- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
Query Optimizer - MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
mysql和postgresql是两个最流行的开源关系数据库。为了帮助在它们之间进行选择,对它们的查询优化器进行了比较。本次会议的目的是总结比较的结果。具体来说,指出优化器相关的优缺点。
展开查看详情
1 .Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL Percona Live, Frankfurt (DE), 7 November 2018 Christian Antognini @ChrisAntognini antognini.ch/blog BASEL BERN BRUGG DÜSSELDORF FRANKFURT A.M. FREIBURG I.BR. GENEVA HAMBURG COPENHAGEN LAUSANNE MUNICH STUTTGART VIENNA ZURICH
2 . @ChrisAntognini Senior principal consultant, trainer and partner at Trivadis christian.antognini@trivadis.com http://antognini.ch Focus: get the most out of database engines Logical and physical database design Query optimizer Application performance management Author of Troubleshooting Oracle Performance (Apress, 2008/14) OakTable Network, Oracle ACE Director 2 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
3 . Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Controlling the Query Optimizer 3. Statistics about Data 4. Data Dictionary Metadata 5. Single-Table Access Paths 6. Joins and Sub-queries 7. Conclusion 8. References 3 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
4 . Introduction 4 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
5 . Compared Products MySQL Community Server 8.0.13 PostgreSQL 11.0 Release date: 10 October 2018 Release date: 18 October 2018 Only the InnoDB engine is covered 5 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
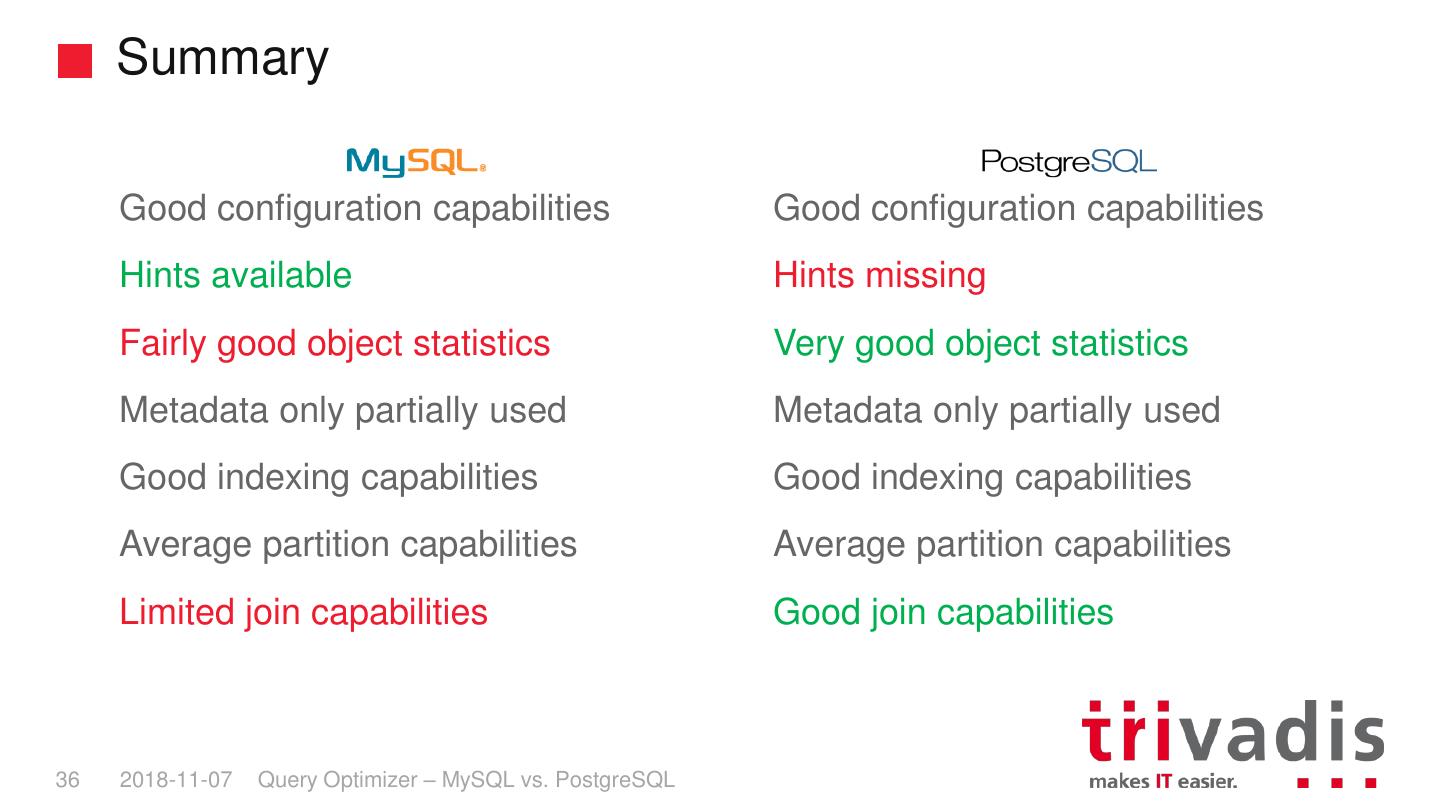
6 . Disclaimer No performance tests were performed No comparison between the execution plans generated by the two query optimizers were performed To compare and to evaluate the two query optimizers only the availability of key features and the ability of the query optimizer to correctly recognize common data patterns was considered 6 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
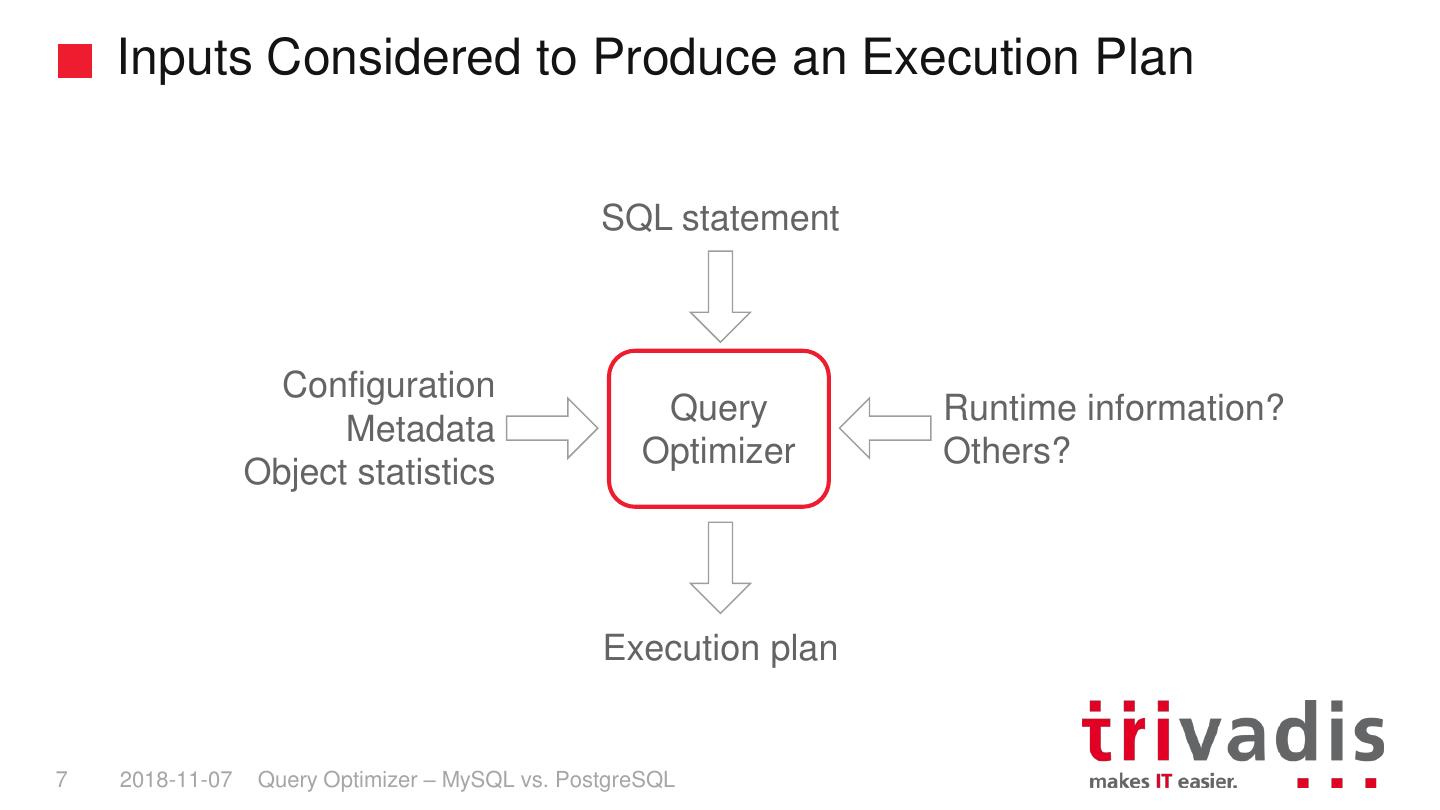
7 . Inputs Considered to Produce an Execution Plan SQL statement Configuration Query Runtime information? Metadata Optimizer Others? Object statistics Execution plan 7 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
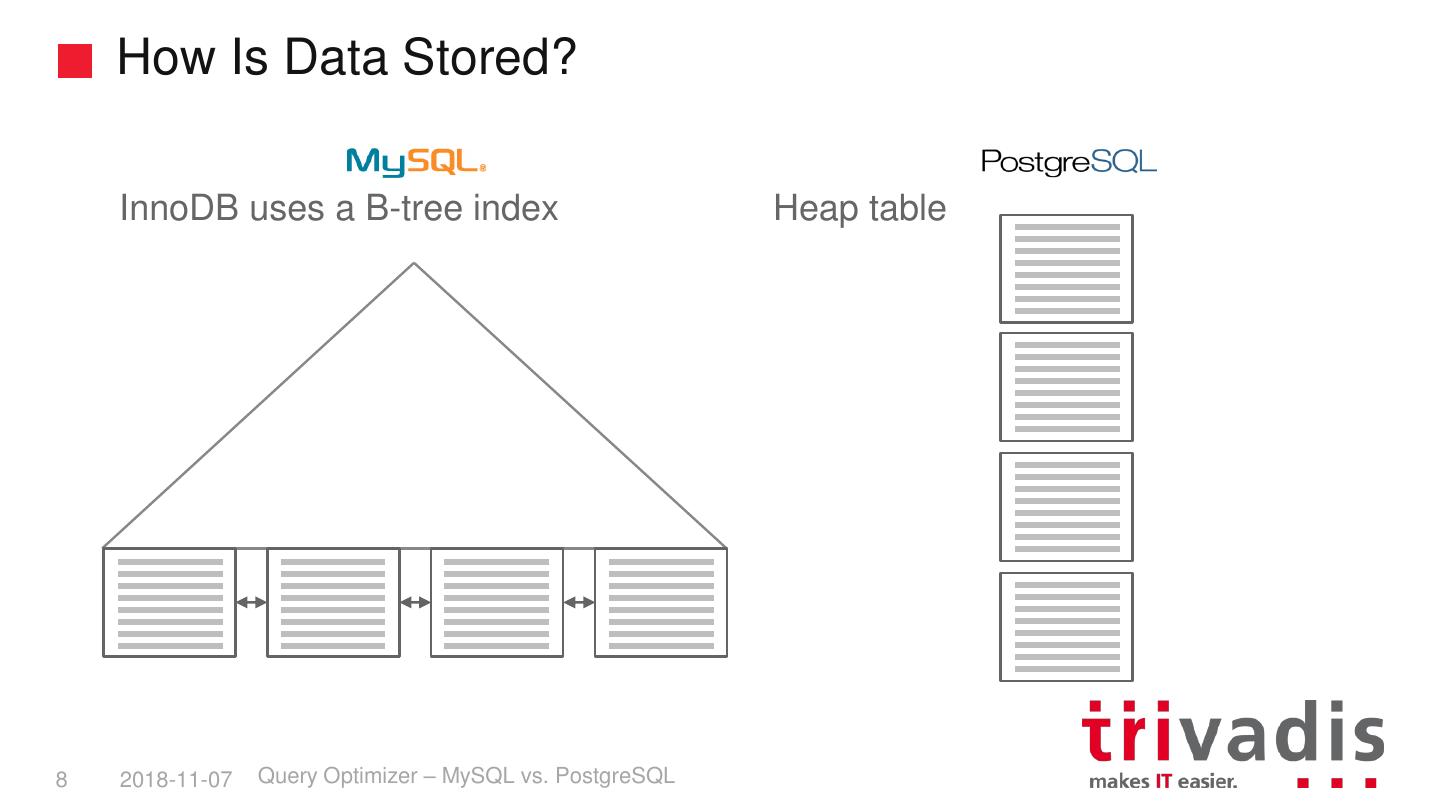
8 . How Is Data Stored? InnoDB uses a B-tree index Heap table 8 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
9 . Controlling the Query Optimizer 9 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
