- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- <iframe src="https://www.slidestalk.com/u888/sparkmlibrpractice?embed" frame border="0" width="640" height="360" scrolling="no" allowfullscreen="true">复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
Spark 机器学习&深度学习实战
展开查看详情
1 .Spark 机器学习 & 深度学习实战 欧 锐 2018/10/31
2 .目录 Spark MLlib 原理 Spark MLlib 实践 Spark-deep-learning 实践
3 .Spark MLlib 原理 01
4 .决策 树找郎君 通俗来说,决策树分类的思想类似于找对象。现想象一个女孩的母亲要给这个女孩介绍男朋友 , 于是 有了下面的对话: 女儿:多大年纪了? 母亲: 26 。 女儿:长的帅不帅? 母亲:挺帅的。 女儿:收入高不? 母亲:不算很高,中等情况。 女儿:是公务员不? 母亲:是,在税务局上班呢。 女儿:那好,我去见见。 训练数据
5 .决策 树找郎君 Code example : https:// github.com / ouyangshourui /spark- mlib - training.git
6 .决策 树找郎君
7 . Machine Learning Overview Machine Learning with Spark Mllib & ML
8 .What is Machine Learning? Machine learning is a field within artificial intelligence (AI ) ; Machine learning algorithms “learn” from data and often produce a predictive model as their output ; AI > Machine learning > Deep Learning
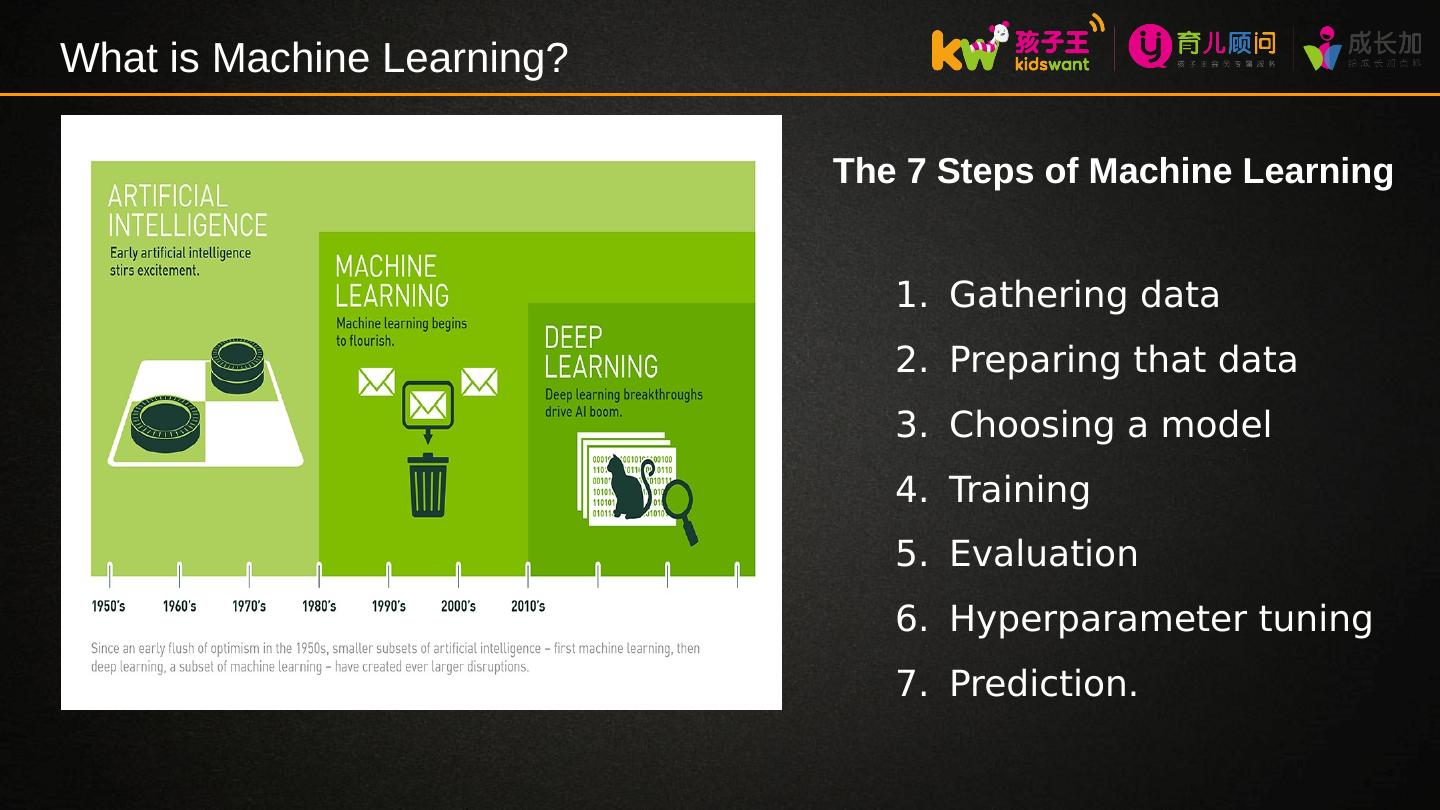
9 .What is Machine Learning? The 7 Steps of Machine Learning Gathering data Preparing that data Choosing a model Training Evaluation Hyperparameter tuning Prediction.
