- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- <iframe src="https://www.slidestalk.com/u9501/High_Performance_PostgreSQL_Tuning_and_Optimization_Guide?embed" frame border="0" width="640" height="360" scrolling="no" allowfullscreen="true">复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
High Performance PostgreSQL, Tuning and Optimization Guide
PostgreSQL是领先的开源数据库之一。现成的默认PostgreSQL配置不会针对任何特定的工作负载进行优化。默认配置的设计方式是,PostgreSQL可以在任何资源最少的系统上运行。PostgreSQL没有在高持久性机器上提供最佳性能,因为它没有使用所有可用的资源。PostgreSQL提供了一个系统,您可以根据工作负载和机器规格调整数据库。除了PostgreSQL之外,我们还可以调整Linux设备,以便数据库加载能够以最佳方式工作。在这里,我们学习了如何调优PostgreSQL,并将看到调优的结果,我们还将接触到一些Linux内核参数调优。
展开查看详情
1 .High Performance PostgreSQL, Tuning and Optimization Guide Ibrar Ahmed Senior Software Engineer @ Percona LLC PostgreSQL Consultant
2 . PostgreSQL Why? ● One of the finest open source relational Support? database which has some object-oriented features. There are many companies providing Object-Relational database management professional support for PostgreSQL. system (RDBMS) ● PostgreSQL is free. ● PostgreSQL is Open Source. ● PostgreSQL Conform to the ANSI-SQL: 2008. ● PostgreSQL is ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation and Durability) Complaint. Licence? PostgreSQL: Released under the PostgreSQL Who? License. (Similar to BSD or MIT) ● Web technology ● Financial ● No-SQL Workload ● Small & Large Scale Business !2
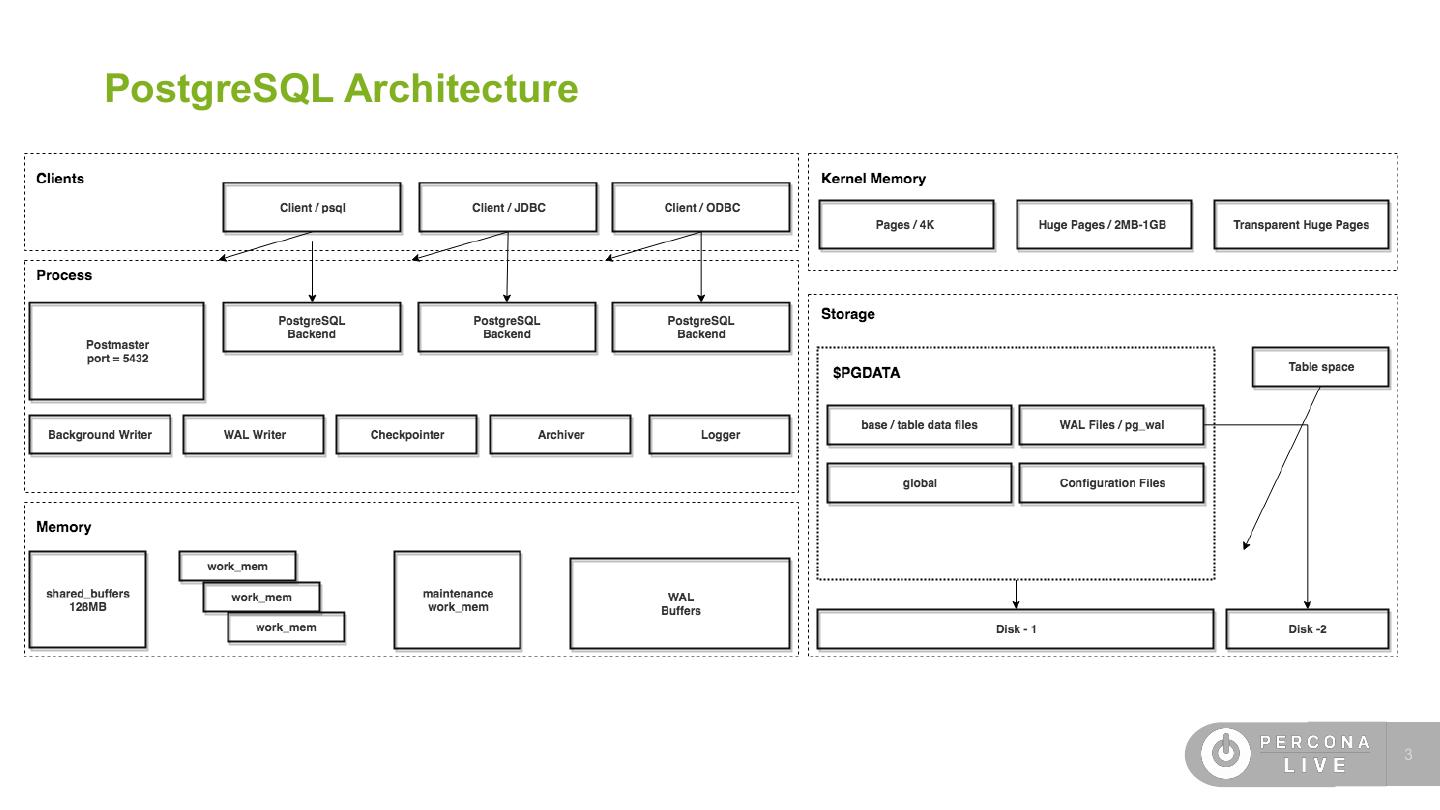
3 .PostgreSQL Architecture !3
4 .Database Performance • Hardware • Operating System (Linux) • Database (PostgreSQL) Configuration • Workload • Queries • Application !4
5 .Tune PostgreSQL !5
6 .PostgreSQL Tuning - Configuration Parameter • shared_buffer • wal_buffers • effective_cache_size • work_mem • maintenance_work_mem • synchronous_commit • checkpoint_timeout • checkpoint_completion_target !6
7 .PostgreSQL Tuning - shared_buffer • PostgreSQL uses its own buffer and also uses kernel buffered I/O. • PostgreSQL buffer is called shared_buffer. • Data is written to shared_buffer then kernel buffer then on the disk. postgresql=# SHOW shared_buffers; shared_buffers ---------------- 128MB (1 row) The proper size for the POSTGRESQL shared buffer cache is the largest useful size that does not adversely affect other activity. —Bruce Momjian !7
8 .PostgreSQL Tuning - shared_buffer !8
9 .PostgreSQL Tuning - wal_buffer • PostgreSQL writes its WAL (write ahead log) record into the buffers and then these buffers are flushed to disk. • Bigger value for wal_buffer in case of lot of concurrent connection gives better performance. !9
10 .PostgreSQL Tuning - effective_cache_size • The effective_cache_size provides an estimate of the memory available for disk caching. • It is just a guideline, not the exact allocated memory or cache size. • It should be large enough to hold most accessed tables, but at the same time small enough to avoid swap. !10