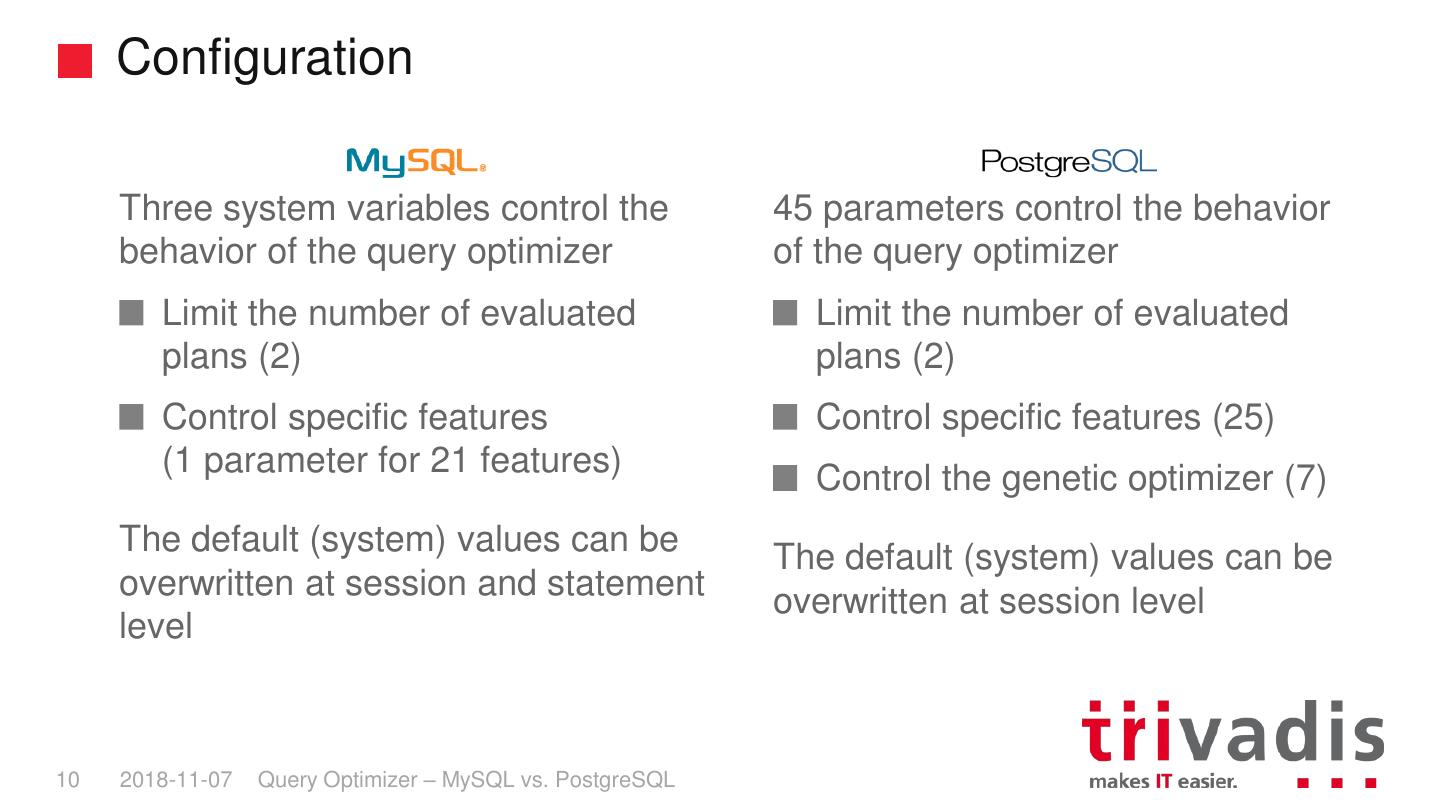
10 . Configuration Three system variables control the 45 parameters control the behavior behavior of the query optimizer of the query optimizer Limit the number of evaluated Limit the number of evaluated plans (2) plans (2) Control specific features Control specific features (25) (1 parameter for 21 features) Control the genetic optimizer (7) The default (system) values can be The default (system) values can be overwritten at session and statement overwritten at session level level 10 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
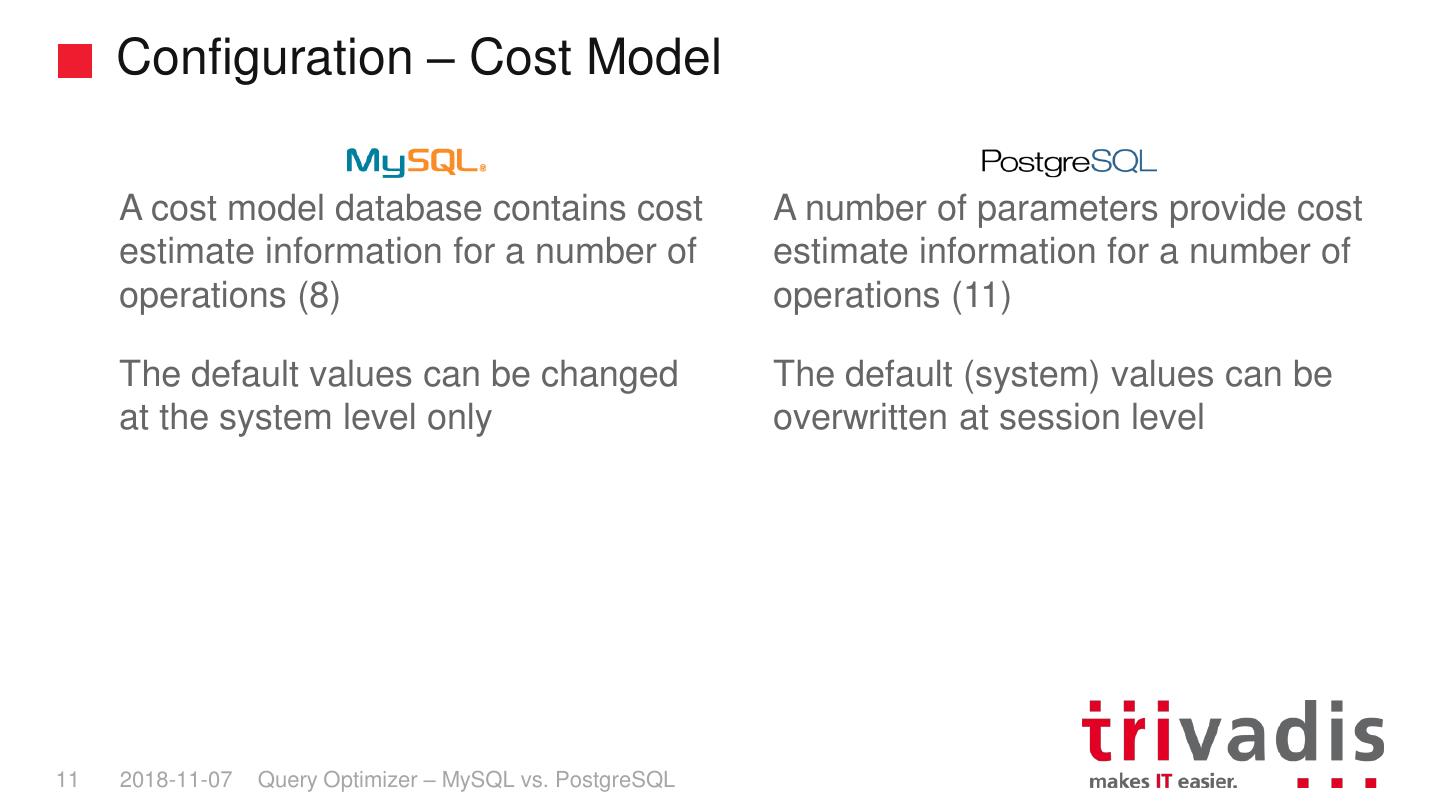
11 . Configuration – Cost Model A cost model database contains cost A number of parameters provide cost estimate information for a number of estimate information for a number of operations (8) operations (11) The default values can be changed The default (system) values can be at the system level only overwritten at session level 11 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