10 .Relationship of Algorithms and Data Volume There are many algorithms for each type of machine learning; There’s no overall “best” algorithm ; Each algorithm has advantages and limitations ; Algorithm choice is often related to data volume; Best approach = simple algorithm + lots of data; Spark is an excellent platform for machine learning over large data sets;
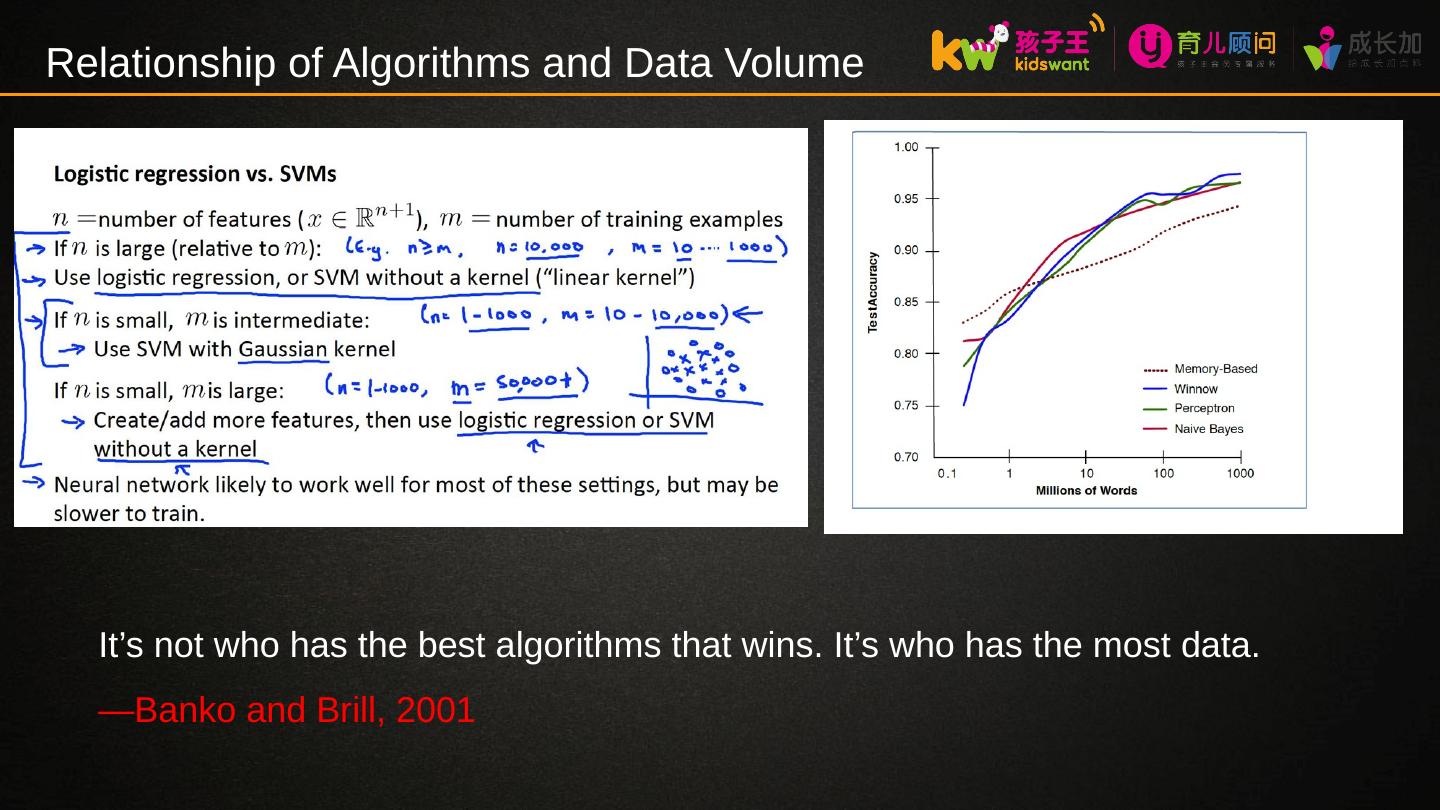
11 .Relationship of Algorithms and Data Volume It’s not who has the best algorithms that wins. It’s who has the most data. — Banko and Brill, 2001
12 .Spark MLlib and Spark ML 1 . Spark MLlib is Spark machine learning library Makes practical machine learning scalable and easy Includes many common machine learning algorithms Includes base data types for efficient calculations at scale Supports scalable statistics and data transformations 2 、 Spark ML is a new higher-level API for machine learning pipelines ->python sklearn Built on top of Spark’s DataFrames API Simple and clean interface for running series of complex tasks Supports most functionality included in Spark MLlib
13 .F eature Engineering 我们都知道特征工程在机器学习中是很重要的,然而特征工程到底是什么?怎么样通俗的理解它呢?打个比方,即使你有再好的渔具,如果给你一片没有鱼的池塘,那也是白费力气的。而特征工程就是找有鱼的那片水域。所以我们可以这么理解, 特征是数据中抽取出来的对结果预测有用的信息 (水域),而 特征工程就是使用专业知识来处理数据,筛选出具有价值的特征 (从 100 个水域中挑选出鱼最多最好的水域)。所以有句话是这么说的: 算法再牛逼,其上限也是由特征工程决定的 ,就像你渔具再好,捕鱼多少也是由水域这个特征决定的。 在 SparkML 中、对于特征工程的操作主要分为 特征提取,特征转化、特征选择 。
