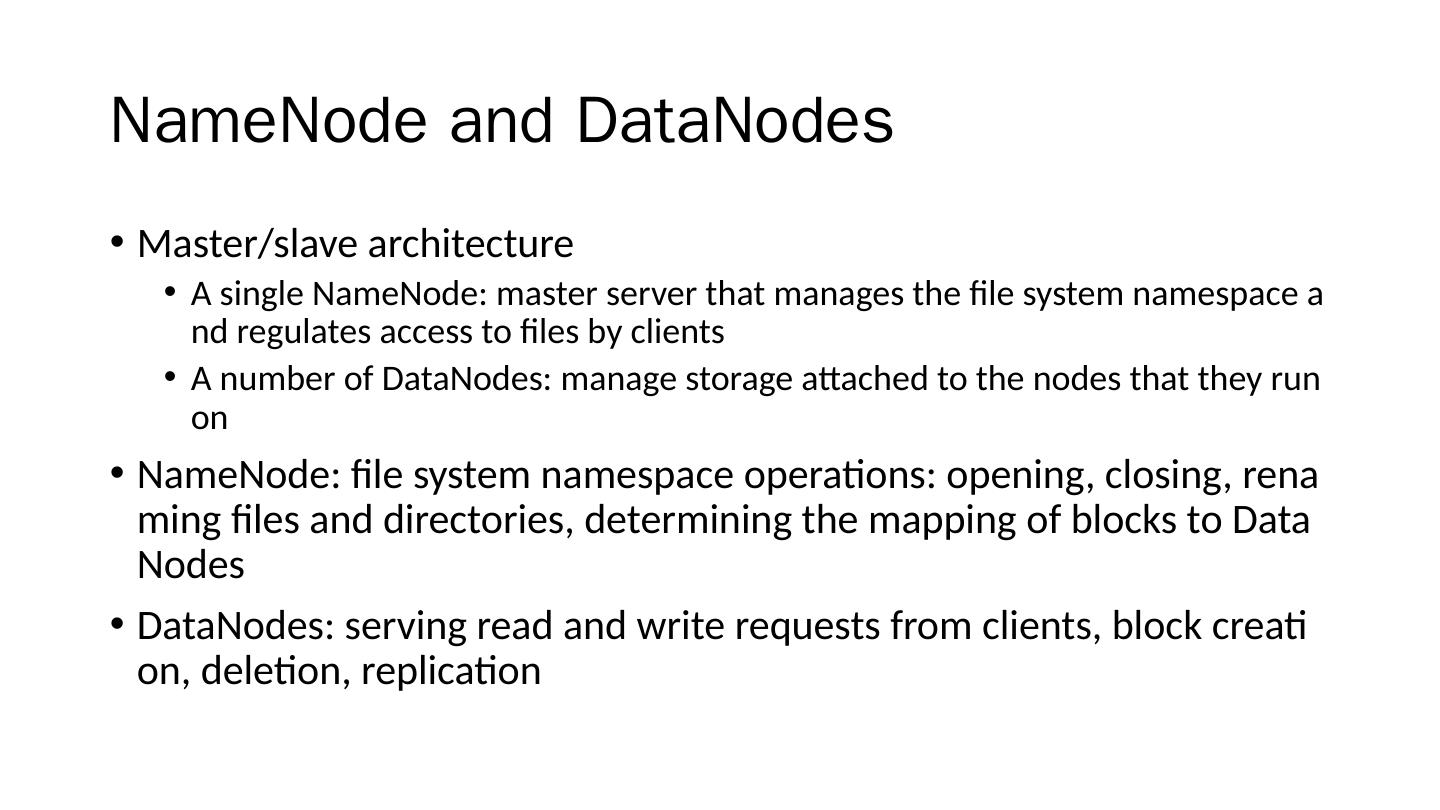
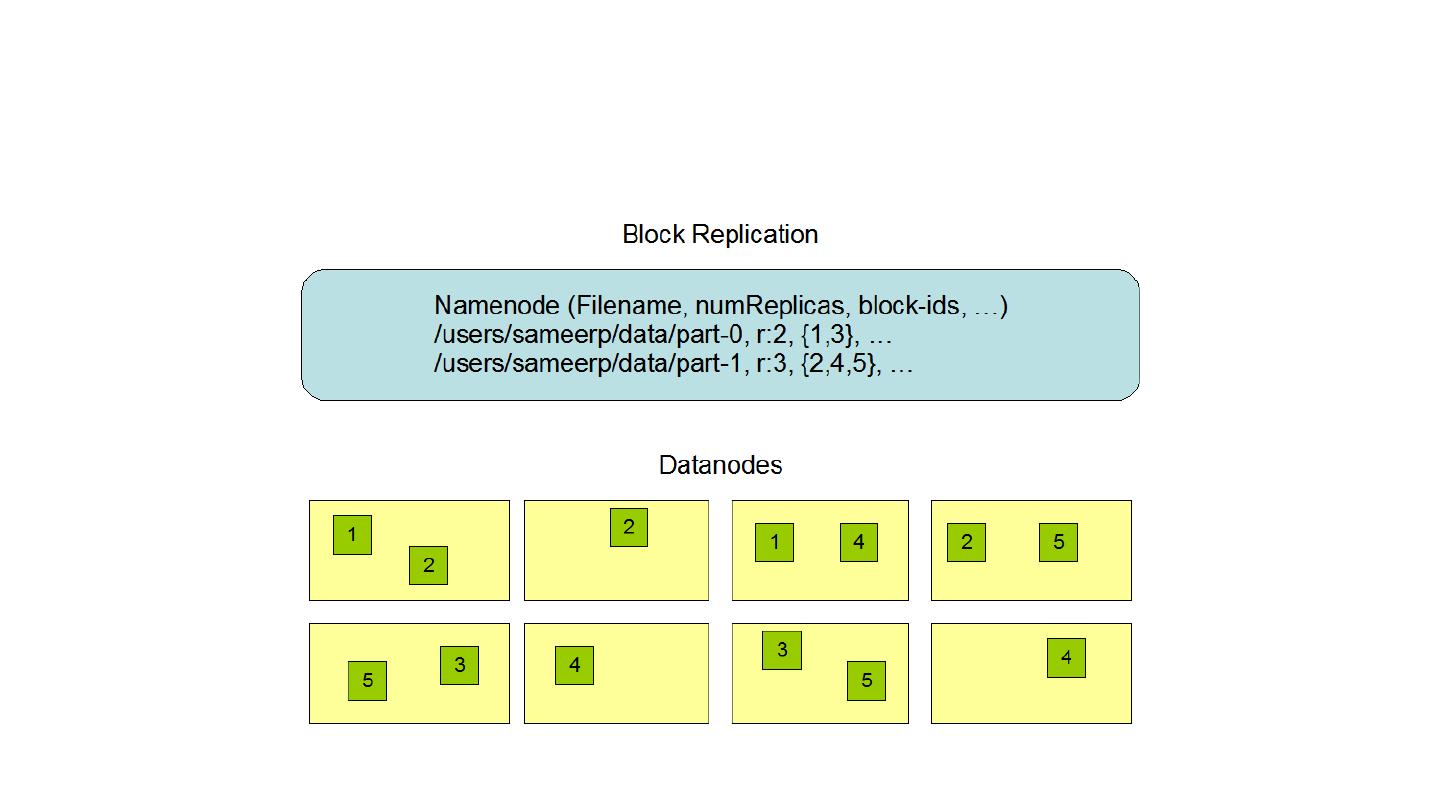
20 .NameNode and DataNodes Master/slave architecture A single NameNode : master server that manages the file system namespace and regulates access to files by clients A number of DataNodes : manage storage attached to the nodes that they run on NameNode : file system