12 . hints_modifiers.sql Hints hints_index.sql hints_optimizer.sql SELECT statement modifiers (4) (Available in EDB Advanced Server) Impact statement syntax Index hints (3) Impact statement syntax Cause error when index missing Optimizer hints (23) Similar to Oracle Database hints Global, query block and object-level Cause warning when syntax is wrong 12 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
13 . Statistics about Data 13 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
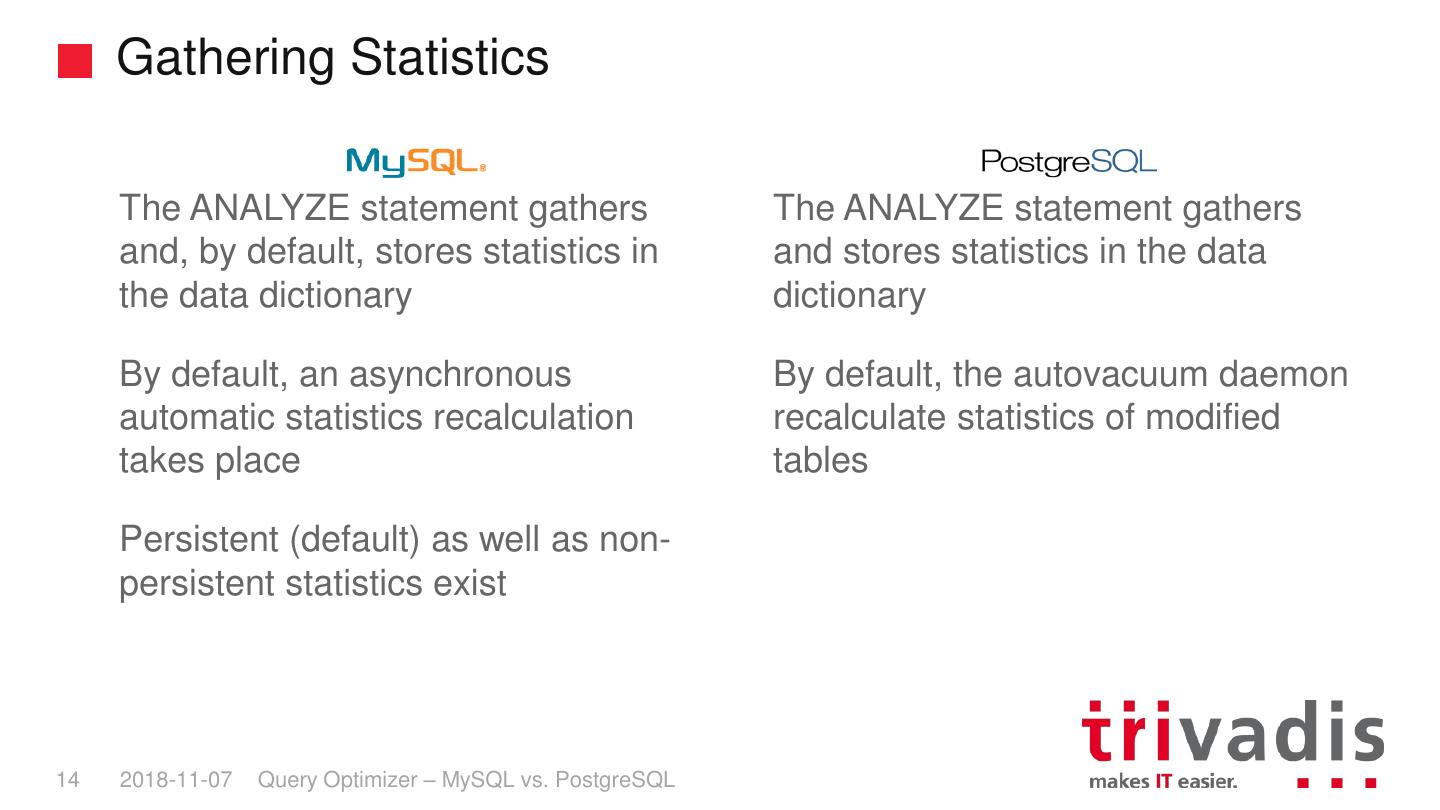
14 . Gathering Statistics The ANALYZE statement gathers The ANALYZE statement gathers and, by default, stores statistics in and stores statistics in the data the data dictionary dictionary By default, an asynchronous By default, the autovacuum daemon automatic statistics recalculation recalculate statistics of modified takes place tables Persistent (default) as well as non- persistent statistics exist 14 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
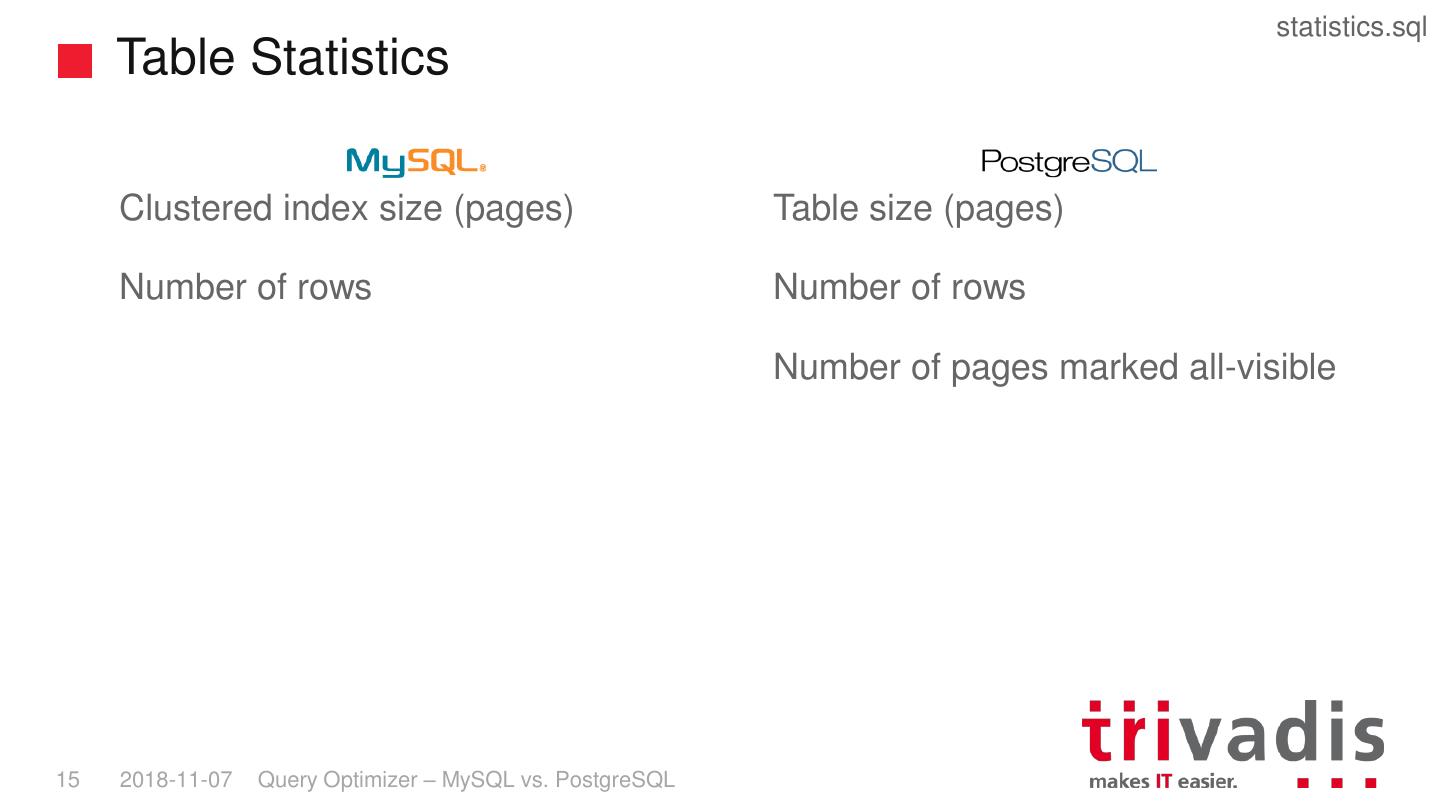
15 . statistics.sql Table Statistics Clustered index size (pages) Table size (pages) Number of rows Number of rows Number of pages marked all-visible 15 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
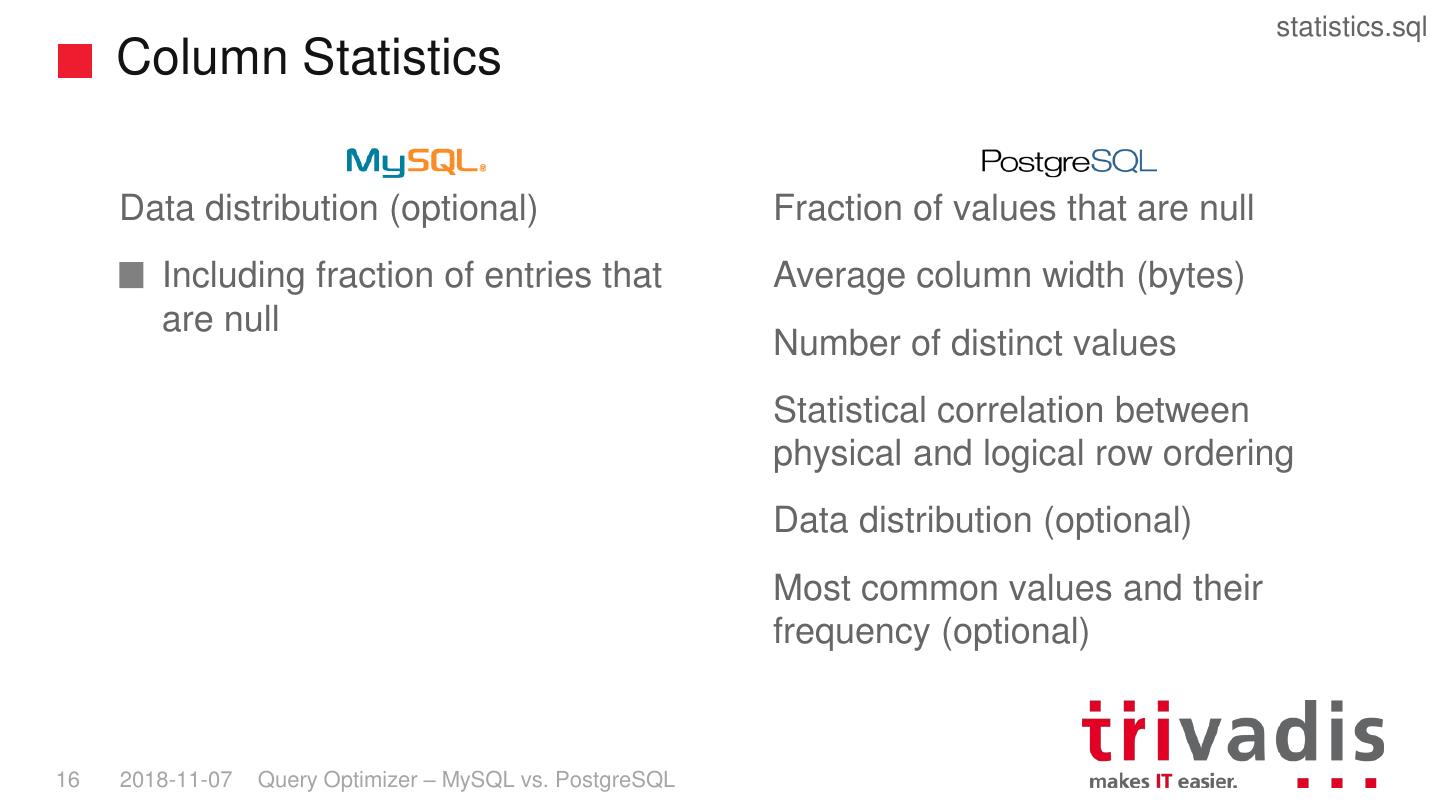