11 . PostgreSQL Tuning - work_mem • This configuration is used for complex sorting. !11
12 .PostgreSQL Tuning - maintenance_work_mem • maintenance_work_mem is a memory setting used for maintenance tasks. • The default value is 64MB. • Setting a large value helps in tasks like VACUUM, RESTORE, CREATE INDEX, ADD FOREIGN KEY and ALTER TABLE. !12
13 .PostgreSQL Tuning - synchronous_commit • This is used to enforce that commit will wait for WAL to be written on disk before returning a success status to the client. • This is a trade-off between performance and reliability. • Increasing reliability decreases performance and vice versa. !13
14 .PostgreSQL Tuning - checkpoint_timeout • PostgreSQL writes changes into WAL. The checkpoint process flushes the data into the data files. • More checkpoints have a negative impact on performance. !14
15 .Tune Linux !15
16 .Linux Tuning - Huge Pages • Linux, by default uses 4K memory pages. • Linux also has Huge Pages, Transparent huge pages. • BSD has Super Pages. • Windows has Large Pages. • Linux default page size is 4K. • Default Huge page size is 2MB. !16
17 .Linux Tuning - vm.swappiness This is another kernel parameter that can affect the performance of the database. • Used to control the swappiness (swapping pages to and from swap memory into RAM) behaviour on a Linux system. !17
18 .Linux Tuning / vm.overcommit_memory and vm.overcommit_ratio • Applications acquire memory and free that memory when it is no longer needed. • But in some cases an application acquires too much memory and does not release it. This can invoke the OOM killer. 1.Heuristic overcommit, Do it intelligently (default); based kernel heuristics 2.Allow overcommit anyway 3.Don’t over commit beyond the overcommit ratio. !18
19 .Linux Tuning - vm.dirty_background_ratio / vm.dirty_background_bytes • The vm.dirty_background_ratio is the percentage of memory filled with dirty pages that need to be flushed to disk. • Flushing is done in the background. The value of this parameter ranges from 0 to 100; !19
20 .Linux Tuning - vm.dirty_ratio / vm.dirty_bytes • The vm.dirty_ratio is the percentage of memory filled with dirty pages that need to be flushed to disk. • Flushing is done in the foreground. The value of this parameter ranges from 0 to 100; !20
21 .Blogs Tuning PostgreSQL Database Parameters to Optimise Performance. https://www.percona.com/blog/2018/08/31/tuning-postgresql-database- parameters-to-optimize-performance/ Tune Linux Kernel Parameters For PostgreSQL Optimisation https://www.percona.com/blog/2018/08/29/tune-linux-kernel-parameters-for- postgresql-optimization/ !21