namespace operations: opening, closing, renaming files and directories, determining the mapping of blocks to DataNodes DataNodes : serving read and write requests from clients, block creation, deletion, replication
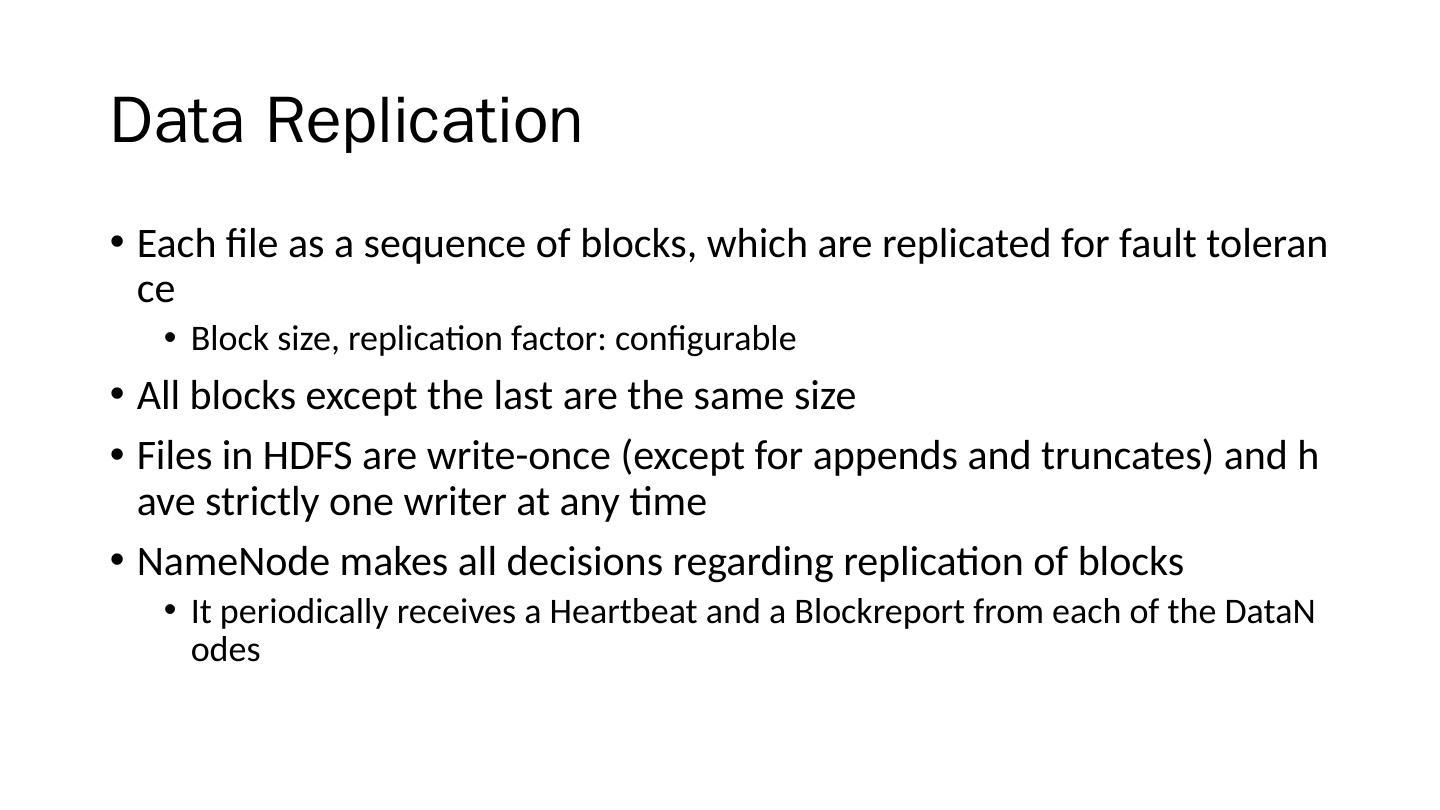
21 .Data Replication Each file as a sequence of blocks, which are replicated for fault tolerance Block size, replication factor: configurable All blocks except the last are the same size Files in HDFS are write-once (except for appends and truncates) and have strictly one writer at any time NameNode makes all decisions regarding replication of blocks It periodically receives a Heartbeat and a Blockreport from each of the DataNodes
22 .