16 . statistics.sql Column Statistics Data distribution (optional) Fraction of values that are null Including fraction of entries that Average column width (bytes) are null Number of distinct values Statistical correlation between physical and logical row ordering Data distribution (optional) Most common values and their frequency (optional) 16 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
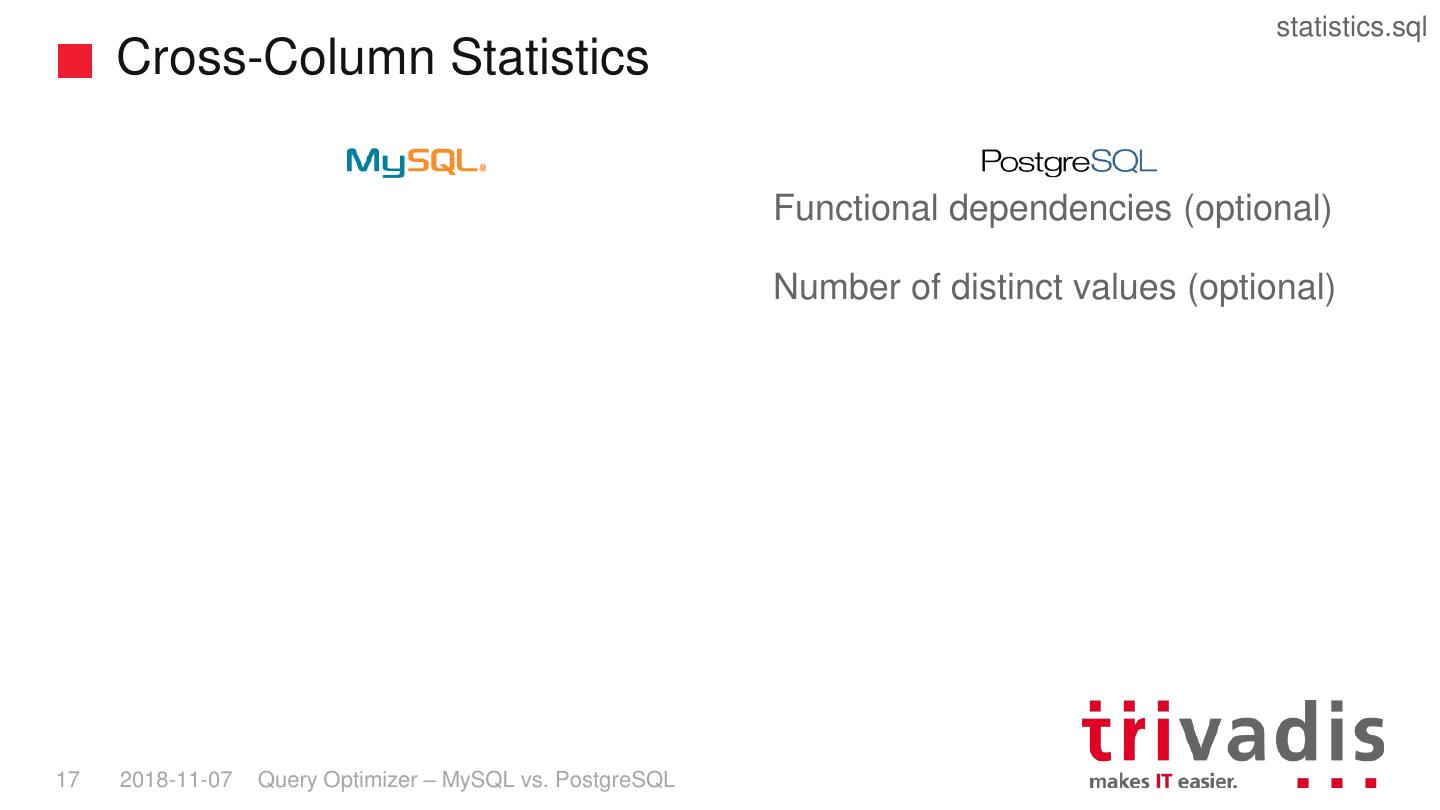
17 . statistics.sql Cross-Column Statistics Functional dependencies (optional) Number of distinct values (optional) 17 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
18 . statistics.sql Index Statistics Index size (pages) Index size (pages) Number of leaf pages Number of indexed rows Number of distinct keys Several values are stored E.g. for index “a,b,c” “a”, “a,b”, “a,b,c”, “a,b,c,PK” 18 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
19 . Data Dictionary Metadata 20 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
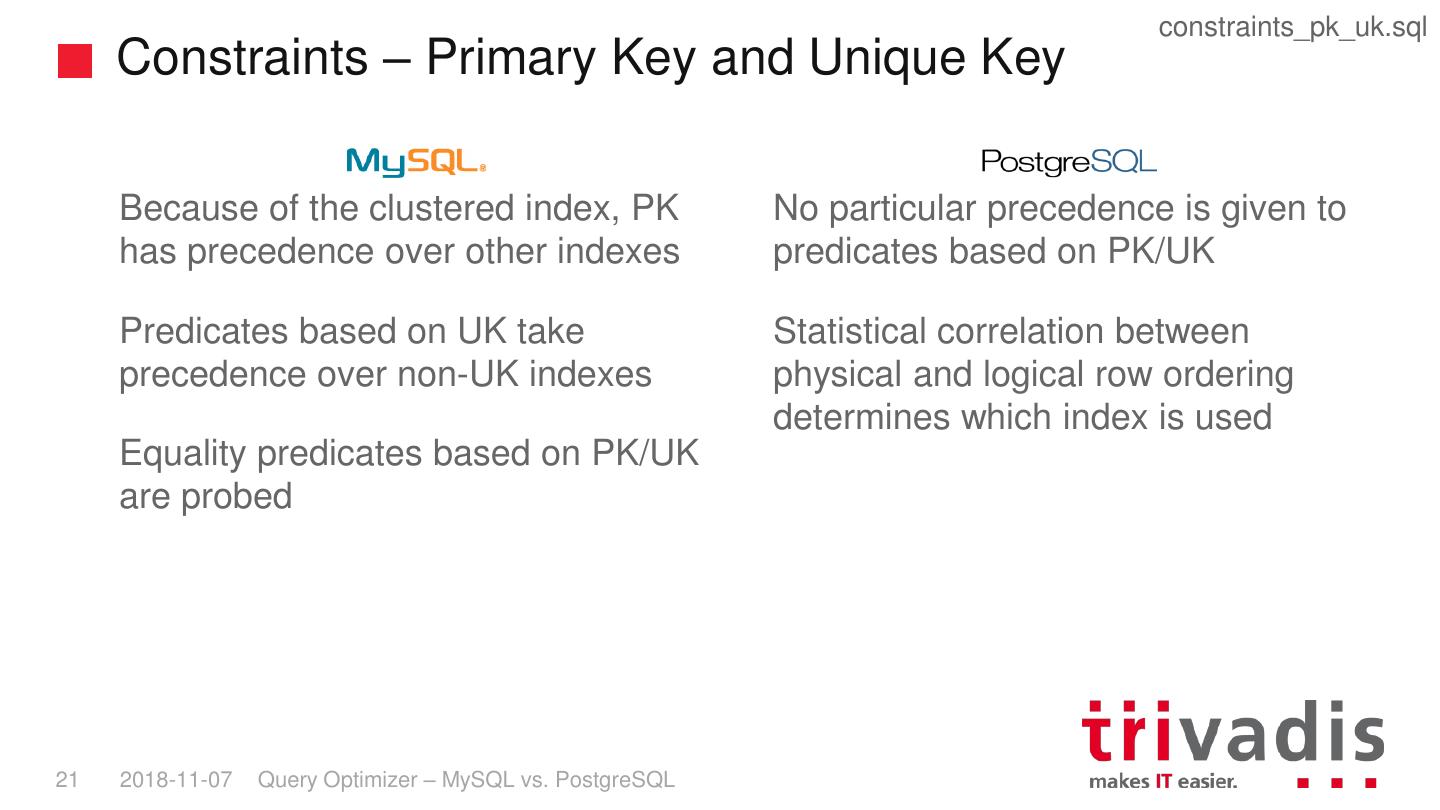
20 . constraints_pk_uk.sql Constraints – Primary Key and Unique Key Because of the clustered index, PK No particular precedence is given to has precedence over other indexes predicates based on PK/UK Predicates based on UK take Statistical correlation between precedence over non-UK indexes physical and logical row ordering determines which index is used Equality predicates based on PK/UK are probed 21 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