14 .F eature Engineering ( TF-IDF ) (Term frequency-inverse document frequency ) TF-IDF 完美的解决了这个问题, TF-IDF 作用就是体现一个文档中词语重要程度。 TF 是某个词或短语在一篇文章中出现的频率。而 IDF ,就是一种对热门词语的惩罚,对于较热门词语 比如 “ 中国 ” 会 给予较小的权重,较少见的词“功夫”给予较大的 权重;
15 .F eature Engineering ( TF-IDF ) 由于 china 在三个文档中都出现了,所以 TF-IDF=0.0 ,而 kungfu 只在第一个文档出现(说明是冷门词),却是第一个文档中出现次数最多的,因此计算出来的 TF-IDF=1.3862943611198906 也是最高的
16 .F eature Engineering ( Bucketizer ) 现在有推荐的需求,产品经理觉得把人分为 50 以上和 50 以下太不精准了,应该分为 20 岁以下 , 20-30 岁, 30-40 岁, 36-50 岁, 50 以上,那么就得用到数值离散化的处理方法 了; 离散化就是把特征进行适当的离散处理,比如上面所说的年龄是个连续的特征 ,但是 我把它分为不同的年龄阶段就是把它离散化了,这样更利于我们分析用户行为进行精准 推荐; Bucketizer 能方便的将一堆数据分成不同的 区间;
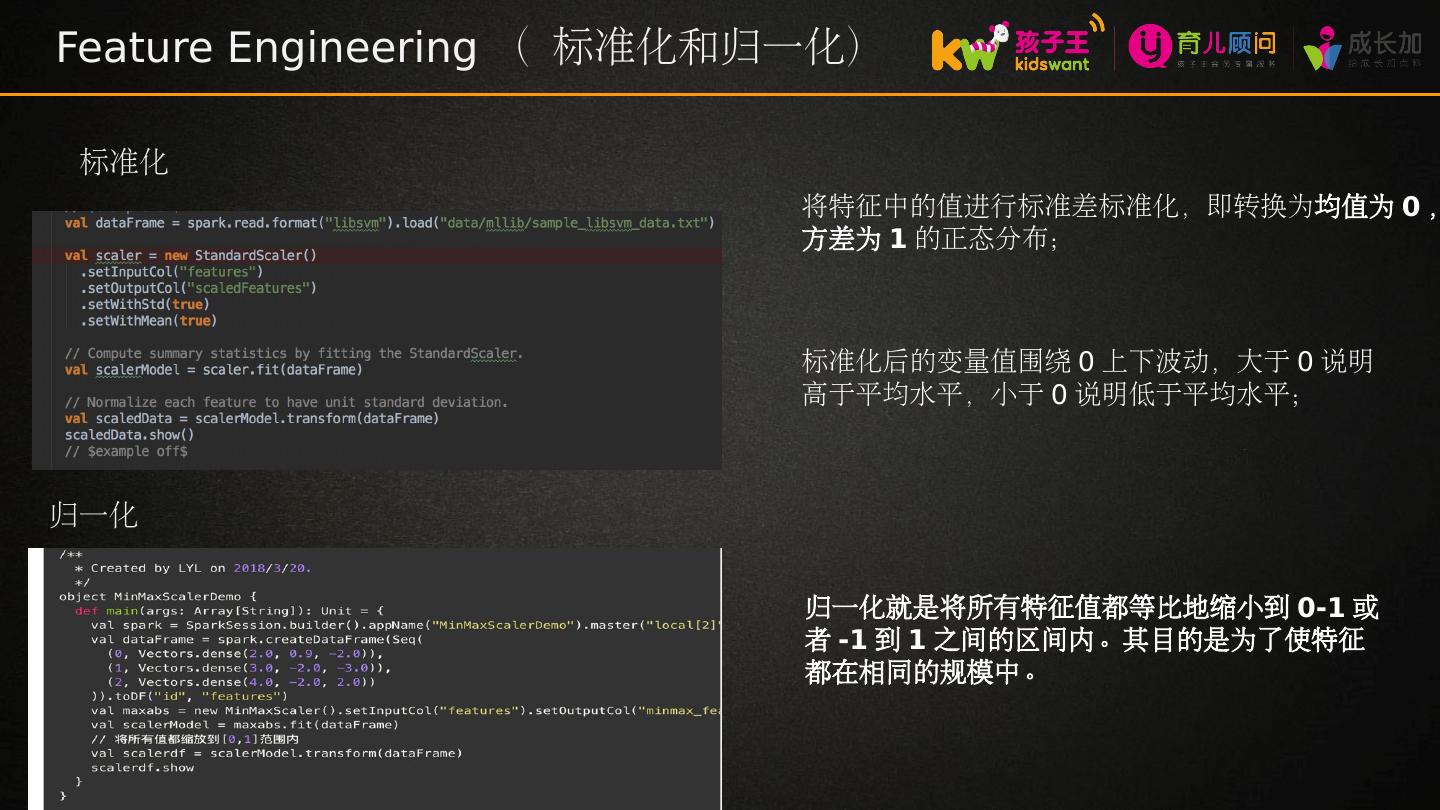
17 .Feature Engineering ( 标准化和归一化) 标准化 将特征中的值进行标准差标准化,即转换为 均值为 0 , 方差 为 1 的正态 分布; 标准化后的变量值围绕 0 上下波动,大于 0 说明高于平均水平,小于 0 说明低于平均 水平; 归一化 归一化就是将所有特征值都等比地缩小到 0-1 或者 -1 到 1 之间的区间内。其目的是为了使特征都在相同的规模中。
18 .Feature Engineering 不断完善中、 接近 sklearn 的功能
19 .Spark MLlib Regularization Spark 在 linear regression 中提供了如下三种 regularzation 参数: L1 : L2: Elastic net : L1+L2 结合的方式,即 elastic net 。这种方式同时兼顾特征选择( L1 )和权重衰减( L2 )
20 .Spark ML Machine learning tasks consist of a (potentially complex) series of steps Data transformations, algorithm training, and model prediction ; These steps can be viewed as a pipeline through which the data travels ; Transformers & Estimators