23 .MapReduce Map tasks Reduce tasks A single master ResourceManager One worker NodeManager per cluster node MRAppMaster per application
24 .YARN: from Hadoop 2
25 .Major Differences between Hadoop 1 and 2 HDFS Federation Resource manager YARN
26 .Hadoop 2: HDFS Federation Two major components in HDFS Namespaces Blocks storage service Hadoop 1 A single namenode manages the entire namespace HDFS federation Multiple namenode servers manage namespaces Horizontal scaling, performance improvement, multiple namespaces
27 .Hadoop 2: YARN Brings significant performance improvements for some applications Supports additional processing models Implements a more flexible execution engine
28 .What is YARN? A resource manager separated from MapReduce in Hadoop 1 The operating system of Hadoop Managing and monitoring workloads Maintaining a multi-tenant environment Implementing security controls Managing high-availability features of Hadoop No longer limited to the I/O intensive, high-latency MapReduce model
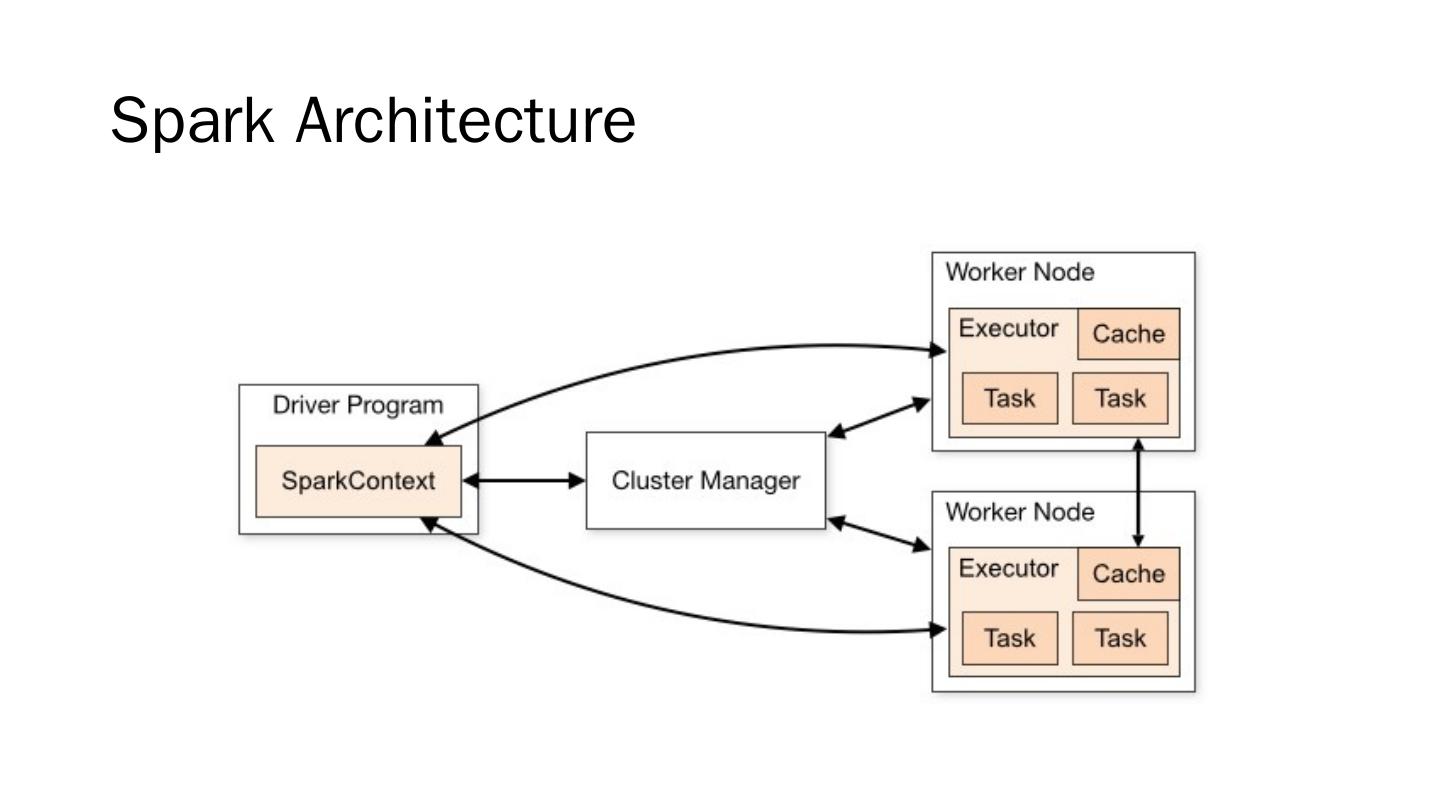