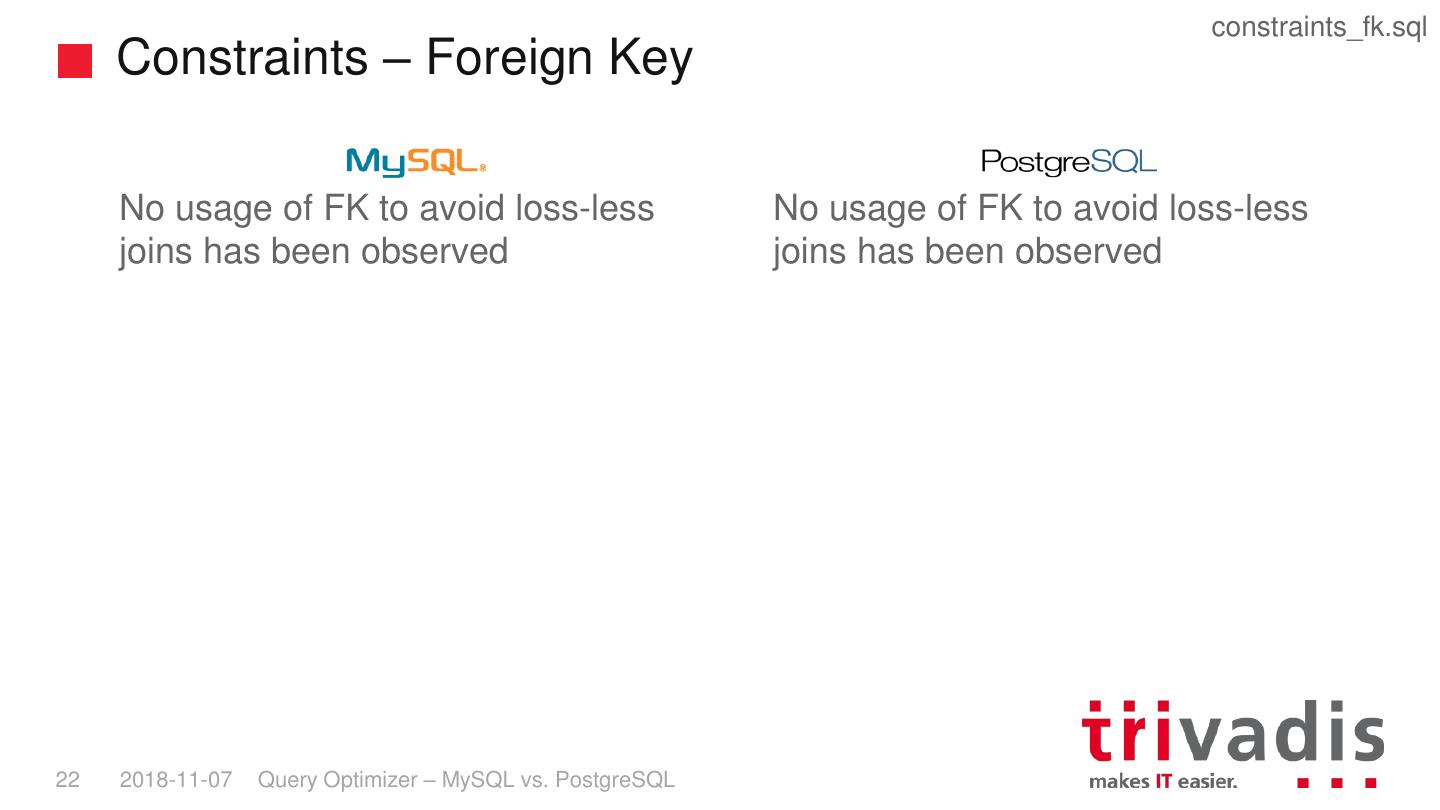
21 . constraints_fk.sql Constraints – Foreign Key No usage of FK to avoid loss-less No usage of FK to avoid loss-less joins has been observed joins has been observed 22 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
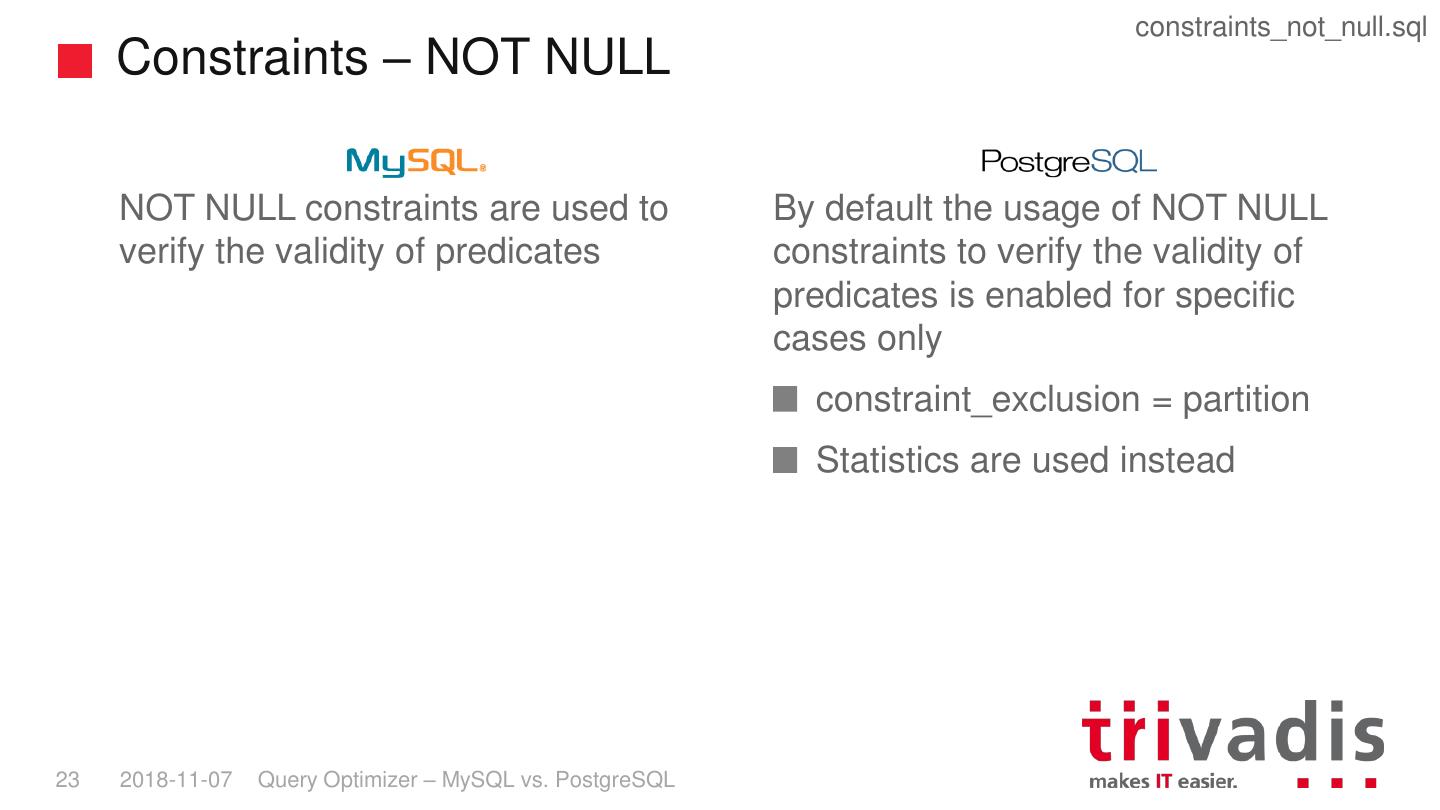
22 . constraints_not_null.sql Constraints – NOT NULL NOT NULL constraints are used to By default the usage of NOT NULL verify the validity of predicates constraints to verify the validity of predicates is enabled for specific cases only constraint_exclusion = partition Statistics are used instead 23 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
23 . constraints_check.sql Constraints – CHECK No usage of CHECK constraints to By default the usage of CHECK verify the validity of predicates has constraints to verify the validity of been observed predicates is enabled for specific cases only Statistics are used instead constraint_exclusion = partition Statistics are used instead 24 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