21 .Spark ML-pipeline A Pipeline represents a series of steps in a machine learning workflow : Each pipeline step can be either a transformer or an estimator A Pipeline takes a DataFrame as input and produces a PipelineModel as output A pipeline is itself is therefore an estimator
22 .Spark Mllib 实践 02
23 .银行信贷的信用 风险 example 我们需要预测什么? 某个人是否会按时还款 这就是标签:此人的 信用度 你用来预测的“是与否”问题或者属性是什么? 申请人的基本信息和社会身份信息:职业,年龄,存款储蓄,婚姻状态等等 …… 这些就是特征,用来构建一个分类模型, 你从中提取出对分类有帮助的特征信息 。 随机森林模型 随机 森林是分类和回归问题中一类常用的融合学习方法。此算法基于训练数据的不同子集构建多棵 决策树 ,组合成一个新的模型。
24 .德国人信用度数据集 { “信用 ” , “ 存款”,“期限”,“历史记录”,“目的”,“数额”,“储蓄”,“是否在职”,“婚姻” , “ 担保人”,“居住时间”,“资产”,“年龄”,“历史信用”,“居住公寓”,“贷款”,“职业” , “ 监护人”,“是否有电话”,“外籍” }
25 .数据元数据定义 & 数据初始化 val rdd = sc.textFile ("data/ germancredit.csv ") val creditDF = parseRDD ( rdd ).map( parseCredit ). toDF ().cache () creditDF.createOrReplaceTempView ("credit")
26 .特征工程 dataframe 初始化之后,你可以用 SQL 命令查询数据了。下面是一些使用 Scala DataFrame 接口查询数据的例子: 计算数值型数据的统计信息,包括计数、均值、标准差、最小值和最大值 。 // 获取存款、数目、住居时长 sqlContext.sql ("SELECT creditability, avg (balance) as avgbalance , avg (amount) as avgamt , avg (duration) as avgdur FROM credit GROUP BY creditability "). show creditDF.describe ("balance").show creditDF.groupBy ("creditability"). avg ("balance").show