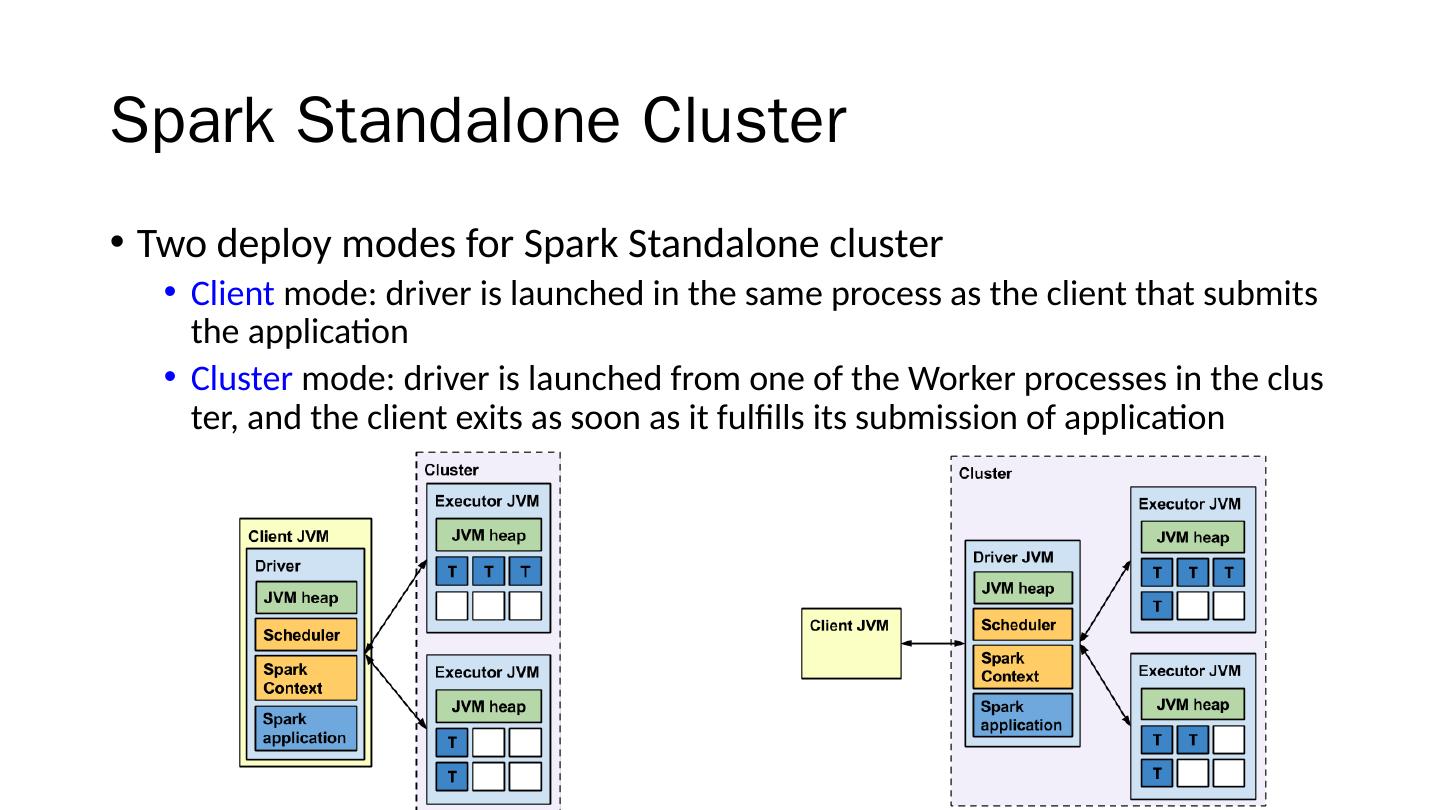
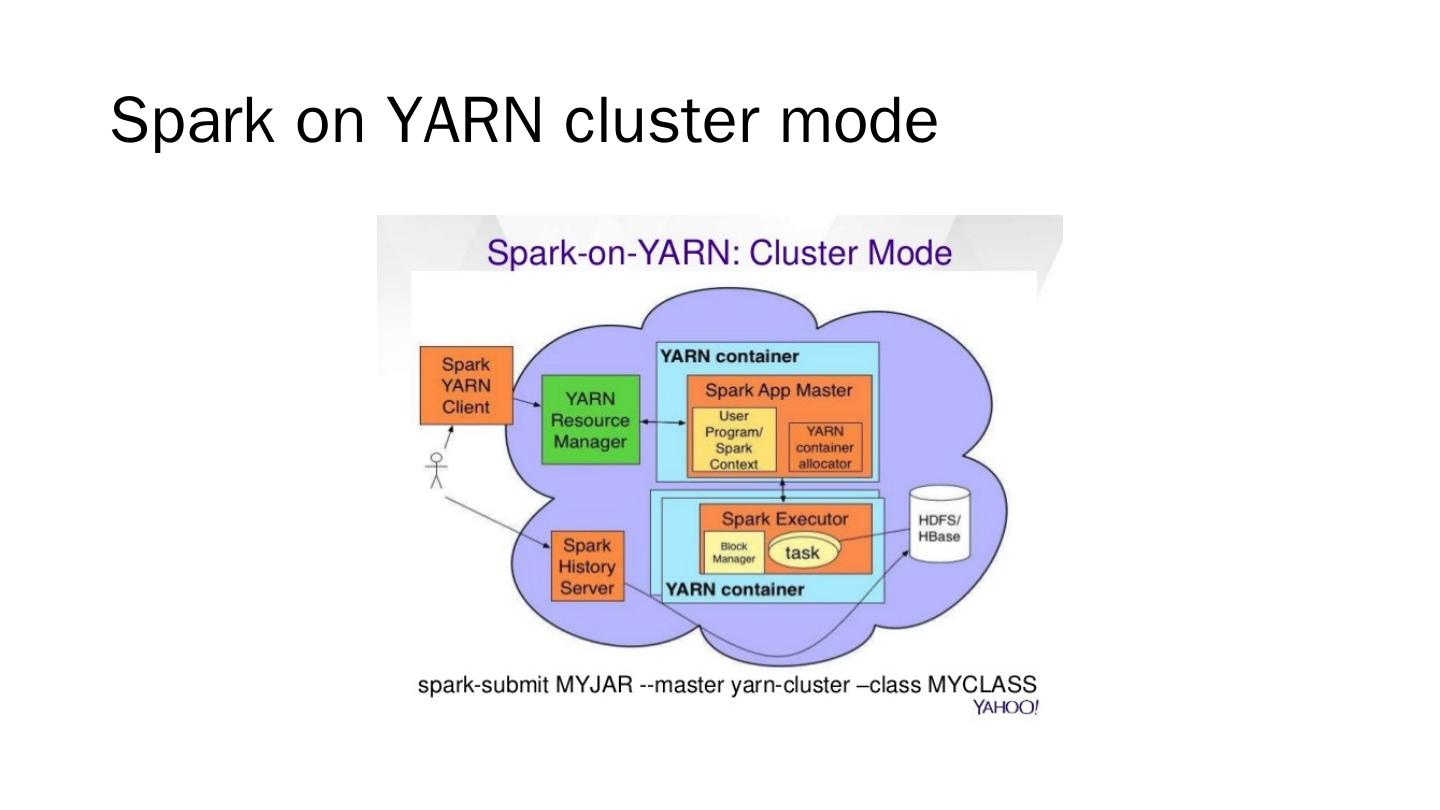
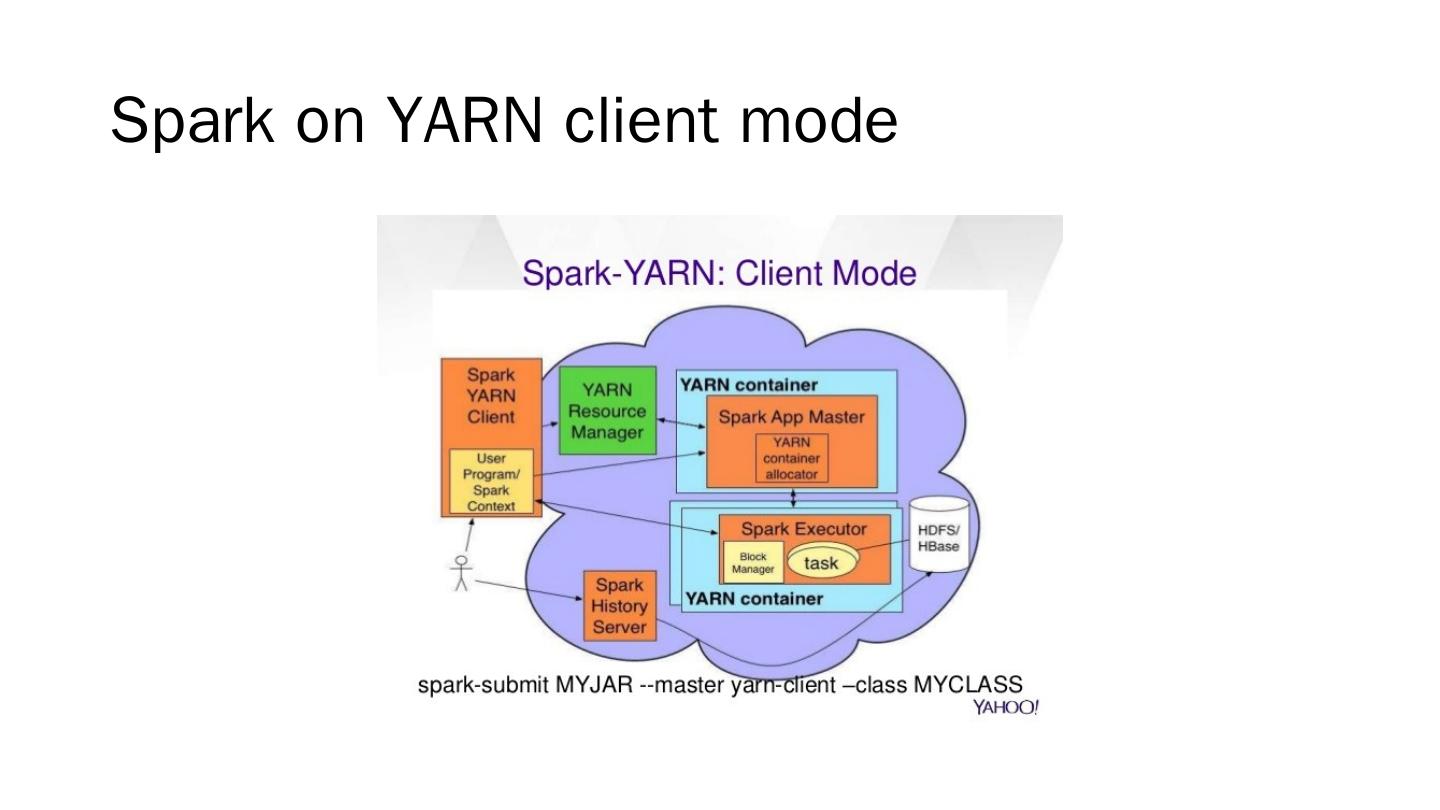
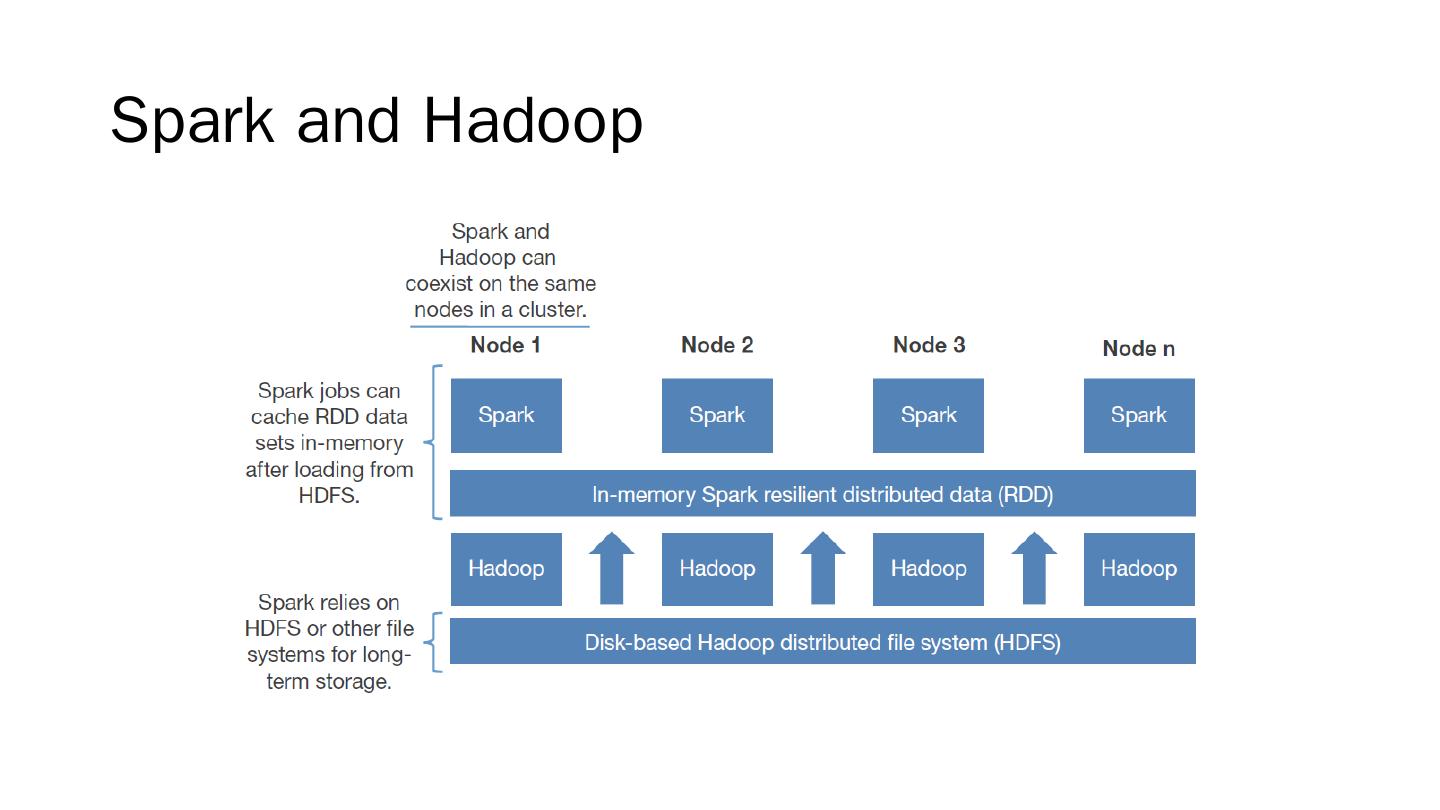
29 .Apache Spark For large-scale data processing http://spark.apache.org/ Current version: 2.1.0