24 . Single-Table Access Paths 25 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
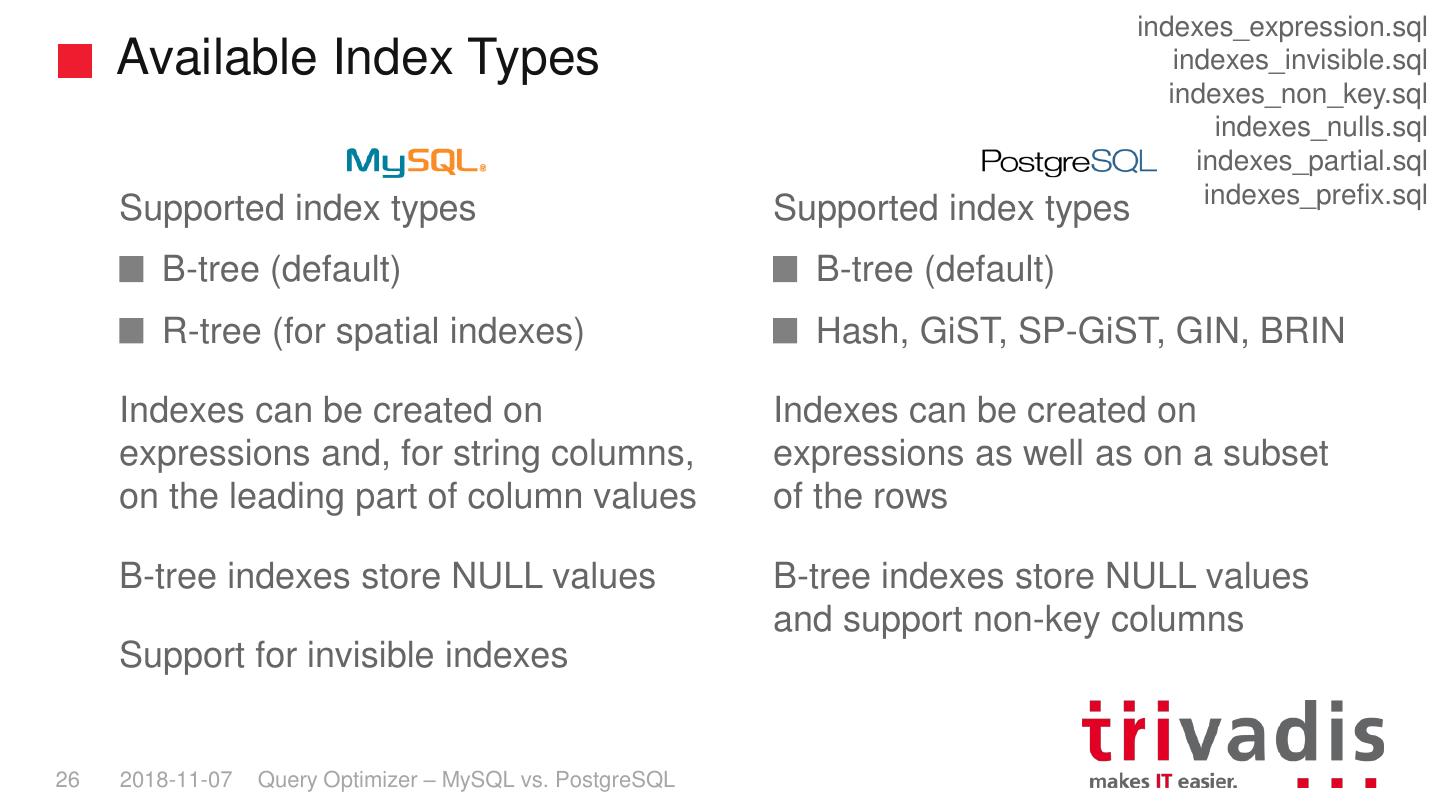
25 . indexes_expression.sql Available Index Types indexes_invisible.sql indexes_non_key.sql indexes_nulls.sql indexes_partial.sql indexes_prefix.sql Supported index types Supported index types B-tree (default) B-tree (default) R-tree (for spatial indexes) Hash, GiST, SP-GiST, GIN, BRIN Indexes can be created on Indexes can be created on expressions and, for string columns, expressions as well as on a subset on the leading part of column values of the rows B-tree indexes store NULL values B-tree indexes store NULL values and support non-key columns Support for invisible indexes 26 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
26 . indexes_order_by.sql Optimization of ORDER BY, MIN and MAX indexes_min_max.sql B-tree indexes can be used to B-tree indexes can be used to optimize ORDER BY, MIN and MAX optimize ORDER BY, MIN and MAX Index scans can be performed in Index scans can be performed in both directions both directions Keys are stored according to the Keys are stored according to the specified order specified order NULLS FIRST/LAST not NULLS FIRST/LAST supported supported 27 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