27 .这些特征经过了变换,存入特征向量中,即一组表示各个维度特征值的数值 向量; 用 VectorAssembler 方法将每个维度的特征都做变换,返回一个新的 dataframe val featureCols = Array ("balance", "duration", "history", "purpose", "amount", "savings", "employment", " instPercent ", " sexMarried ", "guarantors", " residenceDuration ", "assets", "age", " concCredit ", "apartment", "credits", "occupation", "dependents", " hasPhone ", "foreign") val assembler = new VectorAssembler (). setInputCols ( featureCols ). setOutputCol ("features") val df2 = assembler.transform ( creditDF ) println (" featureCols VectorAssembler :") df2.show () val labelIndexer = new StringIndexer (). setInputCol ("creditability"). setOutputCol ("label") val df3 = labelIndexer.fit (df2).transform(df2) df3.show()
28 .数据集被分为训练数据和 测试 数据两个部分, 70% 的数据用来训练模型, 30% 的数据用来测试模型 。 val splitSeed = 5043 val Array ( trainingData , testData ) = df3.randomSplit( Array (0.7, 0.3), splitSeed ) maxDepth :每棵树的最大深度。增加树的深度可以提高模型的效果,但是会延长训练时间。 maxBins :连续特征离散化时选用的最大分桶个数,并且决定每个节点如何分裂。 impurity :计算信息增益的指标 auto :在每个节点分裂时是否自动选择参与的特征个数 seed :随机数生成种子 接着,我们按照下列参数训练一个随机森林分类器:
29 .val classifier = new RandomForestClassifier (). setImpurity (" gini "). setMaxDepth (3). setNumTrees (20) . setFeatureSubsetStrategy ("auto") . setSeed (5043) val model = classifier.fit ( trainingData ) val evaluator = new BinaryClassificationEvaluator (). setLabelCol ("label") val predictions = model.transform ( testData ) model.toDebugString 模型训练