27 . indexes_merge.sql Merging Indexes Two or more B-tree indexes can be When appropriate, B-tree indexes merged at runtime to evaluate are dynamically converted to multiple predicates combined with bitmaps in memory AND or OR One utilization of this feature is to merge indexes to evaluate multiple predicates combined with AND or OR 28 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
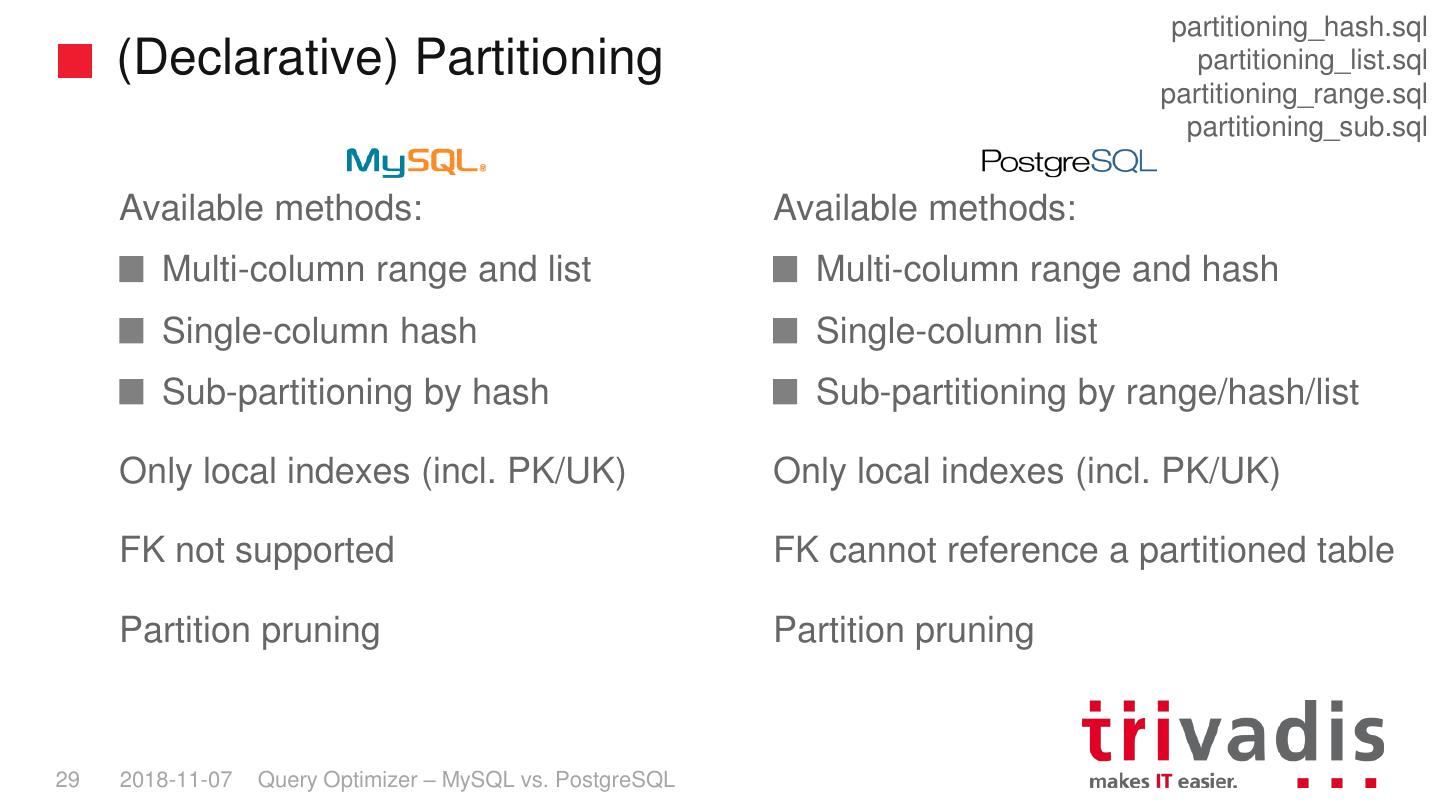
28 . partitioning_hash.sql (Declarative) Partitioning partitioning_list.sql partitioning_range.sql partitioning_sub.sql Available methods: Available methods: Multi-column range and list Multi-column range and hash Single-column hash Single-column list Sub-partitioning by hash Sub-partitioning by range/hash/list Only local indexes (incl. PK/UK) Only local indexes (incl. PK/UK) FK not supported FK cannot reference a partitioned table Partition pruning Partition pruning 29 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL
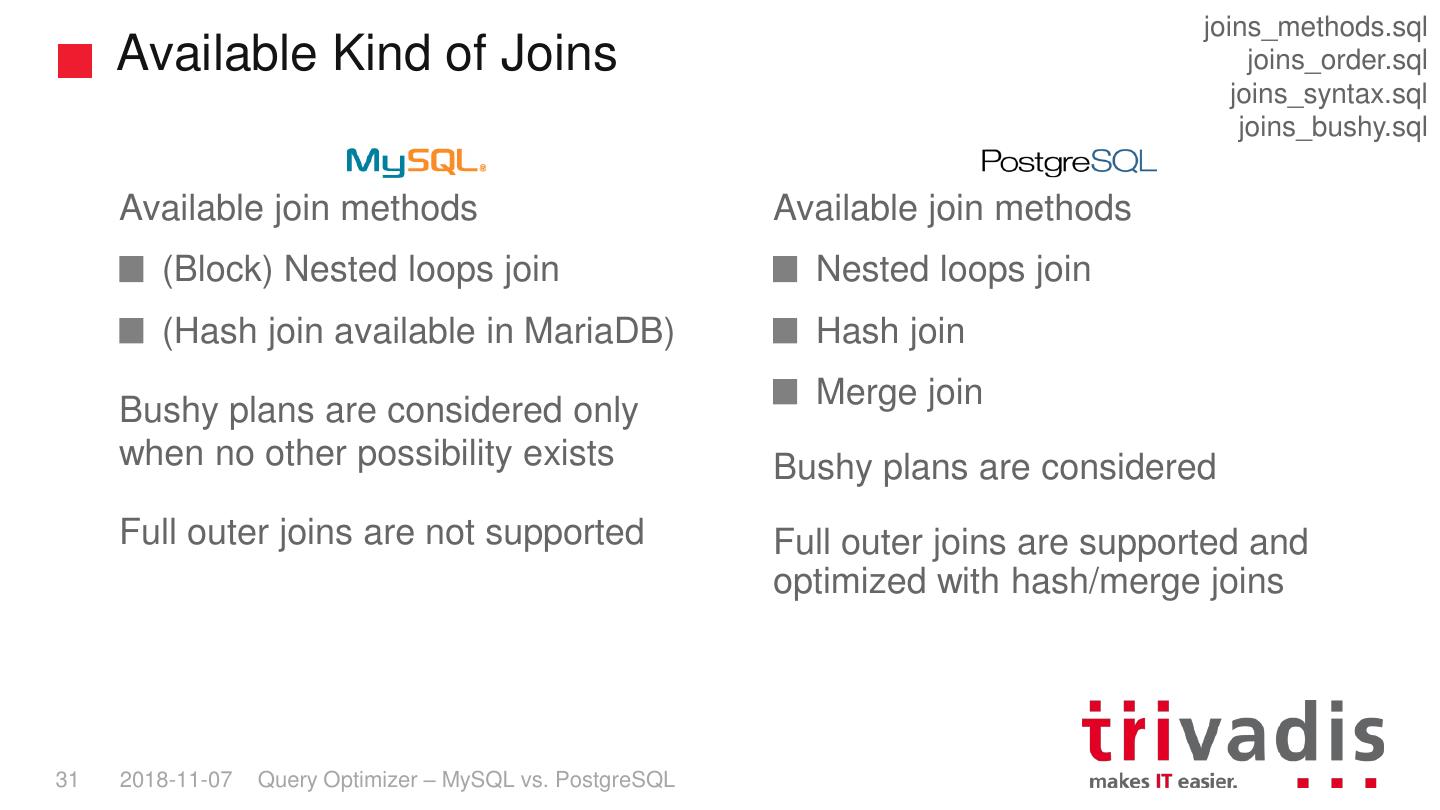
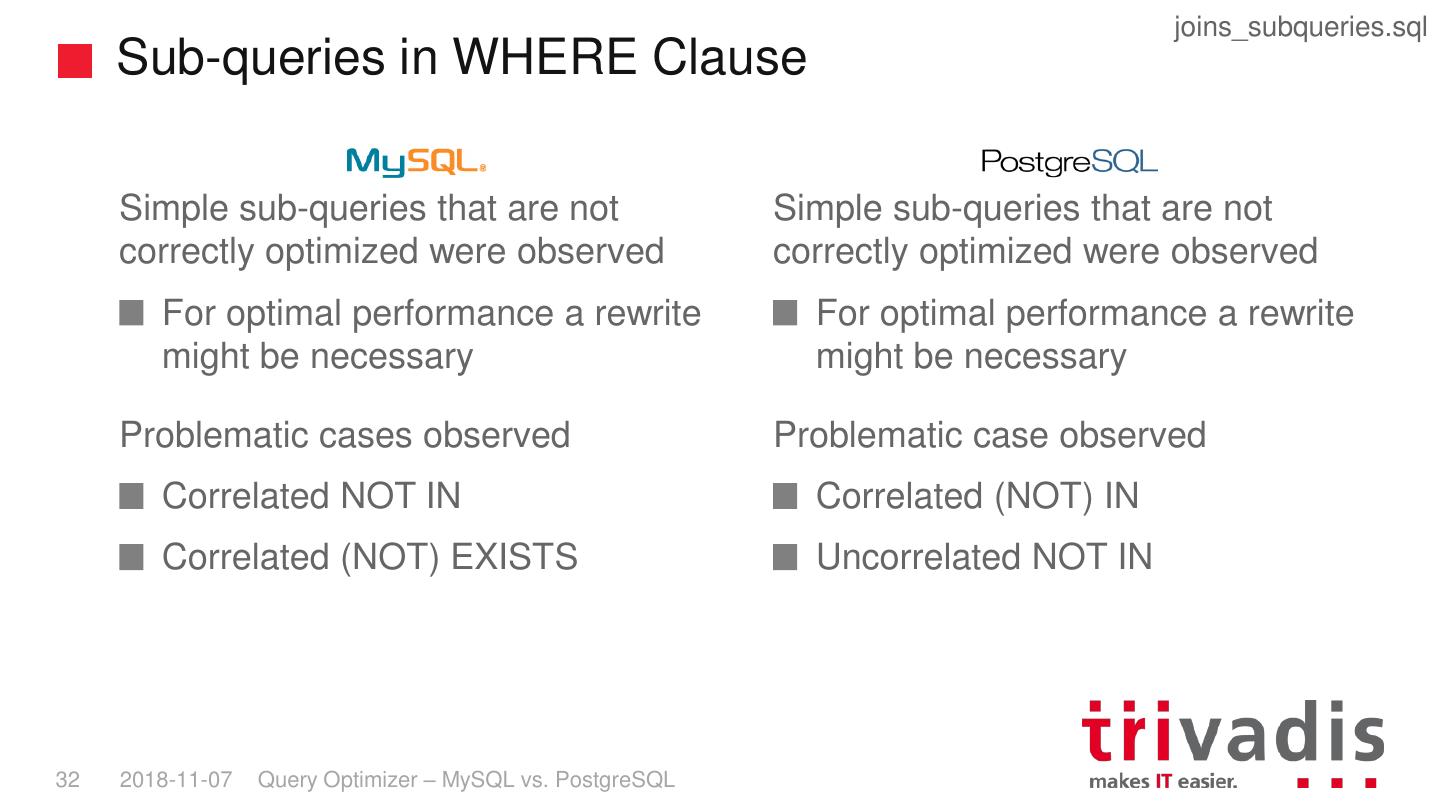
29 . Joins and Sub-queries 30 2018-11-07 Query Optimizer – MySQL vs. PostgreSQL